Senior Block Documentation (Archived)
version 3.2.1 (Changelog)
- 'Junior' and 'Senior' categories no longer exist and blocks are deprecated on Blockly! Blockly now has only one category.
- If loading Blockly code with 'Junior' or 'Senior' blocks, blocks will contain a deprecation warning.
- These blocks are only supported on https://codrone.robolink.com/edu/blockly-archive/
Flight Commands
takeoff()
Block

Code
drone. takeoff()Description
This functions makes the drone take off. CoDrone EDU takes off at an average height of 80 centimeters off the ground. A takeoff block must be used before any other flight command or flight movement. NOTE: The takeoff height cannot be modified.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
land()
Block

Code
drone. land()Description
This function makes the drone land by throttling down safely.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example

emergency_stop()
Block

Code
drone. emergency_stop()Description
Stops all commands to motors. The drone will stop flying immediately.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example

hover()
Block

Code
drone. hover()Description
This function makes the drone hover in place for a duration in seconds.
Parameters
integer duration: the duration of the hover in seconds
Returns
None
Example
move()
Block

Code
drone. set_roll()drone. set_pitch()
drone. set_yaw()
drone. set_throttle()
drone. move()
drone. hover()
Description
Moves the drone for a certain amount of time (in seconds) in a given direction determined by the flight parameters.
Parameters
integer roll: roll power percentage as an integer between -100 and +100
integer pitch: pitch power percentage as an integer between -100 and +100
integer yaw: yaw power percentage as an integer between -100 and +100
integer throttle: throttle power percentage as an integer between -100 and +100
integer duration: duration of the hover, in seconds
Returns
None
Example
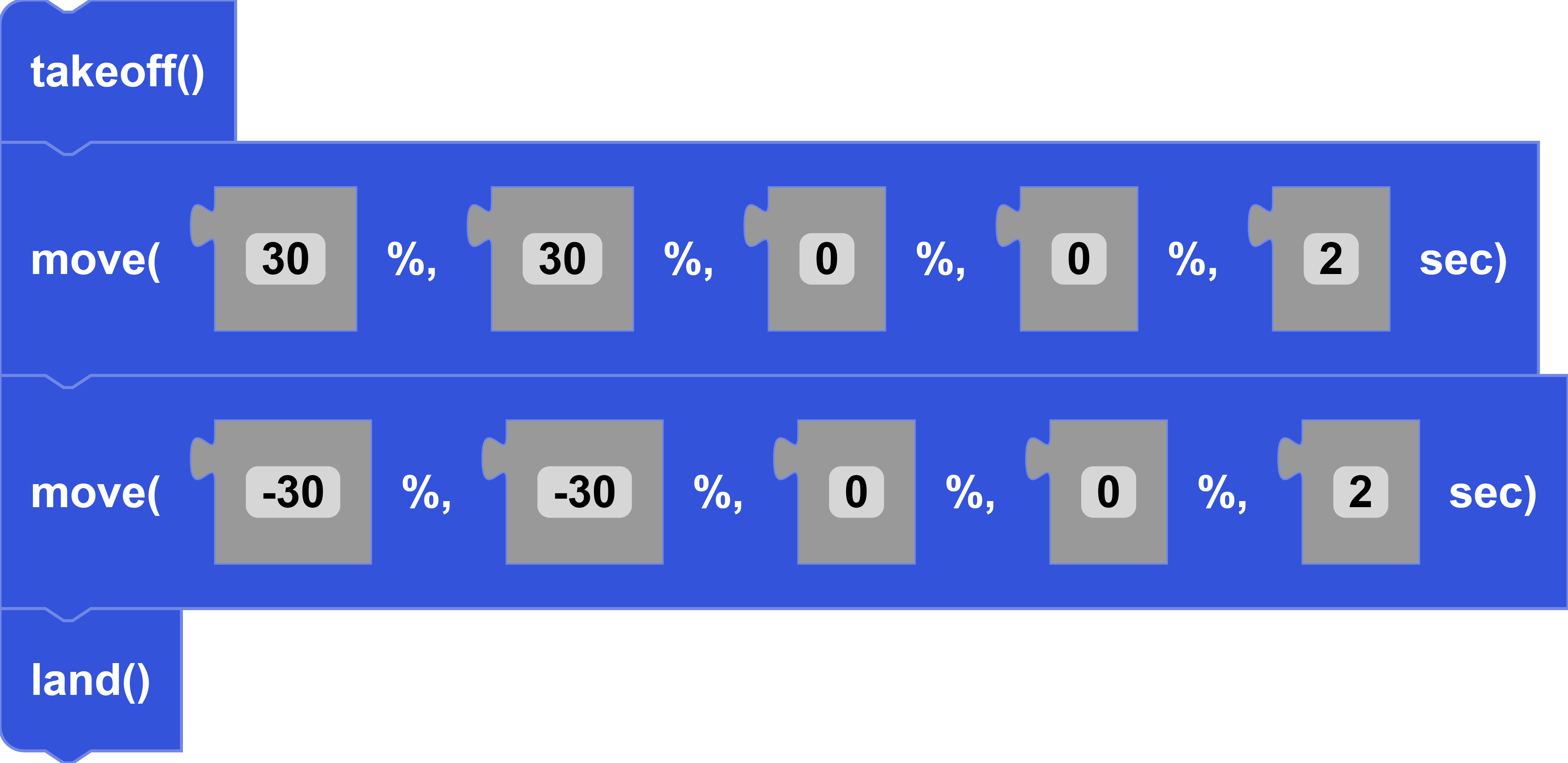
In this example, the drone will move for 2 seconds with the roll and pitch set to 30%. Then, the drone will move for another 2 seconds with the roll and pitch set to -30%.
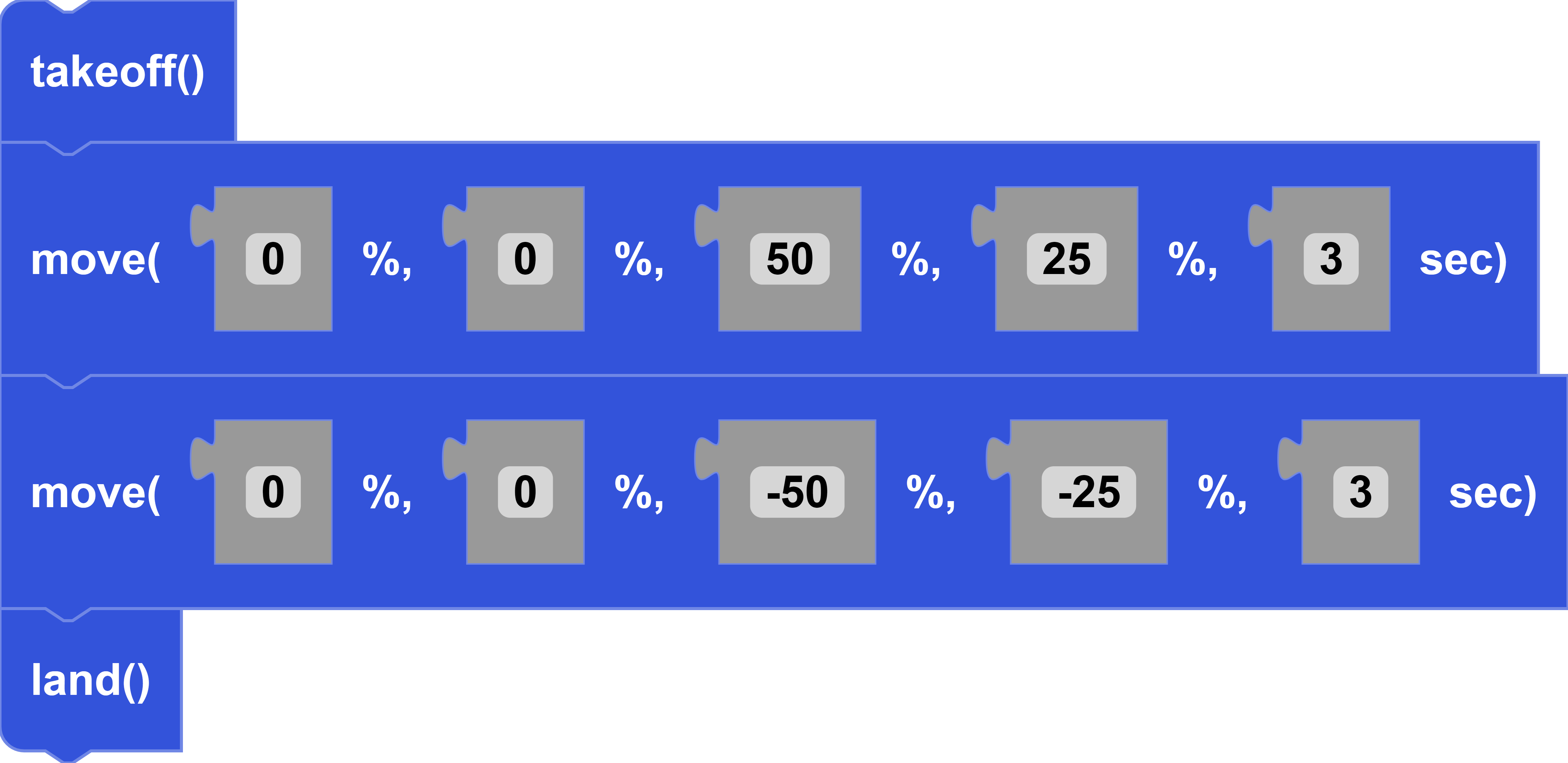
In the example below, the drone will move for 3 seconds with the yaw and throttle set to 50% and 25%. Then, the drone will move for another 3 seconds with the yaw and throttle set to -50% and -25%.
flip()
Block

Code
drone. flip()Description
This functions makes the drone flip back, front, right, or left. Make sure your battery percentage is over 50% for the flip to execute.
Parameters

direction: back, front, right, left
Returns
None
Example
Add a hover or delay block after the flip if you need to stabilize before your next command. The drone takes 3-4 seconds after a flip before it can do another flight command. Not adding a delay after a flip can cause following blocks to not be performed.
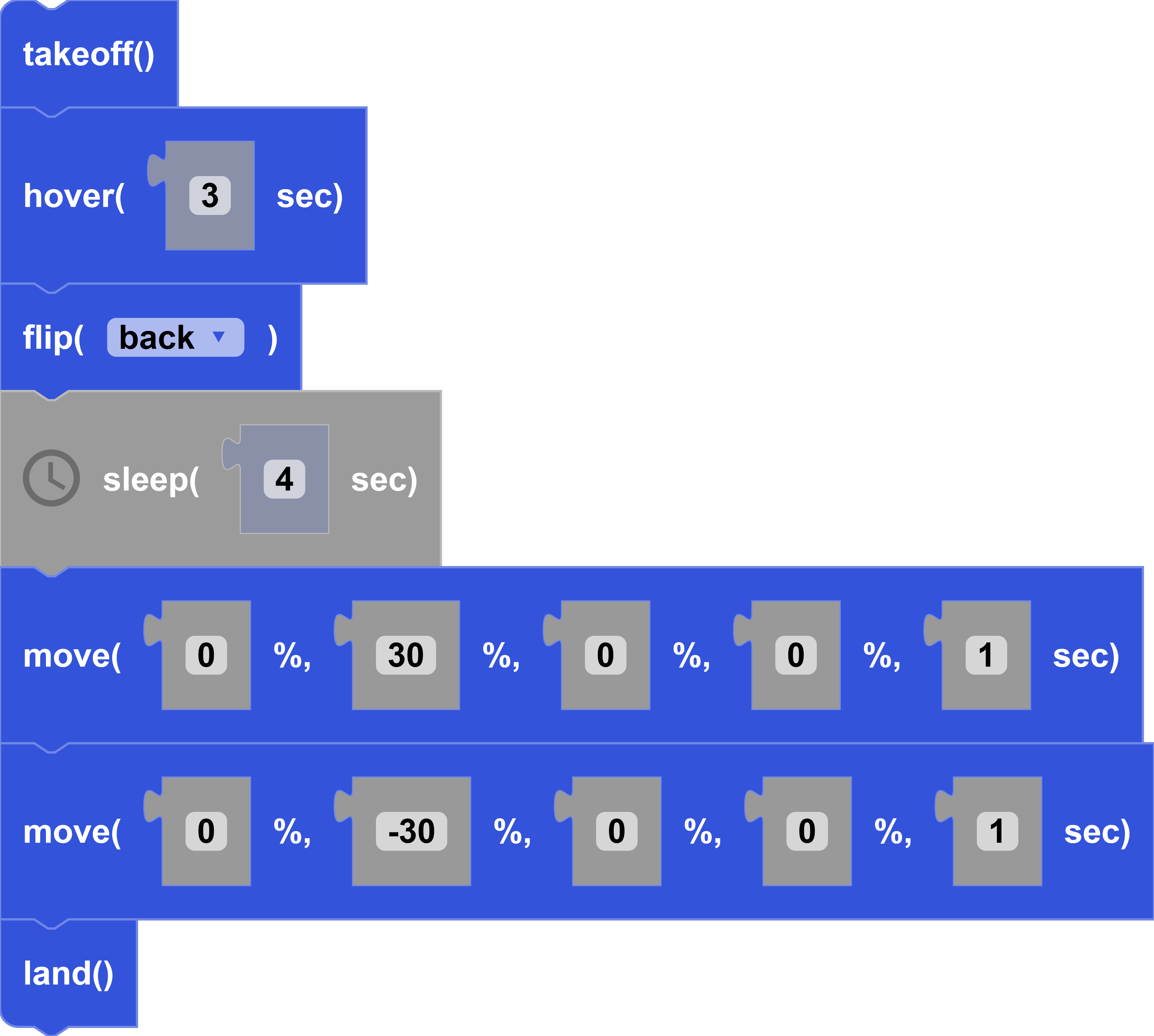
In this example below, after take off, the drone should flip forward and backward (flips might not be executed since a flip needs a wait/sleep block).

move_[direction]()
Block

Code
forward: drone.move_forward()
backward: drone.move_backward()
left: drone.move_left()
right: drone.move_right()
Description
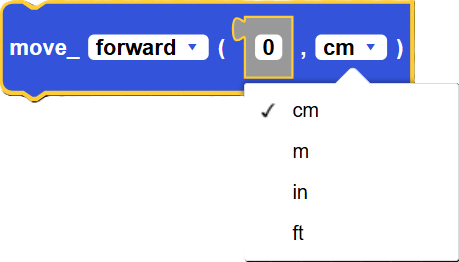
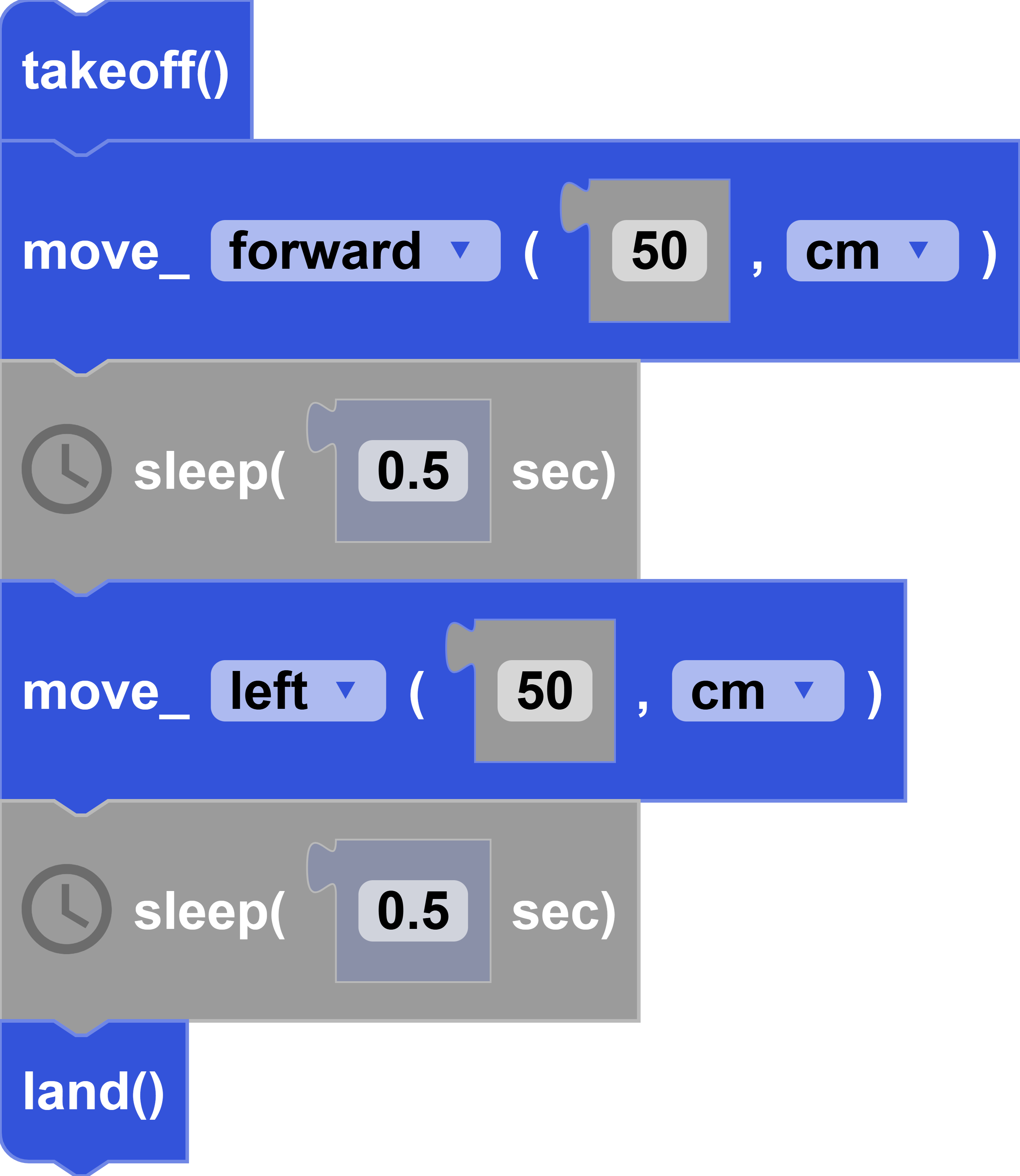
This function flies the drone in a direction for a given distance. The units of the distance can be modified. NOTE: This block may require a "wait" block to prevent skipping the movement command.
Parameters
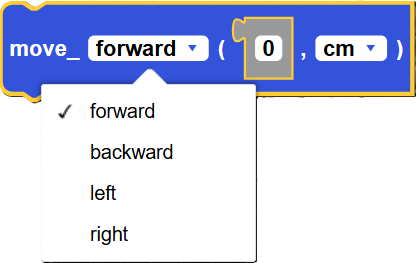
direction: forward, backward, up, down, left, right
float distance: the distance traveled
units: the units of the distance traveled
Returns
None
Example
send_absolute_position()
Block

Code
drone. send_absolute_position()Description
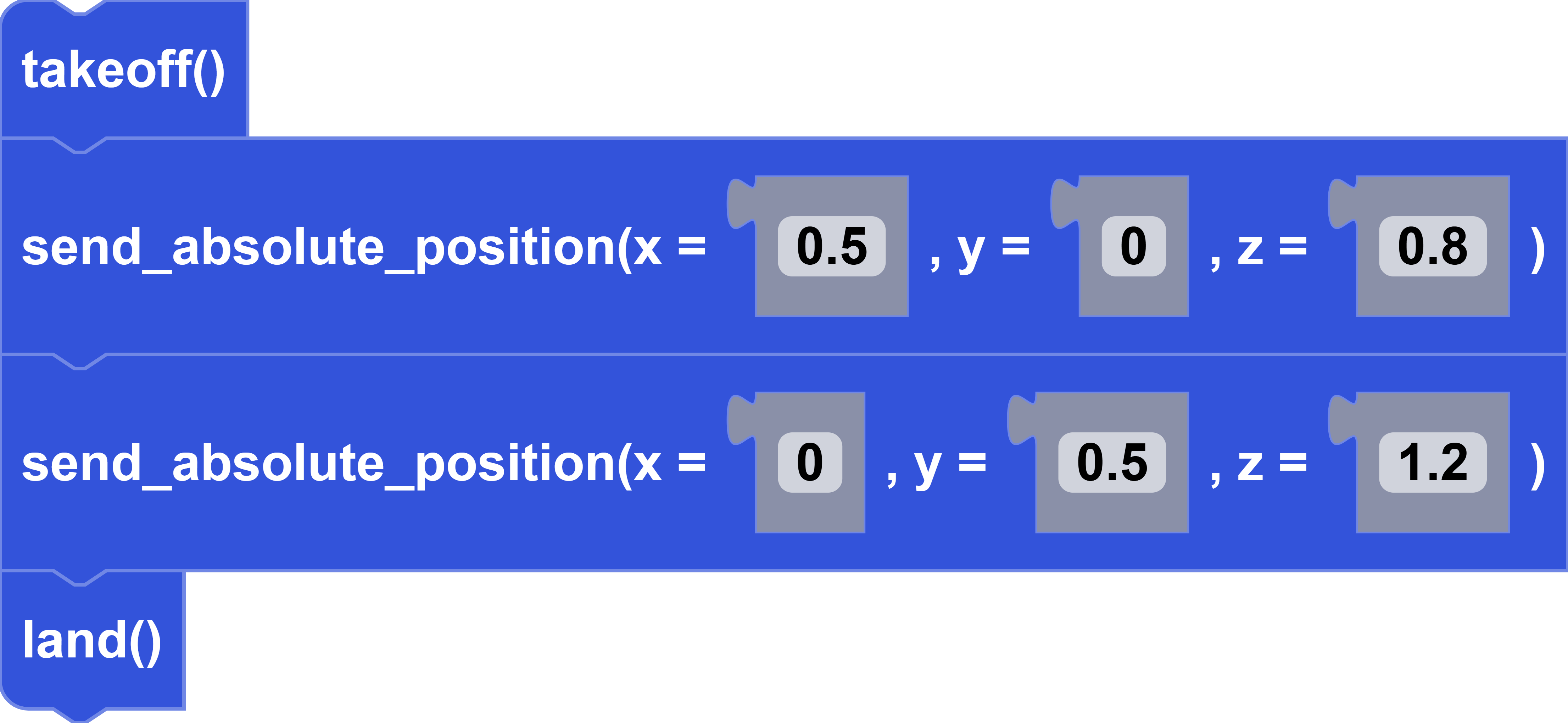
This function flies the drone to a given coordinate/position relative to the position of the first takeoff of the run.
Parameters
float x position: The desired x-position that the drone will fly to
float y position: The desired y-position that the drone will fly to
float z position: The desired z-position that the drone will fly to
Returns
None
Example
turn_degree()
Block

Code
drone. turn_degree()Description
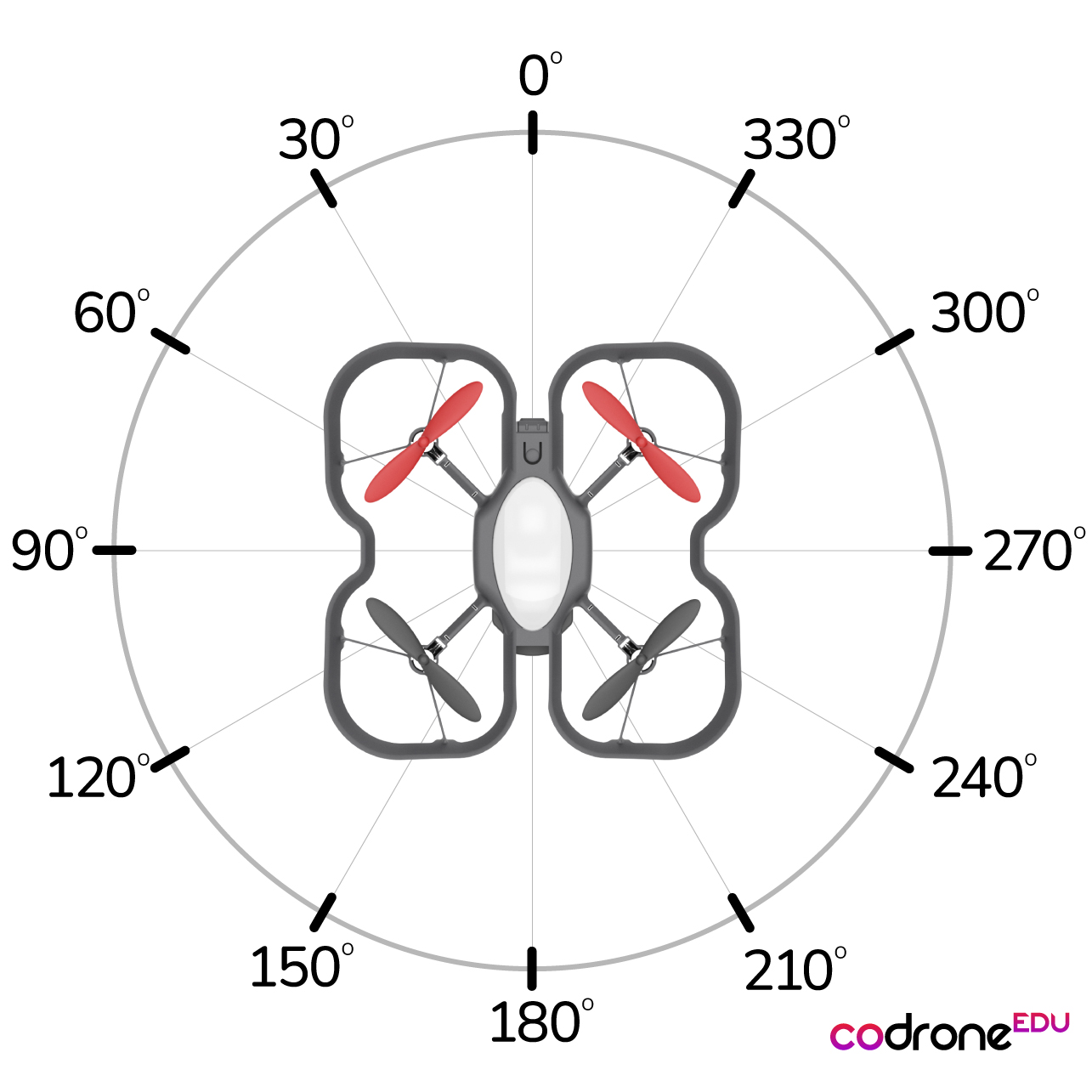
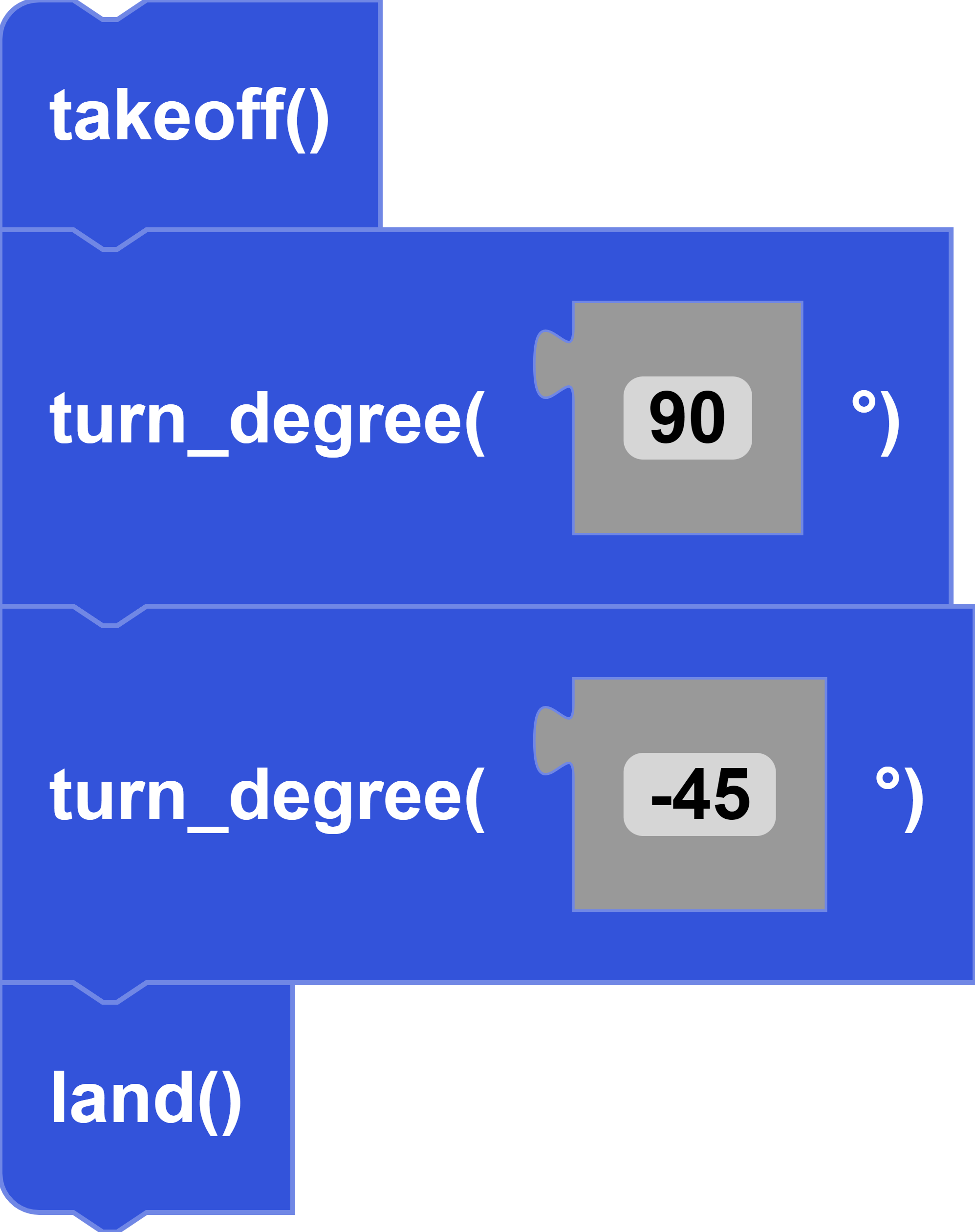
Turns right or left with absolute reference frame to drone's initial heading. Input positive degrees to turn left and negative degrees to turn right. When the drone pairs to the controller after powering on, the current heading will be set as 0 degrees.
Parameters
integer degrees: angle of the turn between -180 and +180
Returns
None
Example
turn_left() / turn_right()
Block
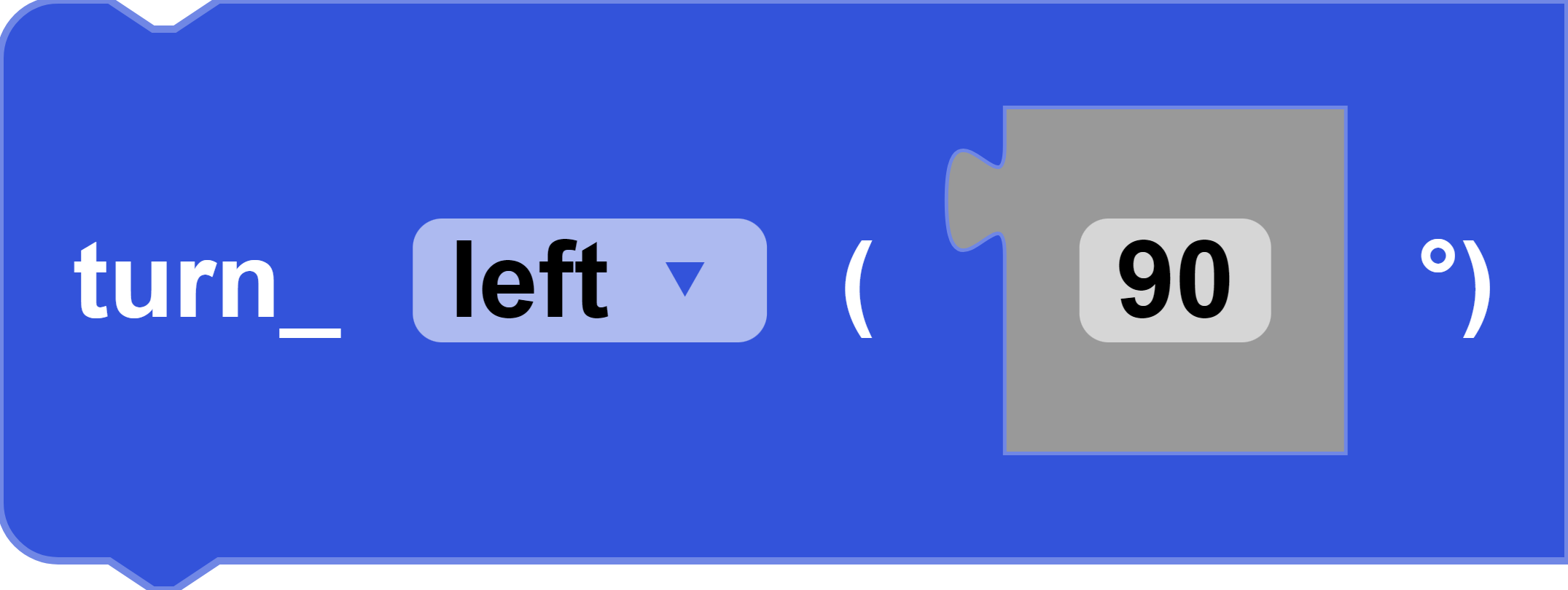
Code
left: drone.turn_left()
right: drone.turn_right()
Description
Turns right or left relative to the drone's current heading.
Parameters
integer degrees: angle of the turn between 0 and 180
Returns
None
Example
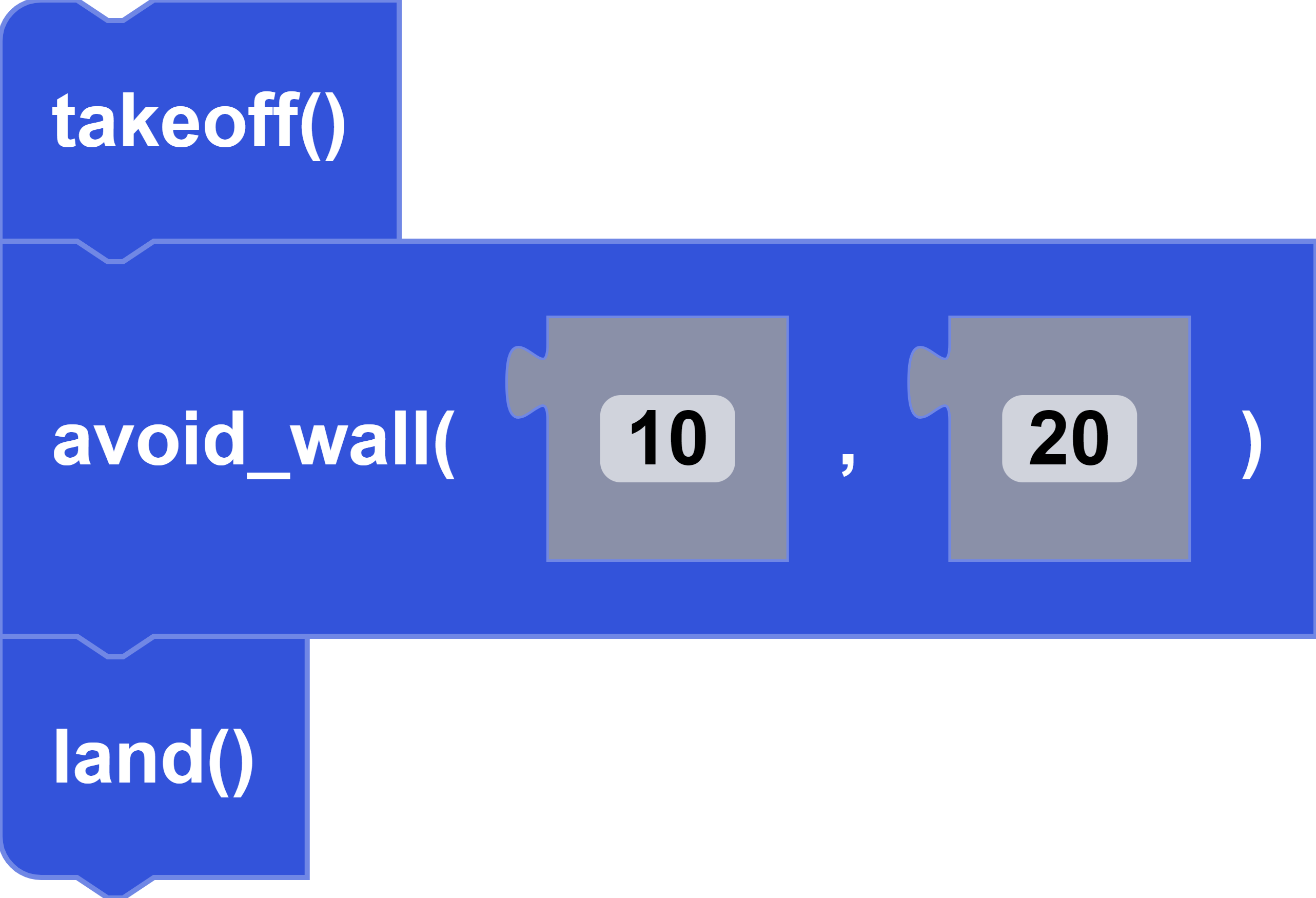
avoid_wall()
Block

Code
drone. avoid_wall()Description
CoDrone EDU will fly forward and stop when an obstacle is detected a given distance away (in centimeters). The block will run until the timeout (in seconds) is finished or the obstacle is found, whichever comes first. The default timeout is 10 seconds for an obstacle detected 20cm away.
Parameters
integer timeout: the timeout duration in seconds
integer distance: the distance, in centimeters, at which the CoDrone EDU will stop to avoid obstacle
Returns
None
Example
Place the drone on the floor a few feet away from a wall. When you run the code, the drone will fly forward until the wall is detected 20 centimeters away. The next block will immediately execute. In this case, the drone will land.
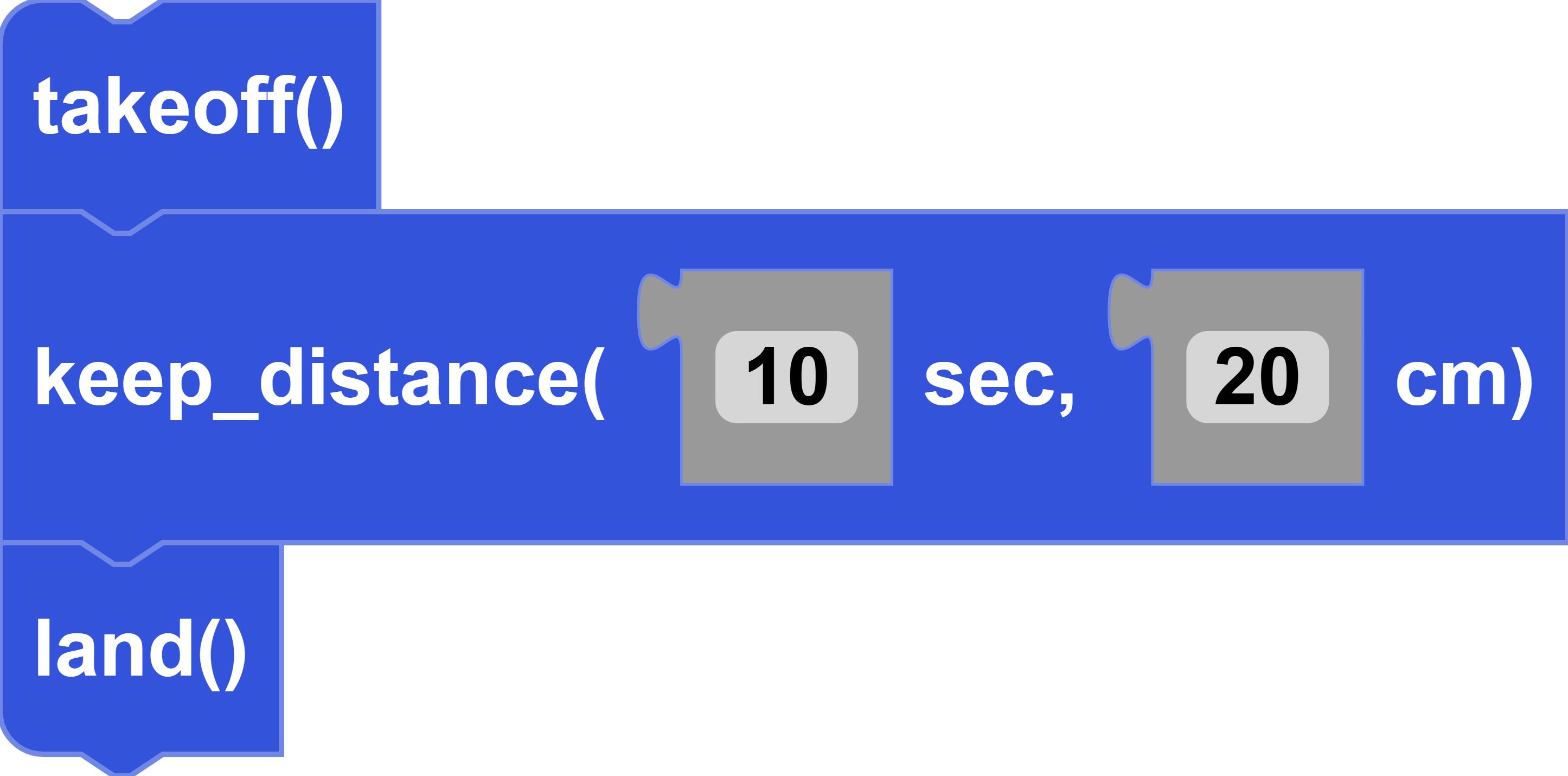
keep_distance()
Block

Code
drone. keep_distance()Description
CoDrone EDU will fly forward and stop when an obstacle is detected a given distance away (in centimeters). The block will run until the timeout (in seconds) is finished or the obstacle is found, whichever comes first. The default timeout is 10 seconds for an obstacle detected 20cm away.
Parameters
integer timeout: the timeout duration in seconds
integer distance: the distance, in centimeters, at which the CoDrone EDU will stop to avoid obstacle
Returns
None
Example
Place the drone on the floor a few feet away from a wall. When you run the code, the drone will fly forward until the wall is detected 20 centimeters away. The next block will immediately execute. In this case, the drone will land.
Flight Variables
set_roll()
Block

Code
drone. set_roll()Description
This function sets the roll direction variable but will not send a move command. Negative values will move the drone to the left and positive values will move the drone to the right.
Parameters
integer power: the power/speed of the drone between -100 and 100
Returns
None
Example
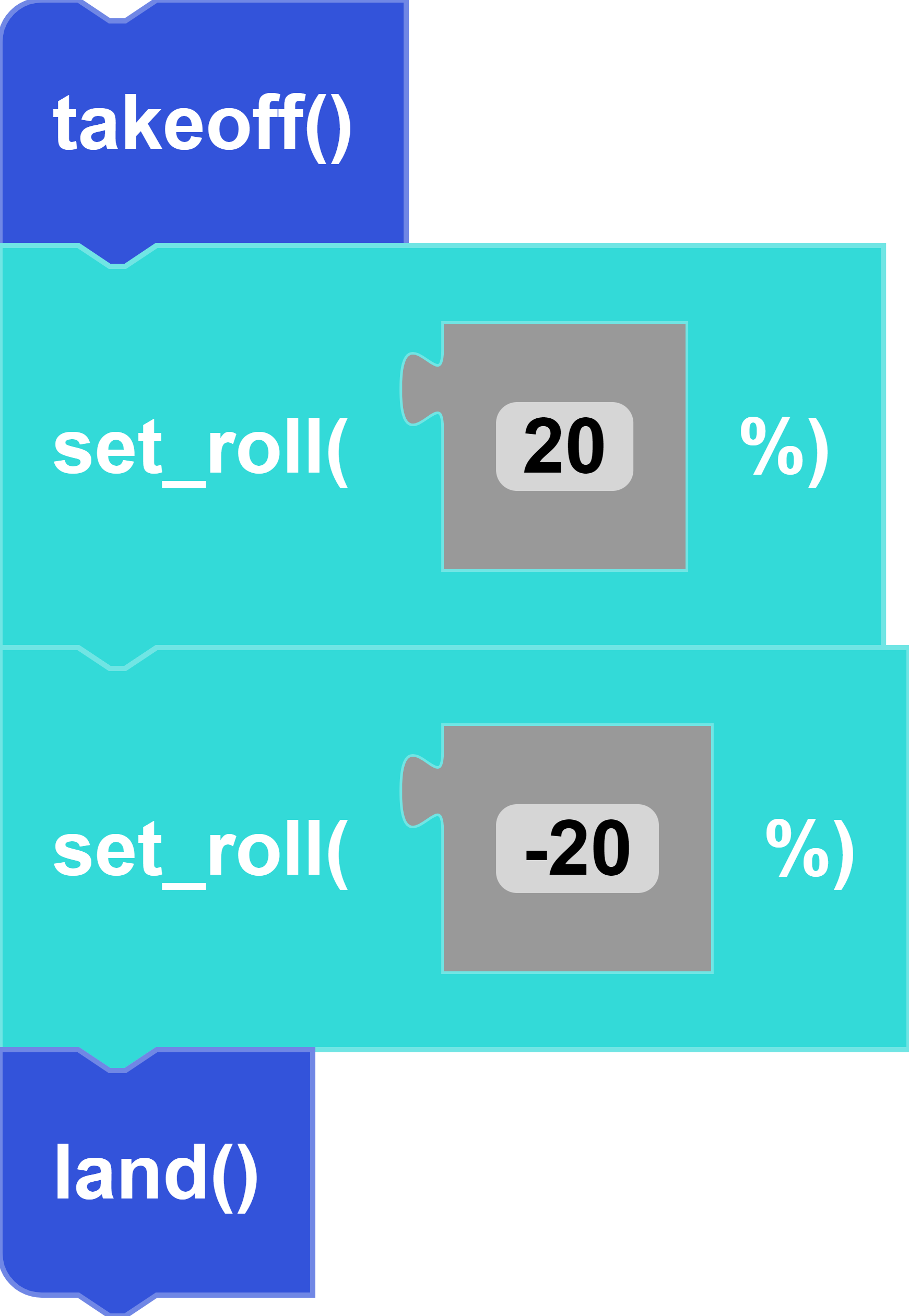
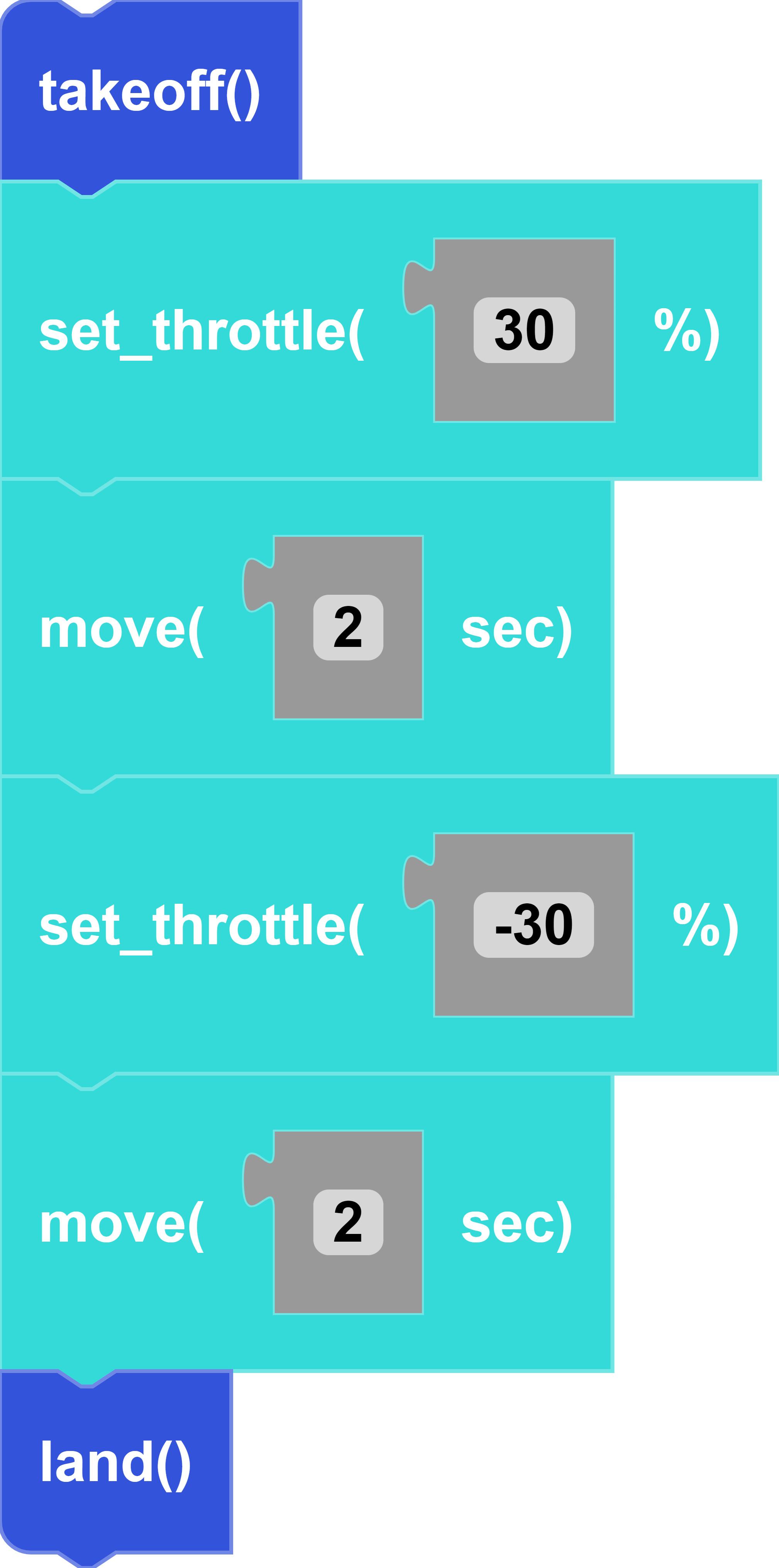
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its roll variable at 20% for rightward movement and then sets its roll variable at -20% for leftward movement. This will not make the drone move yet.
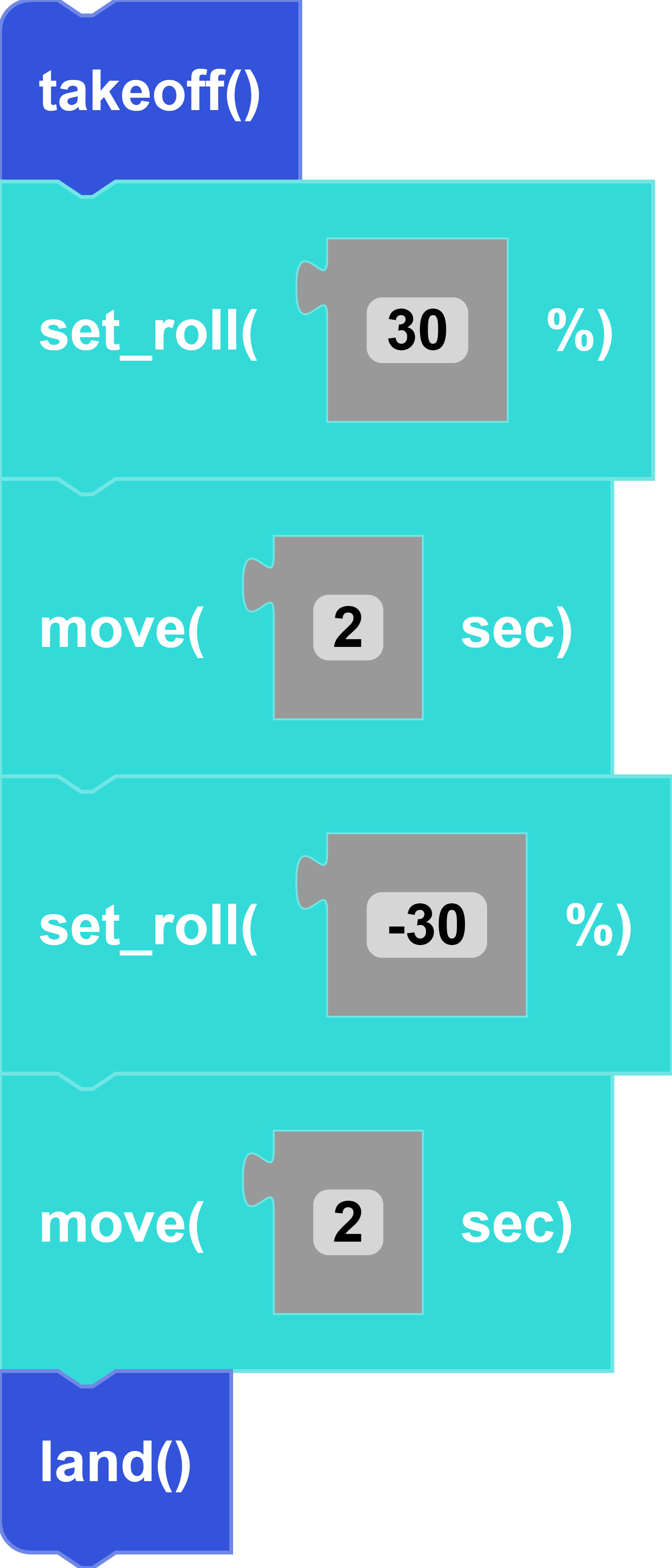
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its roll variable at 30% for rightward movement and moves for 2 seconds. And then the drone sets its roll variable at -30% for leftward movement and moves for 2 seconds.
set_pitch()
Block

Code
drone. set_pitch()Description
This function sets the pitch direction variable but will not send a move command. Negative values will move the drone backward and positive values will move the drone forward.
Parameters
integer power: the power/speed of the drone between -100 and 100
Returns
None
Example
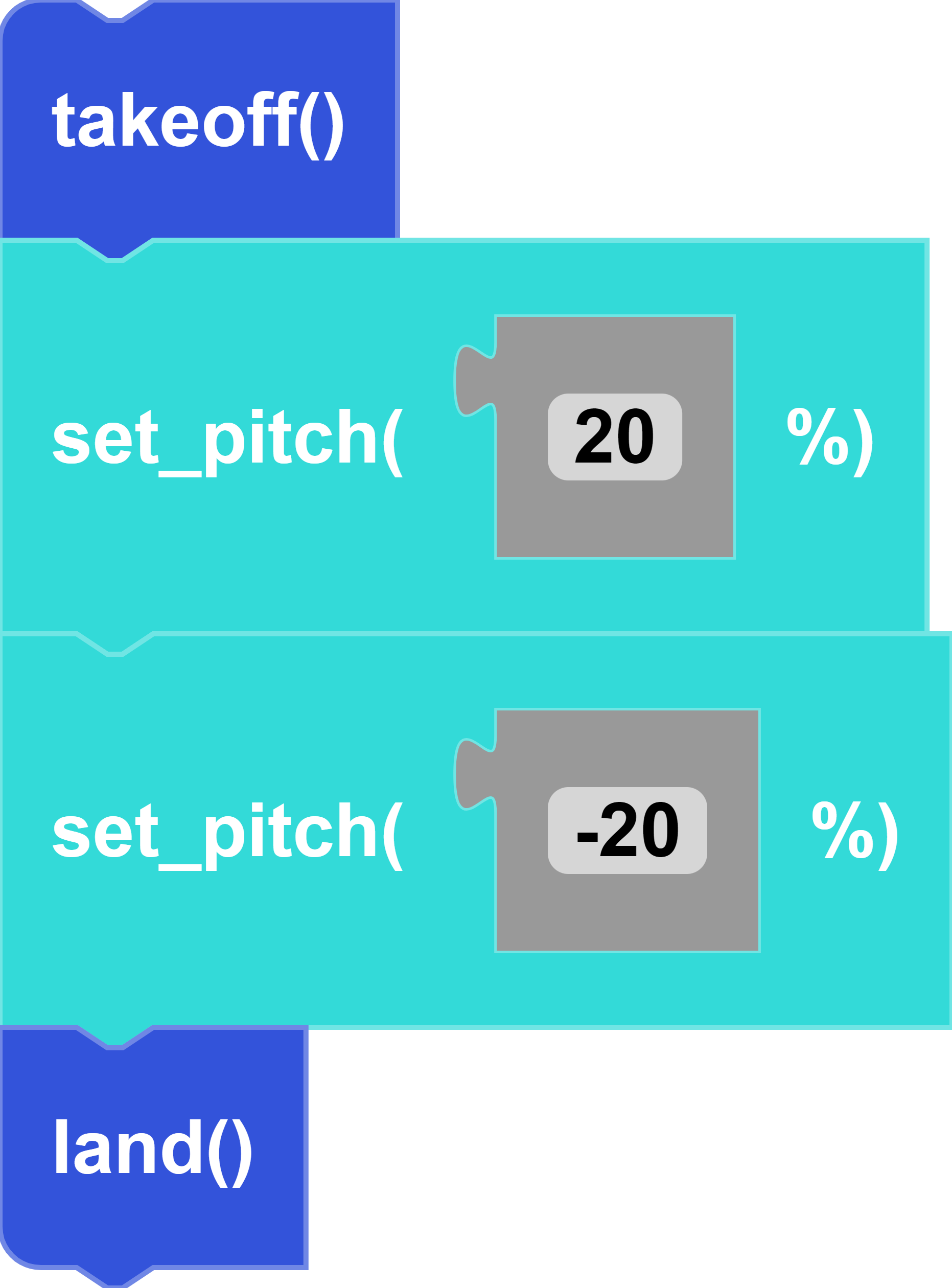
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its pitch variable at 20% for forward movement and then sets its pitch variable at -20% for backward movement. This will not make the drone move yet.
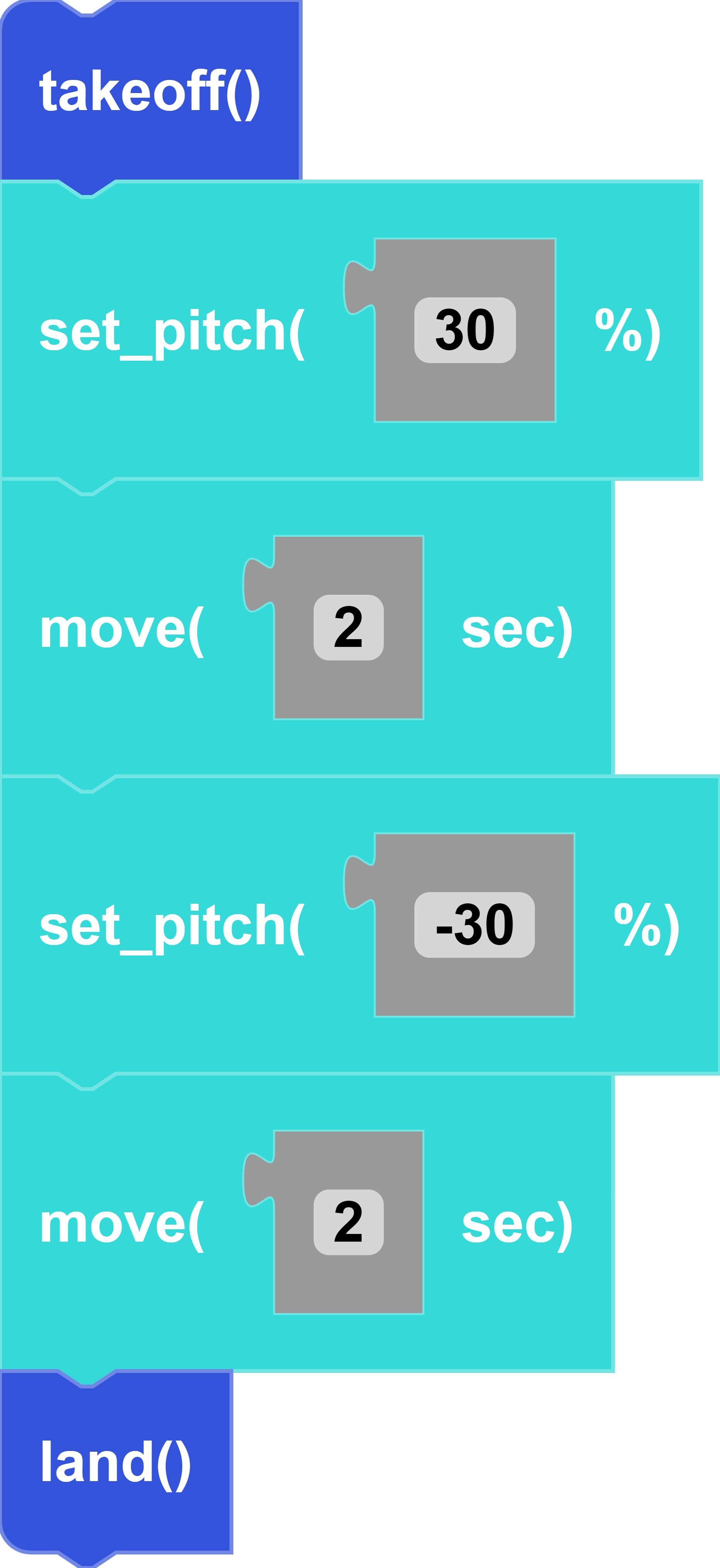
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its pitch variable at 30% for forward movement and moves for 2 seconds. And then the drone sets its pitch variable at -30% for backward movement and moves for 2 seconds.
set_yaw()
Block
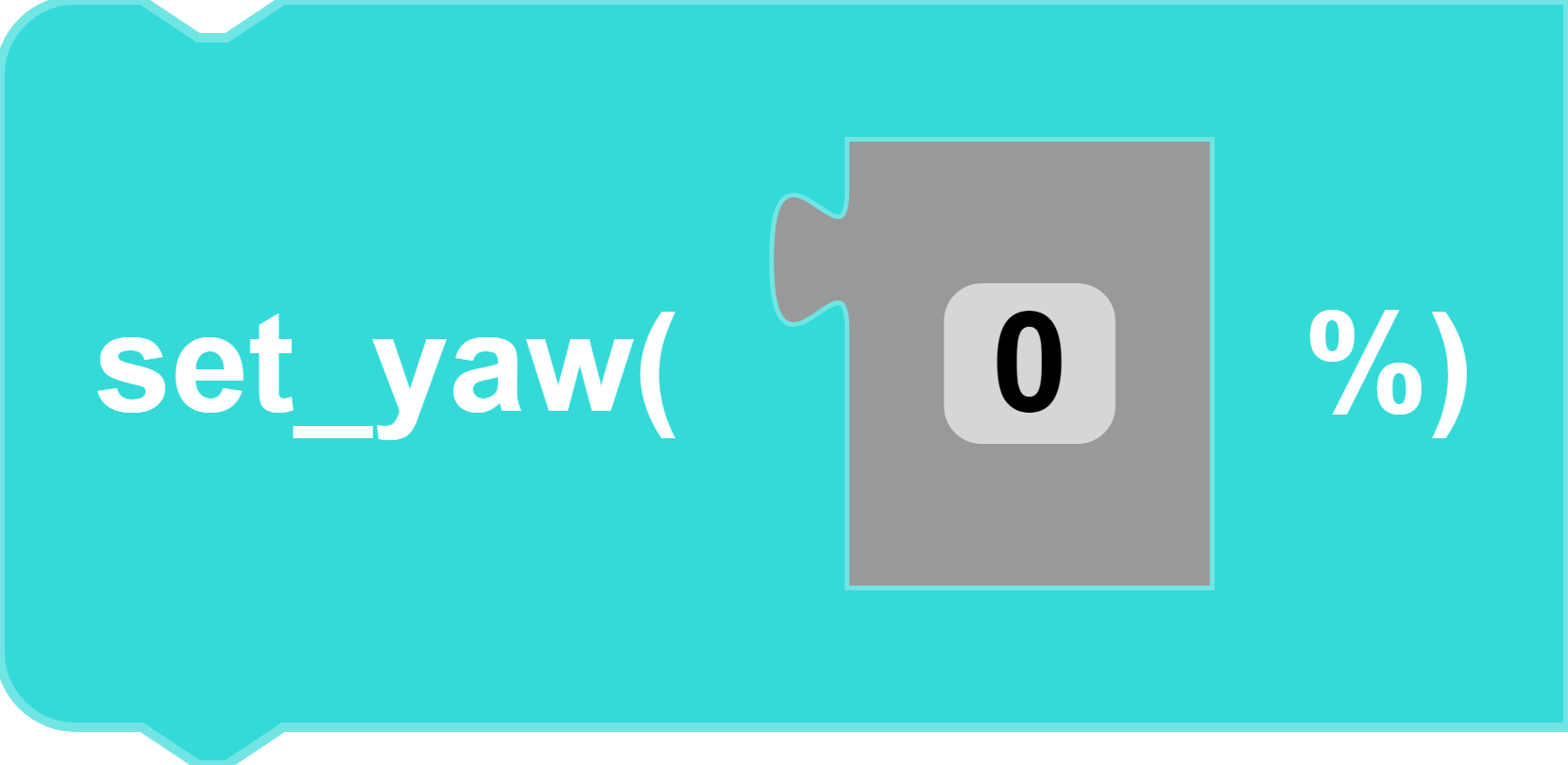
Code
drone. set_yaw()Description
This function sets the yaw direction variable but will not send a move command. Negative values will turn the drone to the right and positive values will turn the drone to the left.
Parameters
integer power: the power/speed of the drone between -100 and 100
Returns
None
Example
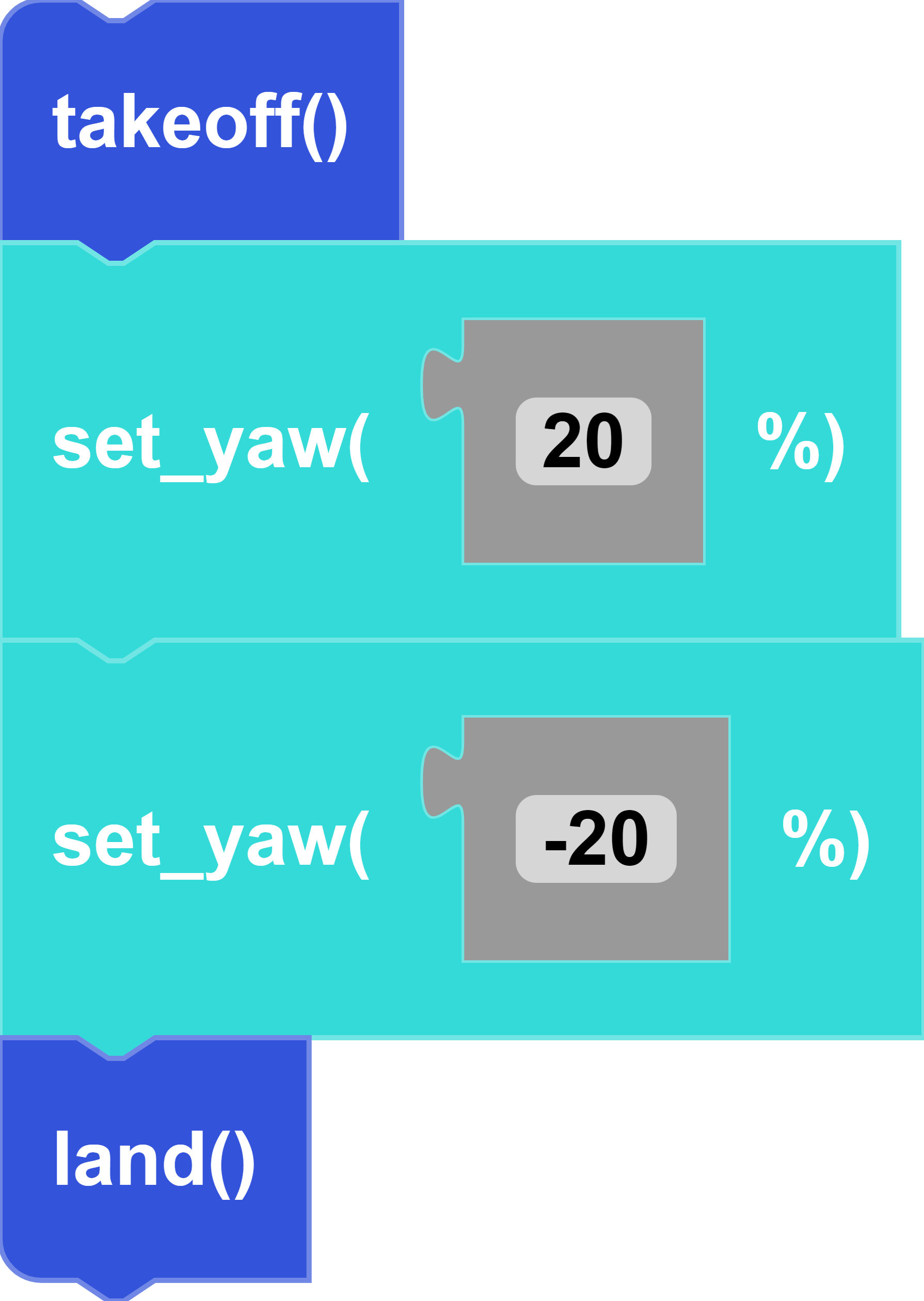
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its yaw variable at 20% for left turns and then sets its yaw variable at -20% for right turns. This will not make the drone move yet.
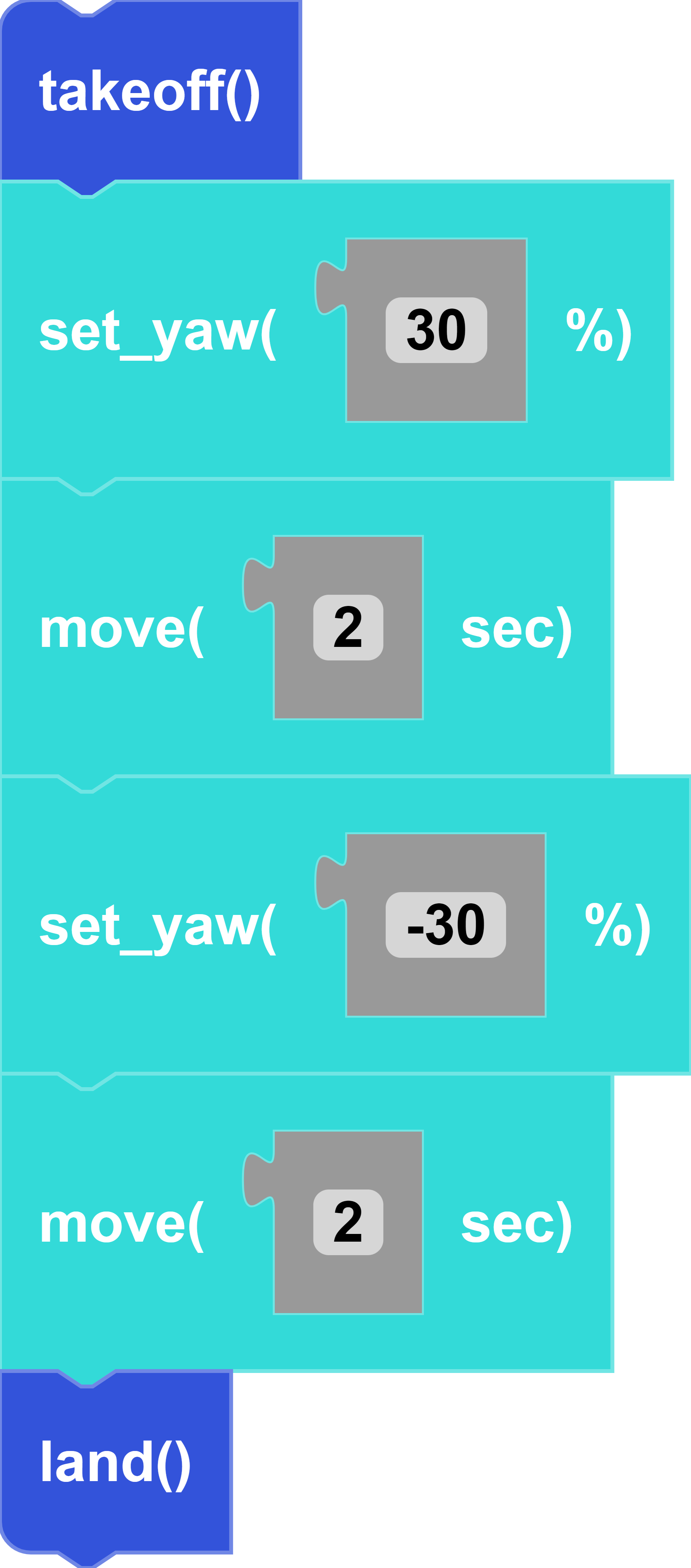
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its yaw variable at 30% for left turns and moves for 2 seconds. And then the drone sets its yaw variable at -30% for right turns and moves for 2 seconds.
set_throttle()
Block
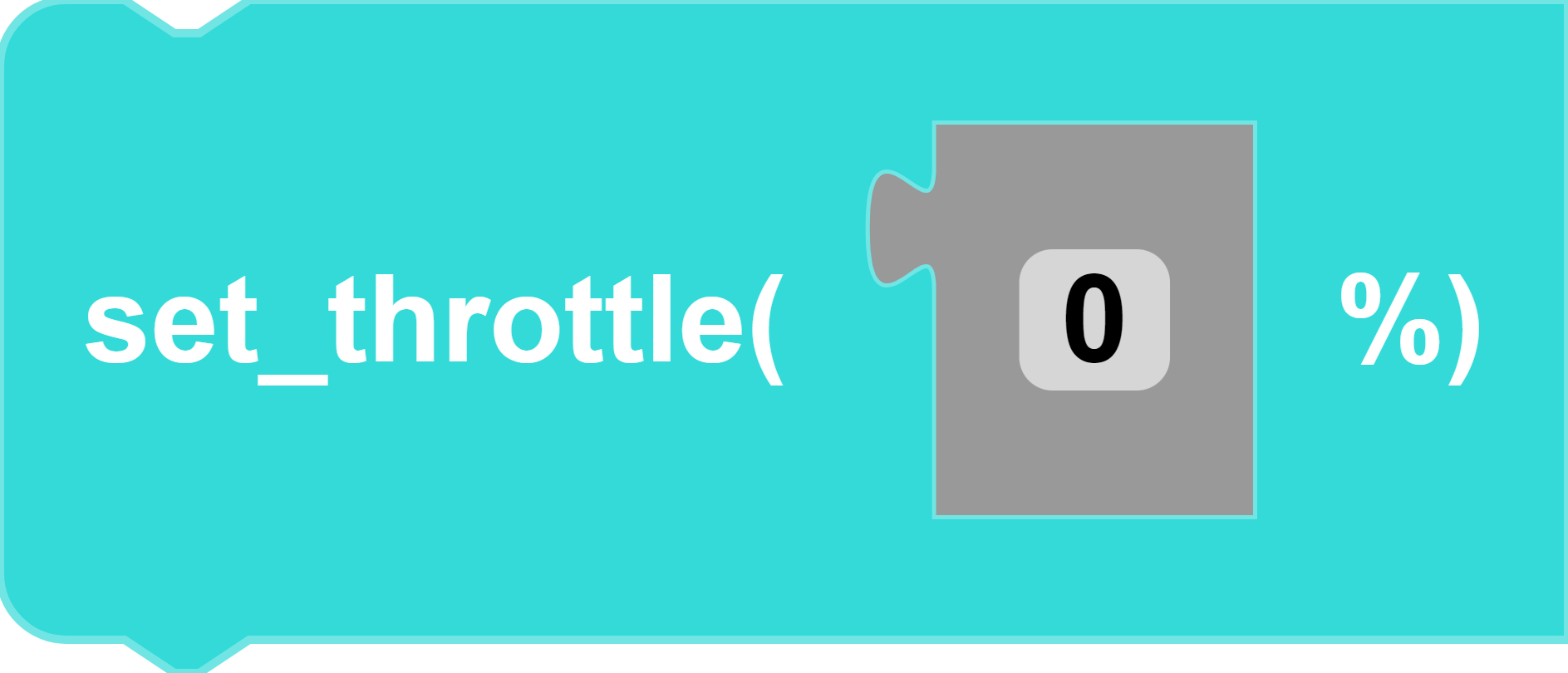
Code
drone. set_throttle()Description
This function sets the throttle direction variable but will not send a move command. Negative values will move the drone downward and positive values will move the drone upward.
Parameters
integer power: the power/speed of the drone between -100 and 100
Returns
None
Example
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its throttle variable at 20% for upward movement and then sets its throttle variable at -20% for downward movement. This will not make the drone move yet.
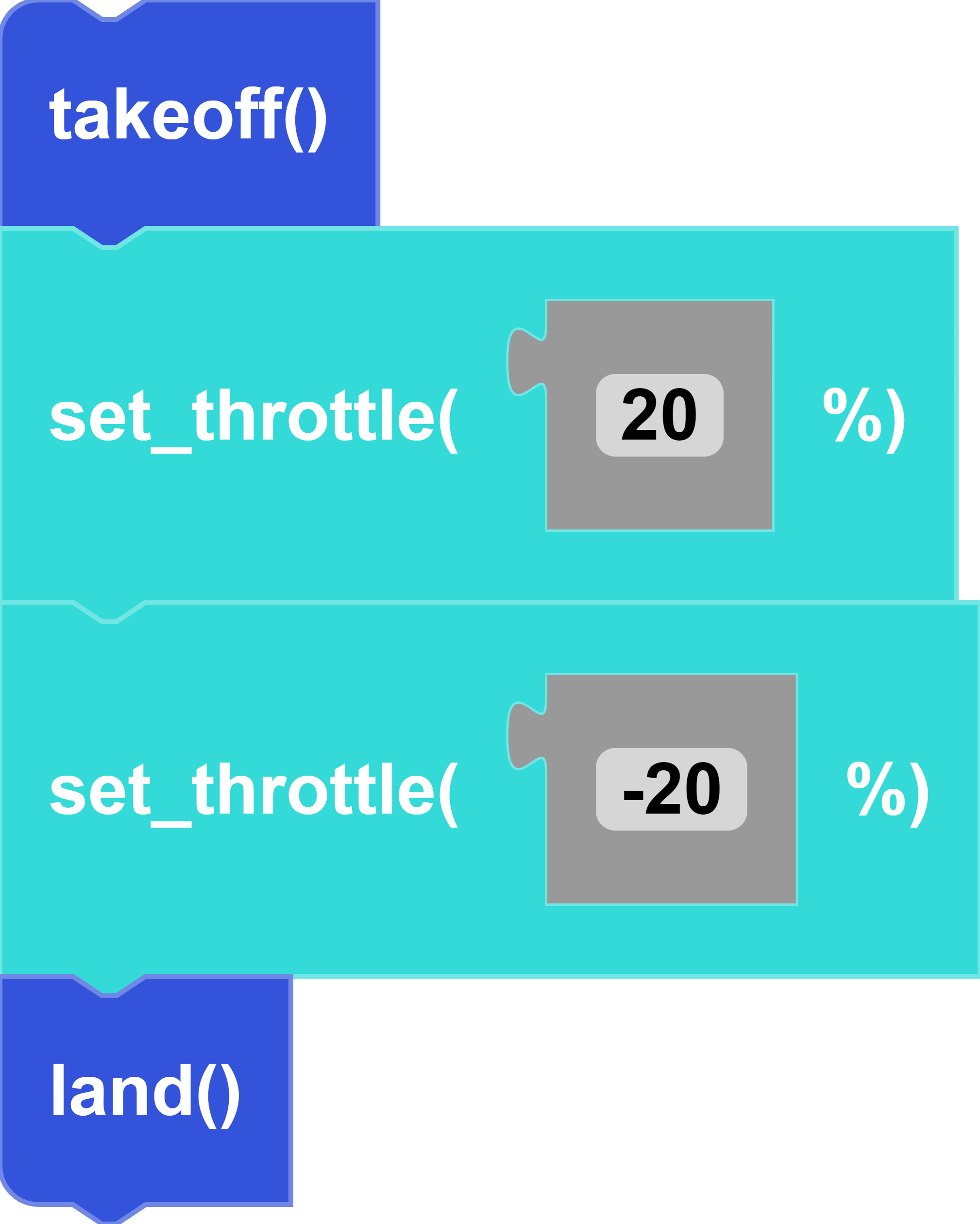
In this example, after taking off, the drone sets its throttle variable at 30% for upward movement and moves for 2 seconds. And then the drone sets its throttle variable at -30% for downward movement and moves for 2 seconds.
move()
Block

Code
drone. move()Description
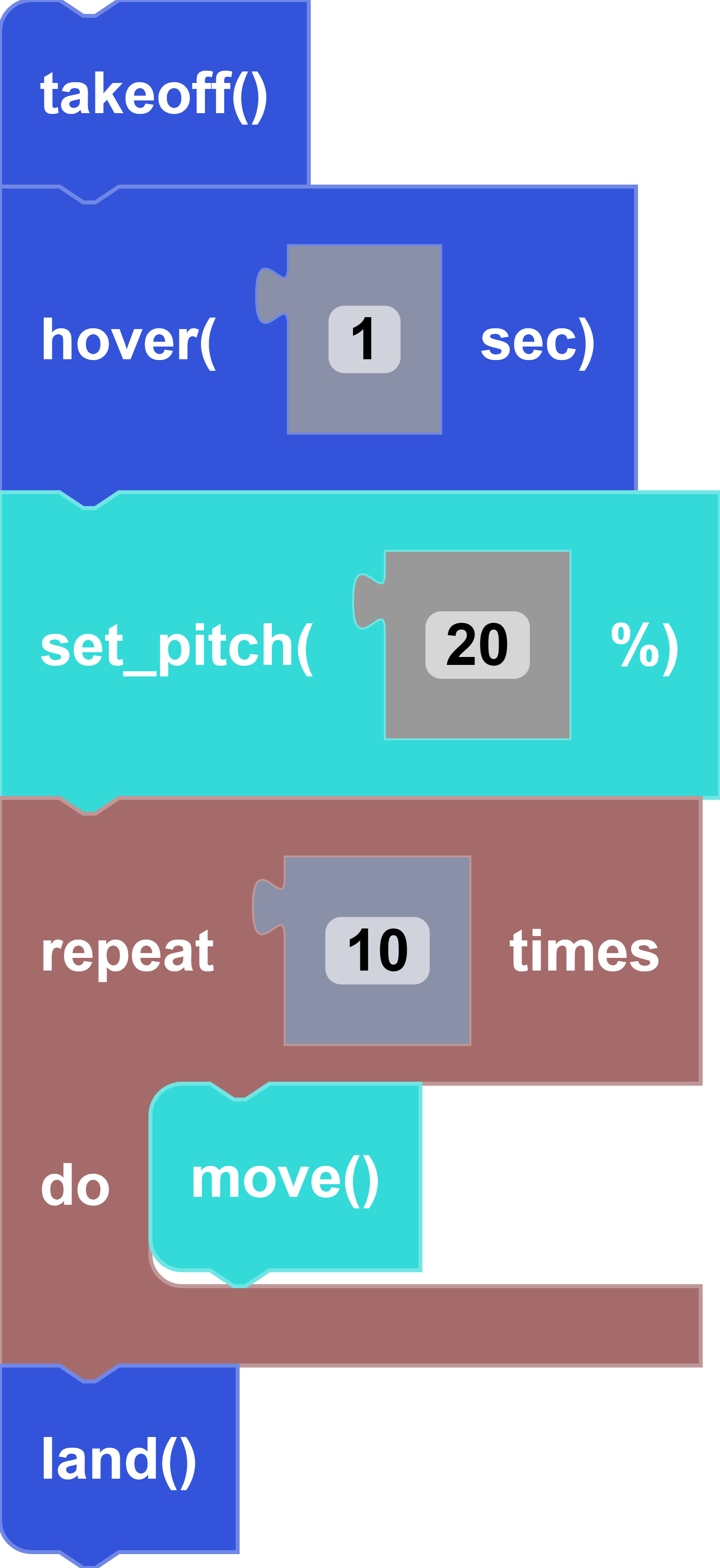
Moves CoDrone EDU in the direction set by the flight variables with the smallest duration possible (about 0.01 seconds). Since it has no specified duration, it is often used inside of a loop to check sensors simultaneously.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
move([duration])
Block

Code
drone. move()Description
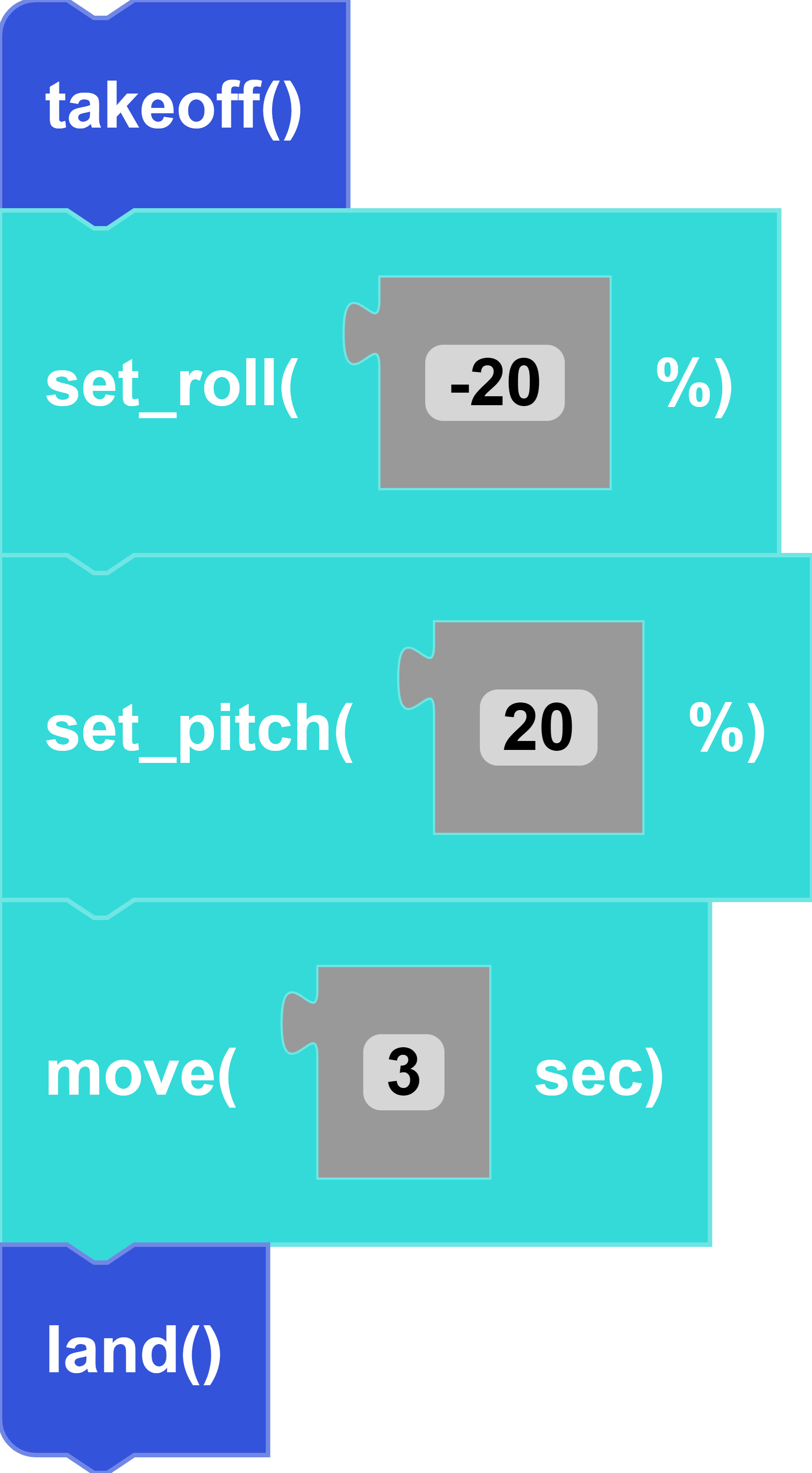
Moves CoDrone EDU for a duration in seconds in the direction set by the flight variables.
Parameters
integer duration: the duration of the movement in seconds
Returns
None
Example
set_trim()
Block

Code
drone. set_trim()Description
Sets the trim values to adjust for any drifting while CoDrone EDU is flying. Set the trim values in the opposite direction of drift. For example, if the drone is drifting to the right, set roll to a negative value.
Parameters
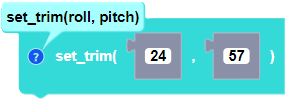
integer roll: the trim value to adjust for roll drifting, between -100 and 100
integer pitch: the trim value to adjust for pitch drifting, between -100 and 100
Returns
None
Example
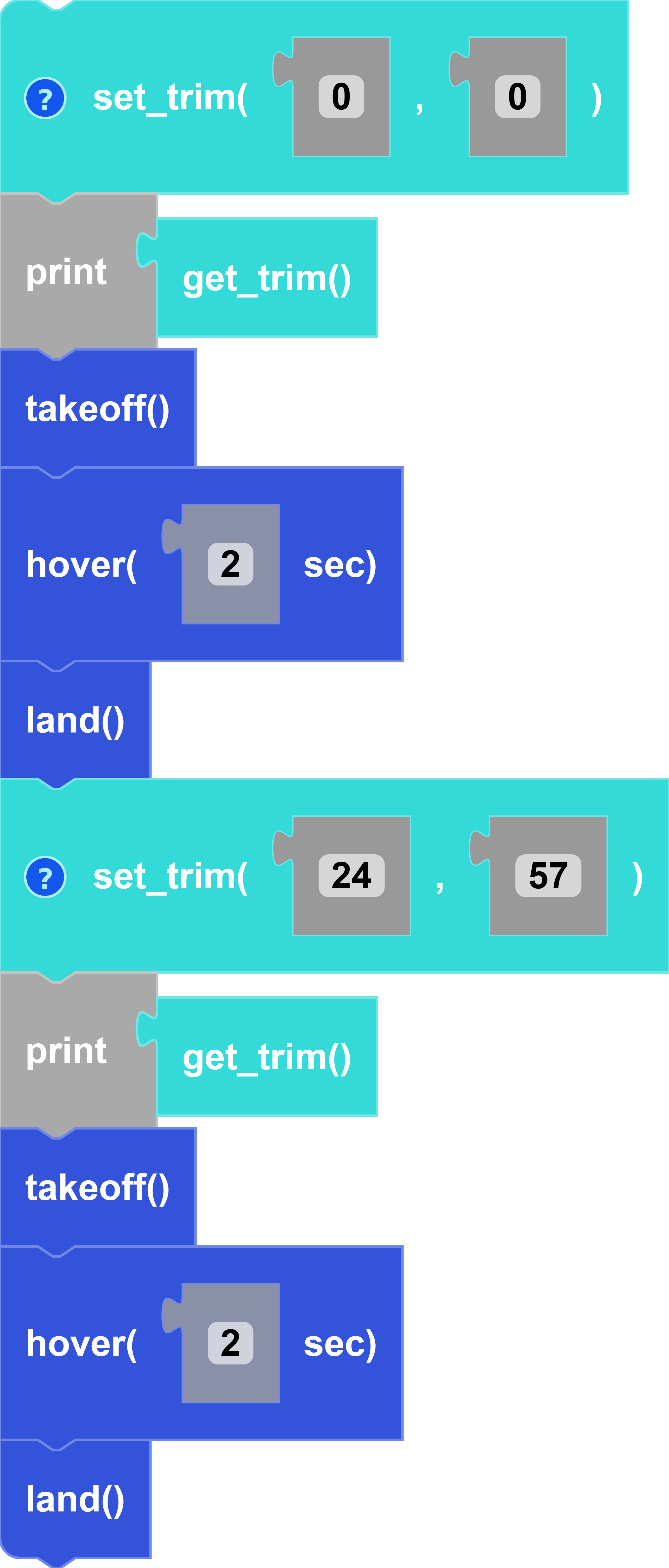
get_trim()
Block

Code
drone. get_trim()Description
Returns the current trim values. Combine with a print statement to see the results printed to the console.
Parameters
None
Returns
integer roll: the trim value for the roll movement, between -100 and 100
integer pitch: the trim value for the pitch movement, between -100 and 100
Example
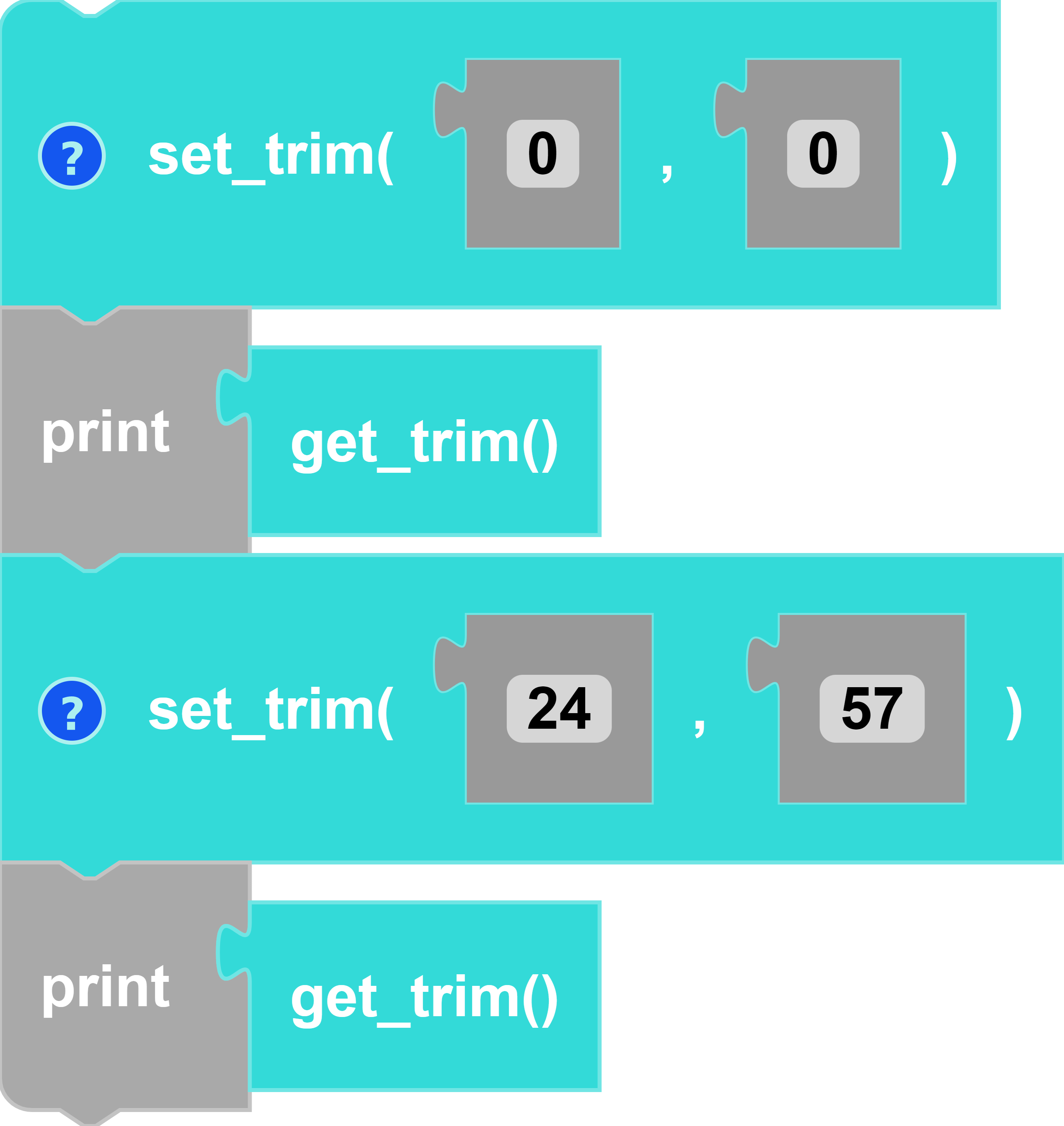
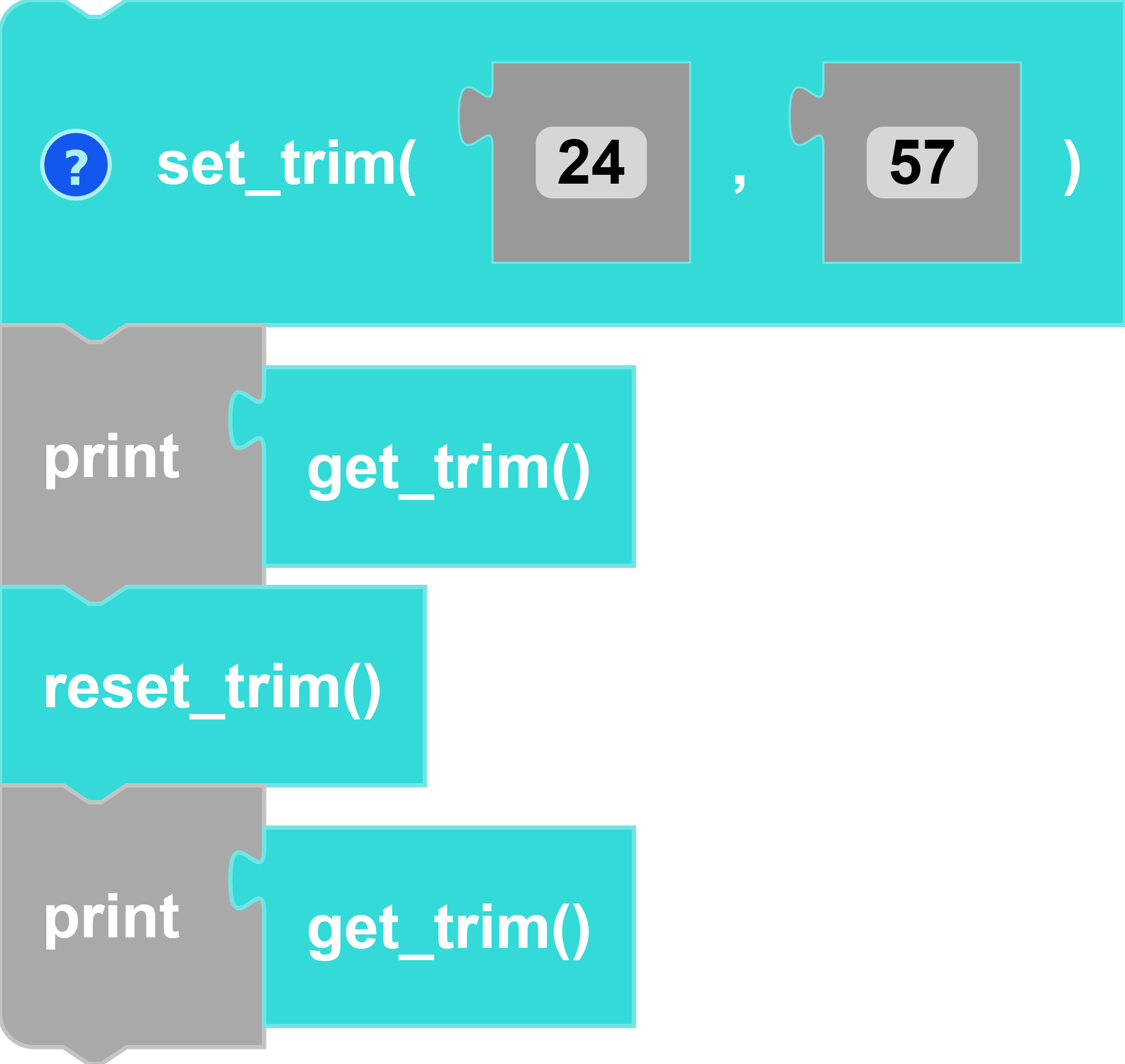
reset_trim()
Block

Code
drone. reset_trim()Description
Resets the trim values to (0,0).
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
Lights
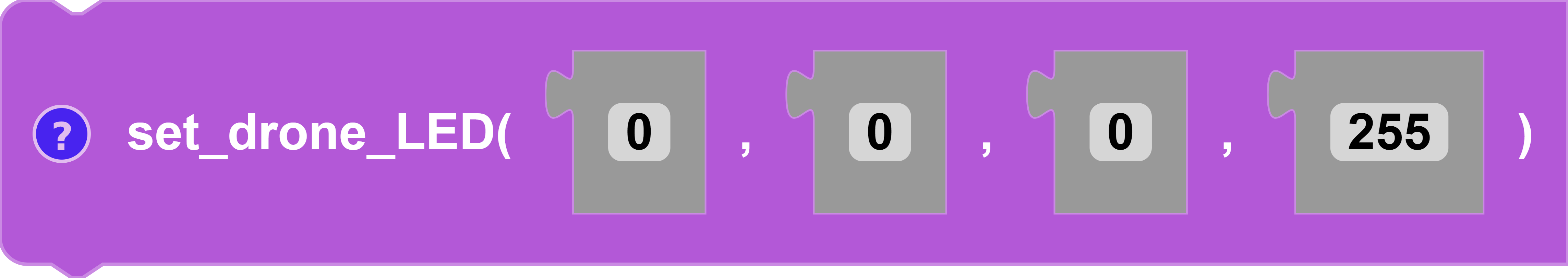
set_drone_LED()
Block
Code
drone. set_drone_LED()Description
Sets the color of CoDrone EDU's LED. Colors are set by using its RGB (red, green, blue) equivalent values.
Parameters

integer red: pixel value for the color red between 0 and 255
integer green: pixel value for the color green between 0 and 255
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue between 0 and 255
integer brightness: brightness of the drone LED between 0 and 255
Returns
None
Example

drone_LED_off()
Block
Code
drone. drone_LED_off()Description
Turns off CoDrone EDU's LED.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
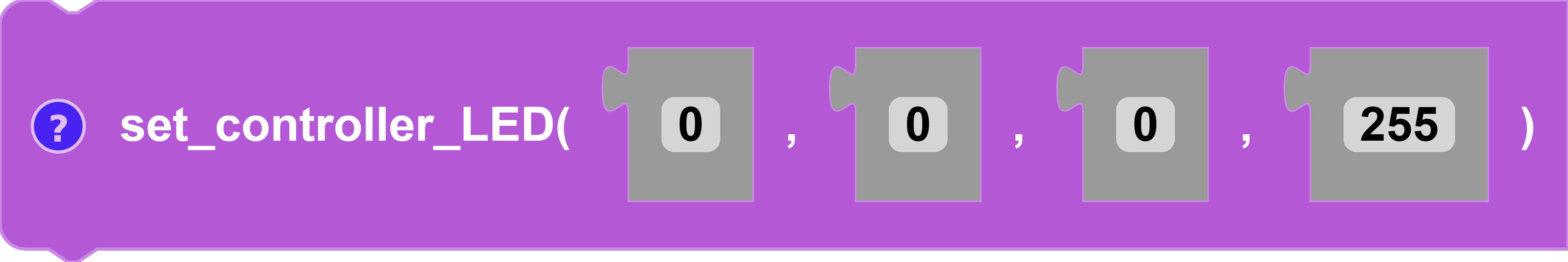
set_controller_LED()
Block
Code
drone. set_controller_LED()Description
Sets the color of CoDrone EDU's controller LED. Colors are set by using its RGB (red, green, blue) equivalent values.
Parameters

integer red: pixel value for the color red between 0 and 255
integer green: pixel value for the color green between 0 and 255
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue between 0 and 255
integer brightness: brightness of the controller LED between 0 and 255
Returns
None
Example

controller_LED_off()
Block

Code
drone. controller_LED_off()Description
Turns off the CoDrone EDU's controller LED.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
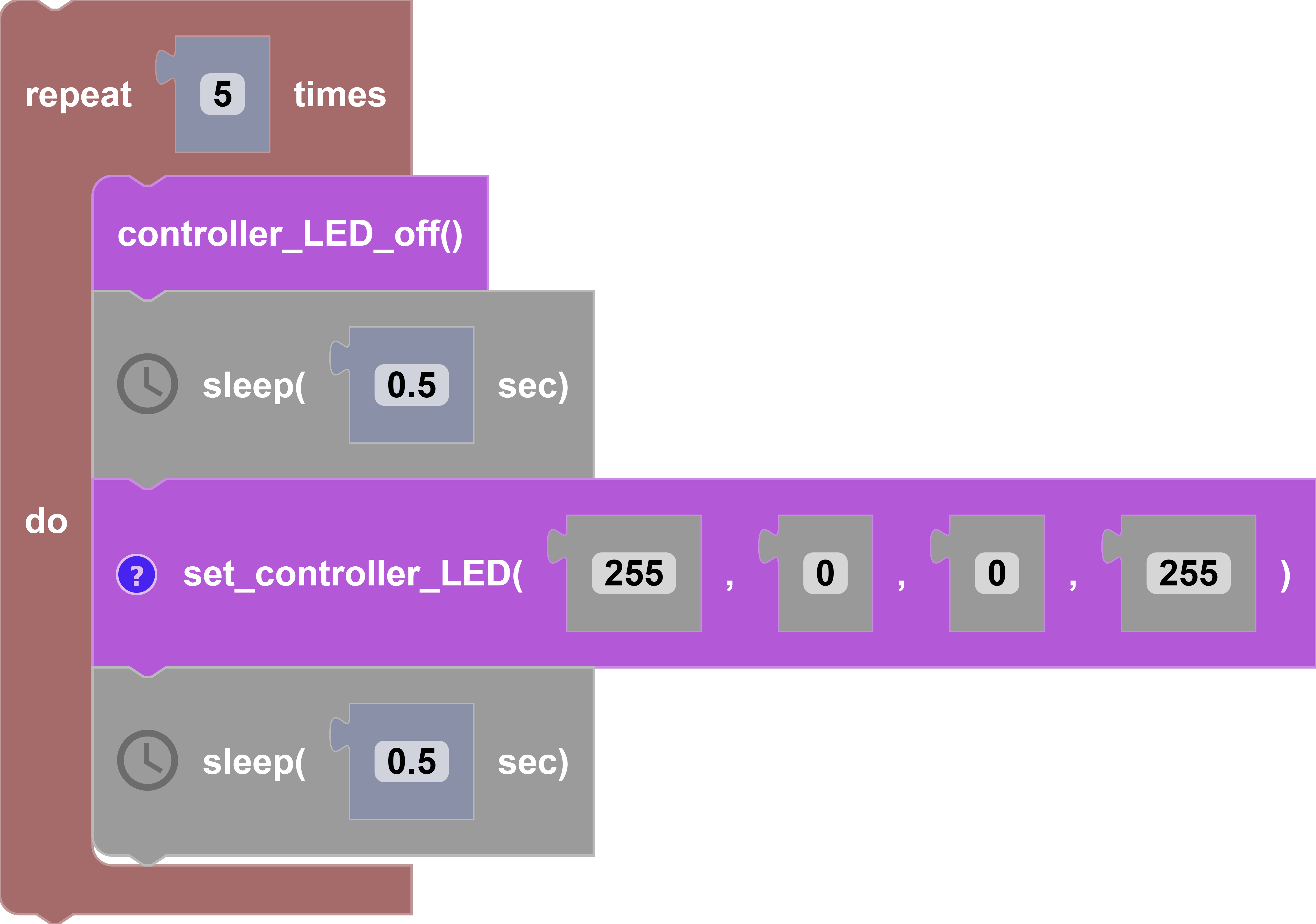
Sensors
get_range()
Block

Code
front: drone.get_front_range()
bottom: drone.get_bottom_range()
Description
Returns the calculated distance from either the front or bottom infrared (IR) range sensor to the surface. The sensor range is up to 1.5m.
NOTE: The front range sensor will not be able to get an exact reading of 0 due to light scattering and interference. The lowest value you may see is approximately 9mm (0.9cm) by covering the sensor.
NOTE: The bottom range sensor will be able to get an exact reading of 0 if the drone is sitting on a surface. If the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range sensor turns off (causing a reading of 0), so that the color sensor can turn on and detect color without any interference. It is safe to assume that if the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range or height is 0.
Parameters

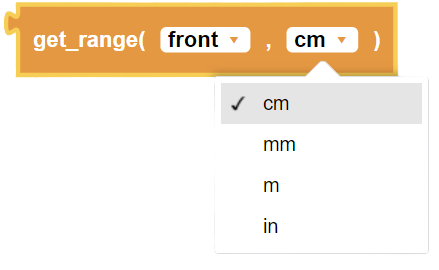
type: front, bottom
unit: cm, mm, in, m
Returns
float distance: float value in the units selected
Example
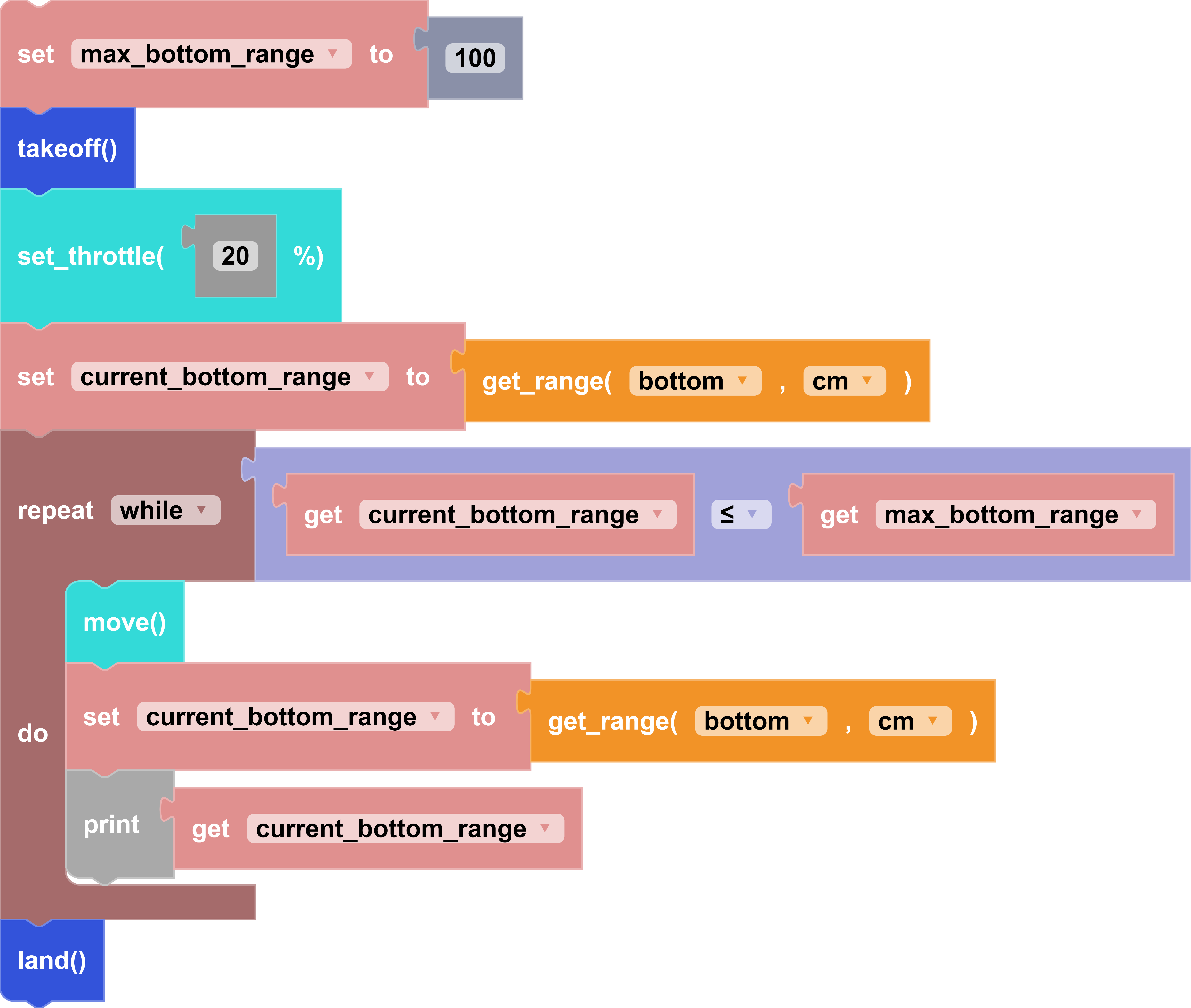
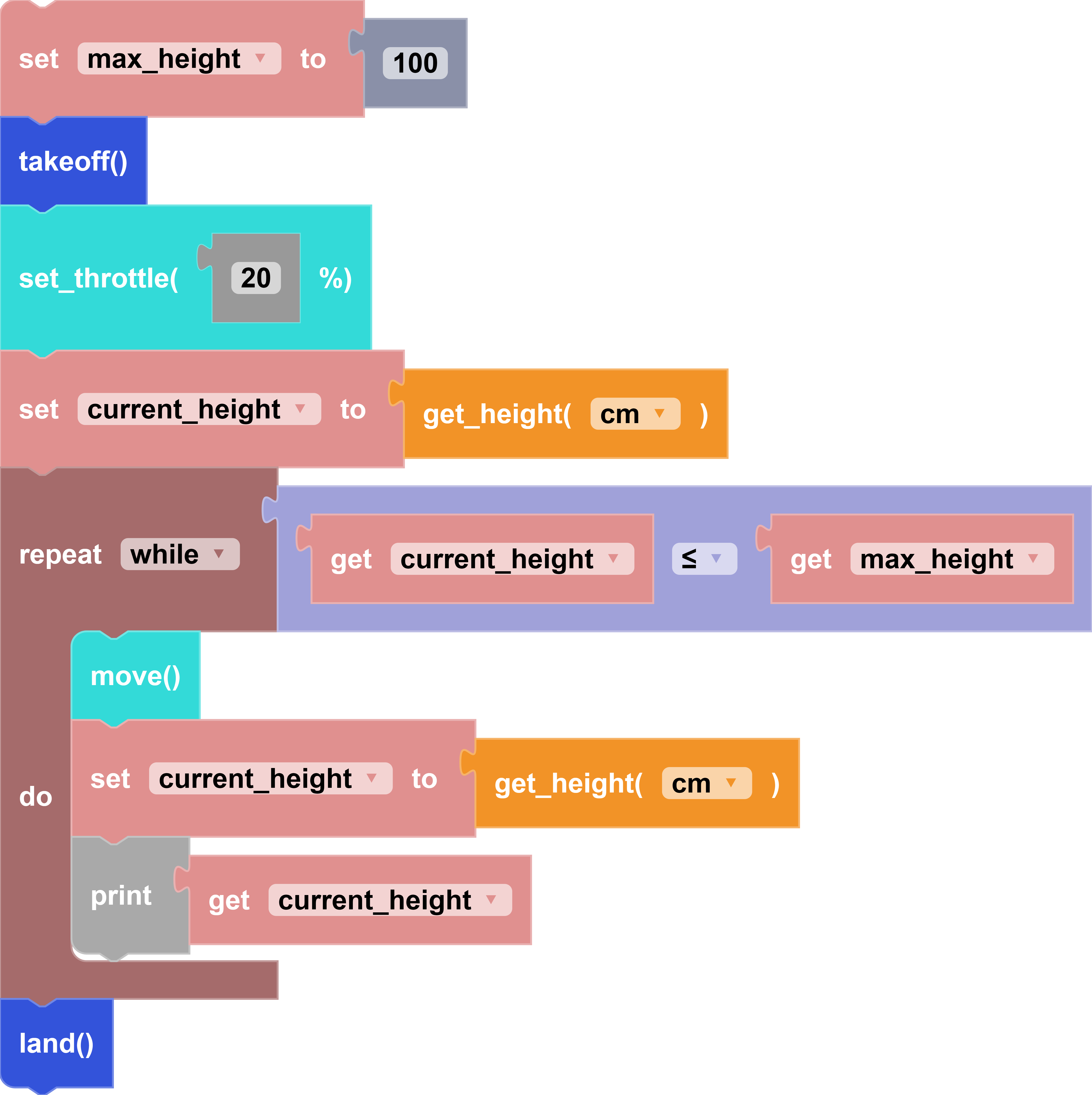
In this example, after takeoff, the drone has its throttle set at 20% power, moving upward. Before entering the loop, it checks if the drone has already reached the maximum bottom range (set as 100), measured in centimeters. If not, it will continuously fly upward until the current bottom range is more than the max bottom range.
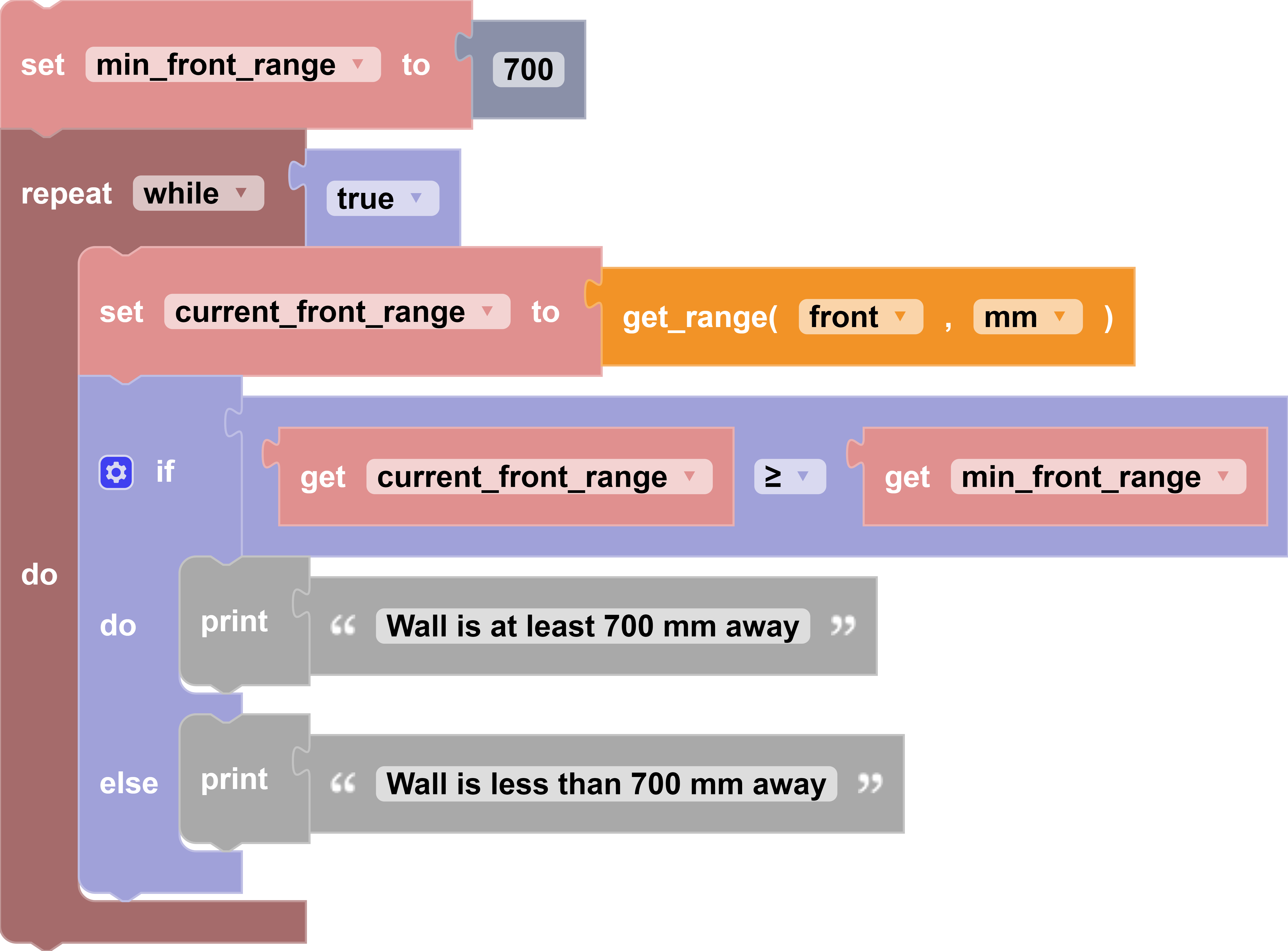
In this example below, run the program, manually point the drone to a wall, and then move it aroun until the drone is less than 70 cm away from a wall. Click the Stop button if you want to stop running the program.
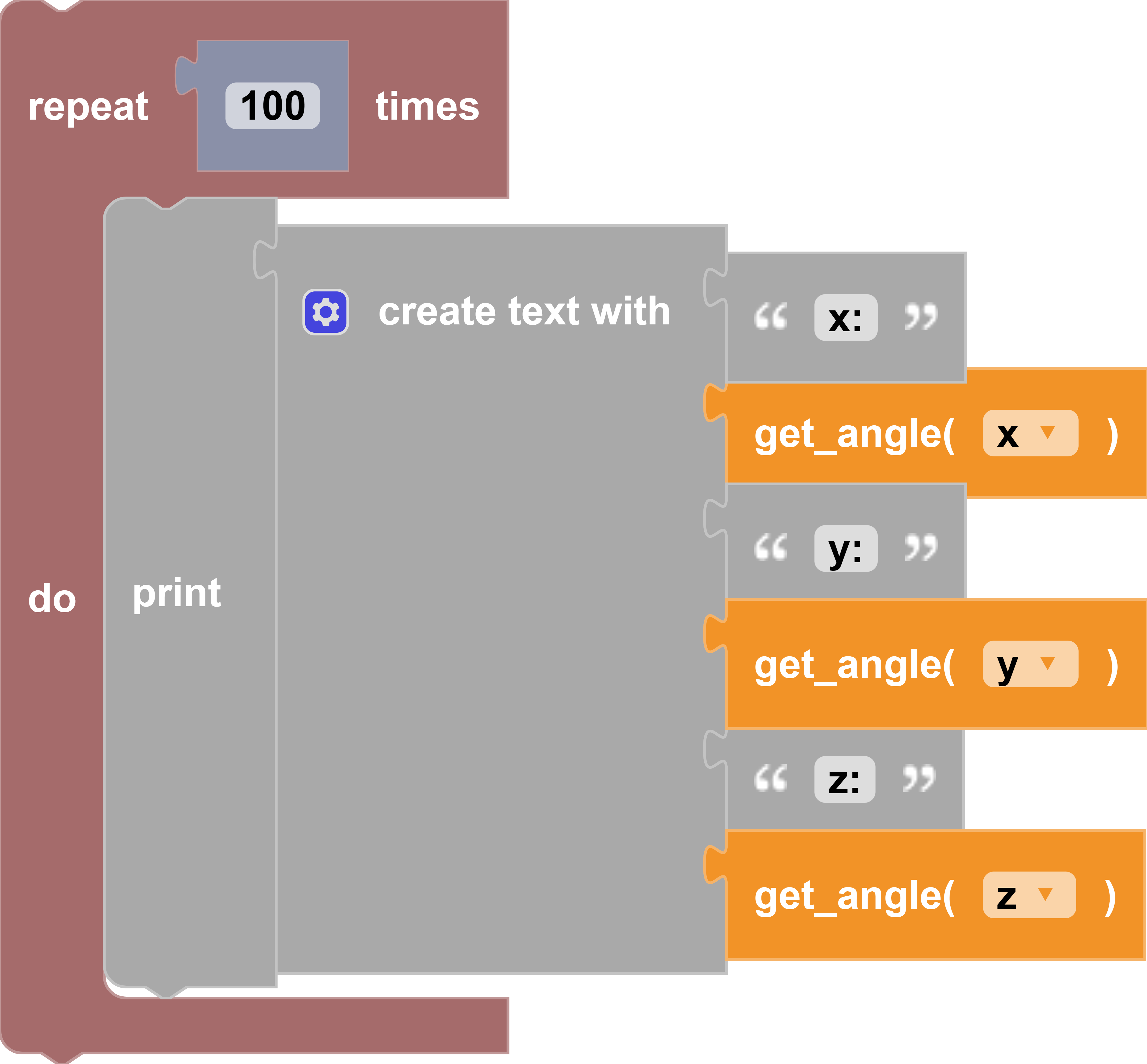
get_angle()
Block

Code
x: drone.get_angle_x()
y: drone.get_angle_y()
z: drone.get_angle_z()
Description
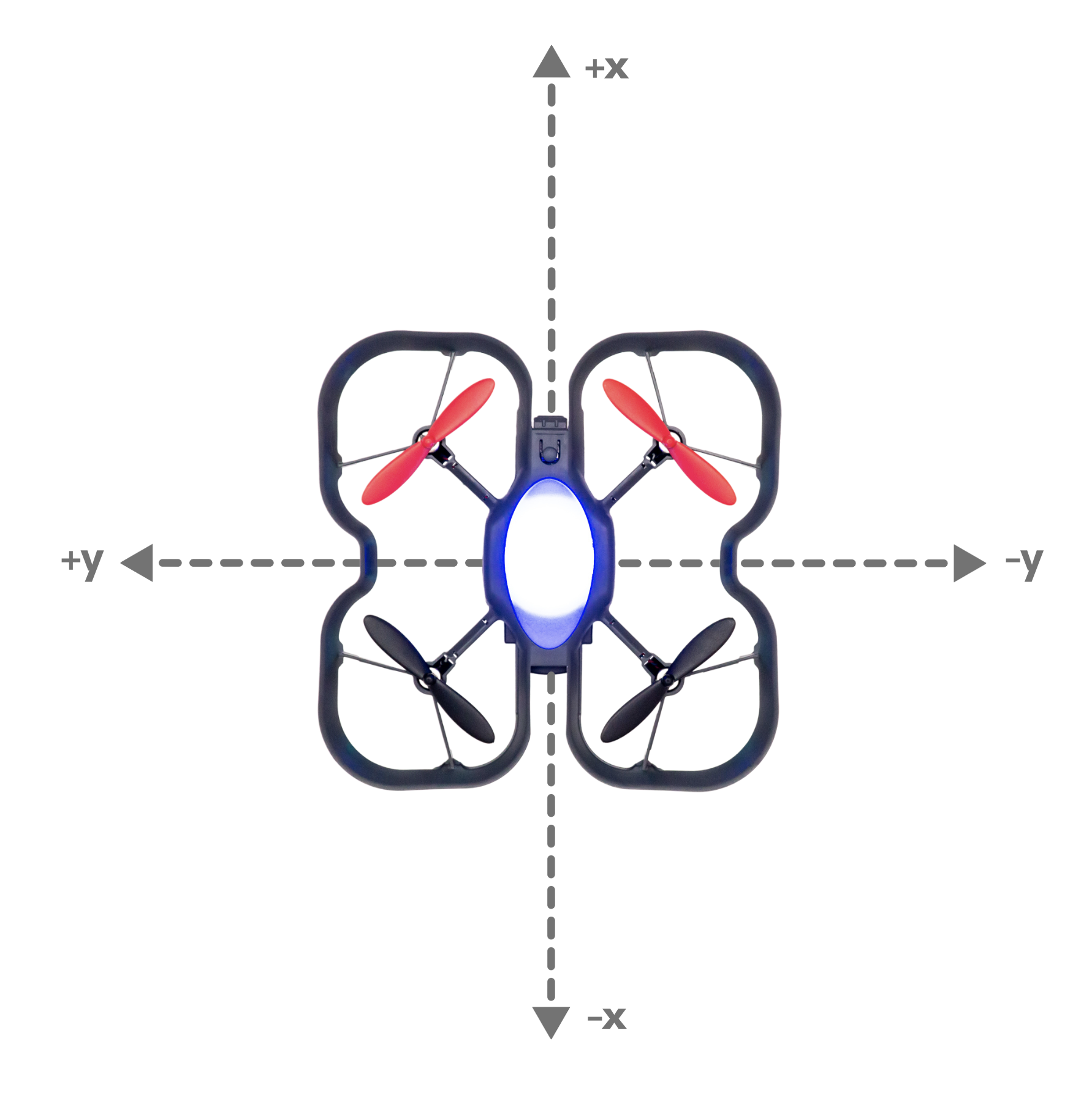
This function returns the current gyroscope angle measurement for either the x (roll),y (pitch), or z (yaw) axis. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Parameters

axis: x, y, z
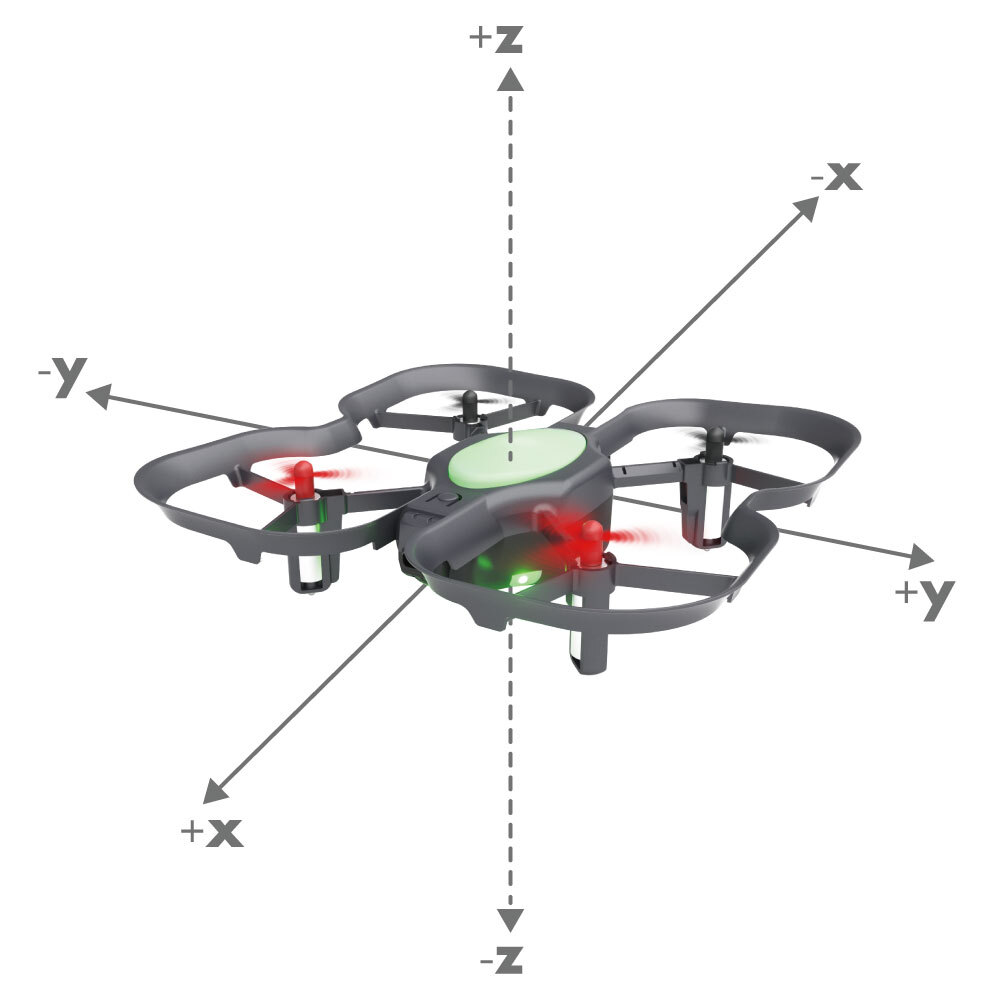
Returns
integer angle: gyroscope angle measurement for the given axis, in degrees
Example
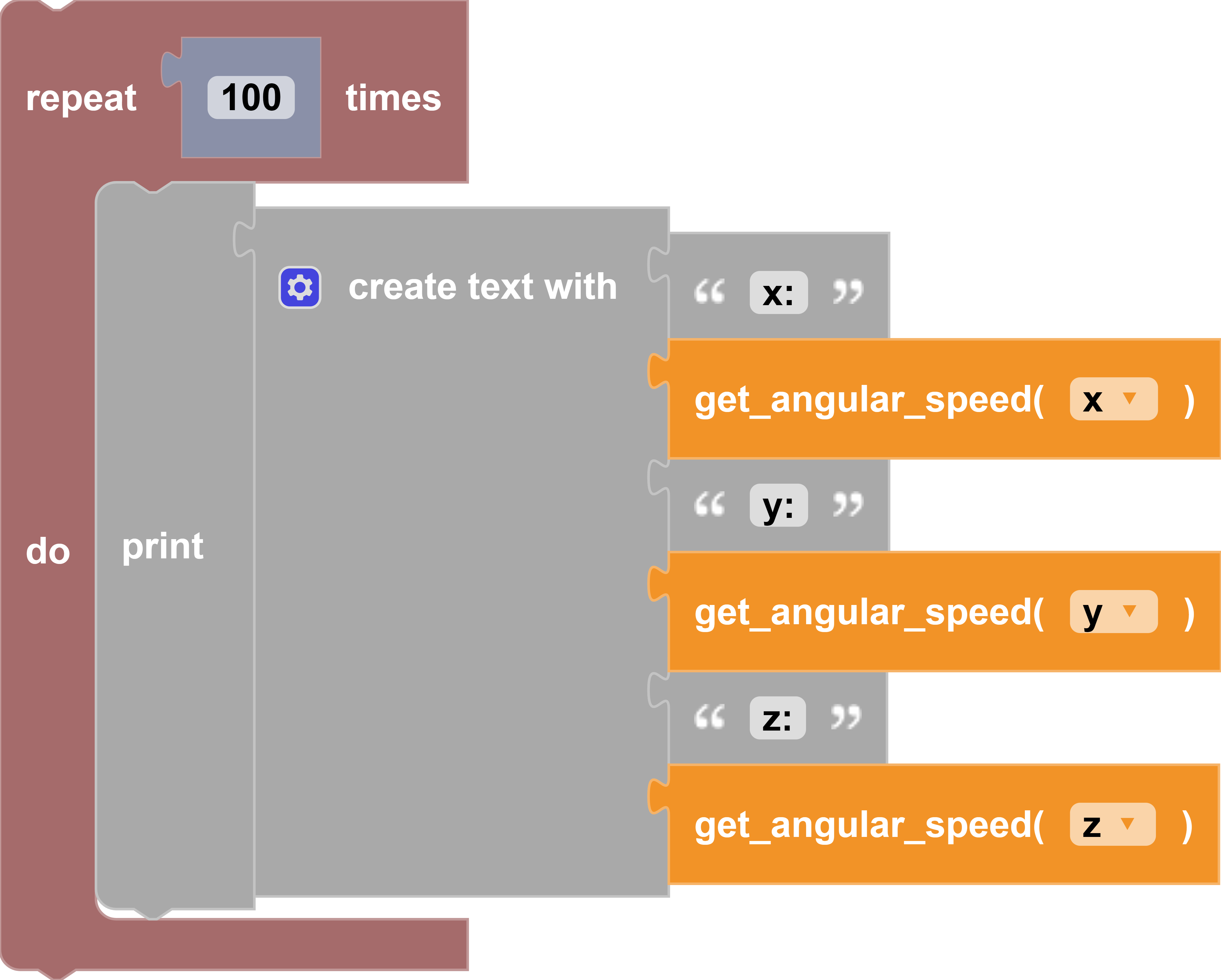
get_angular_speed()
Block

Code
x: drone.get_angular_speed_x()
y: drone.get_angular_speed_y()
z: drone.get_angular_speed_z()
Description
This function returns the current angular velocity in degrees per second for either the x (roll),y (pitch), or z (yaw) axis.
Parameters
type: x, y, z

Returns
integer angular velocity: the angular velocity of the drone, in degrees per second
Example
get_accel()
Block

Code
x: drone.get_accel_x()
y: drone.get_accel_y()
z: drone.get_accel_z()
Description
This function returns the current acceleration on either the x, y, or z axis in units of .
Note: 1g =

Parameters

type: x, y, z
Returns
integer acceleration: positive or negative acceleration of the drone, in
Example
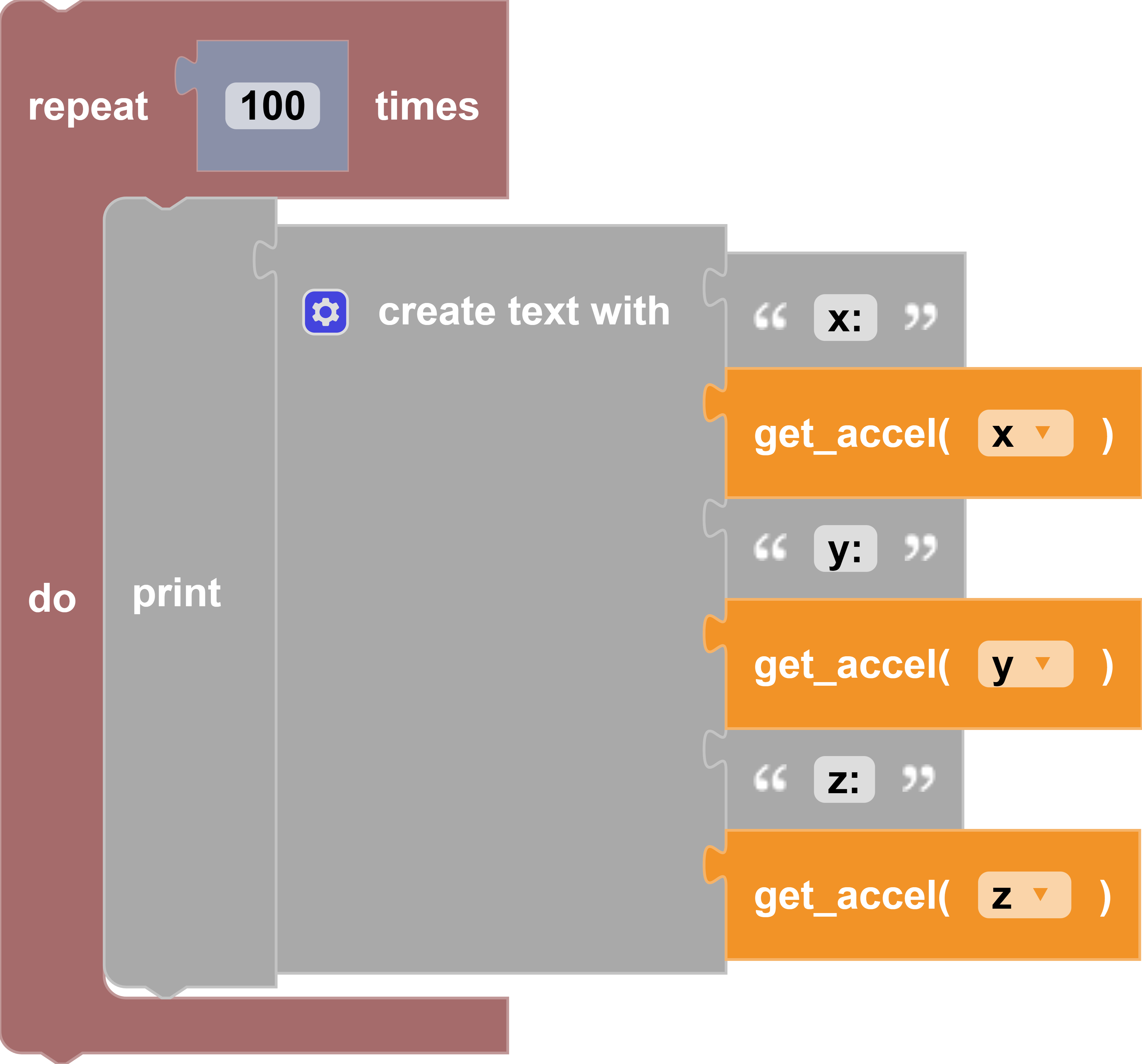
get_pos()
Block

Code
x: drone.get_pos_x()
y: drone.get_pos_y()
z: drone.get_pos_z()
Description
Returns the current estimated position of the CoDrone EDU using the optical flow sensor. NOTE: The drone's position values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Parameters
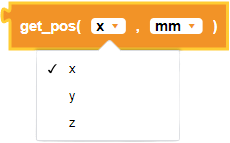
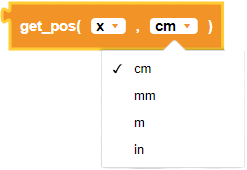
axis: x, y, z
unit: mm, cm, in, m

Returns
float position: x,y, or z value in units selected
Example
In this example, after takeoff, the console prints the x-y-z coordinates of the drone's position, in centimeters. Then, prints the x-y-z coordinates again after moving for 2 seconds.
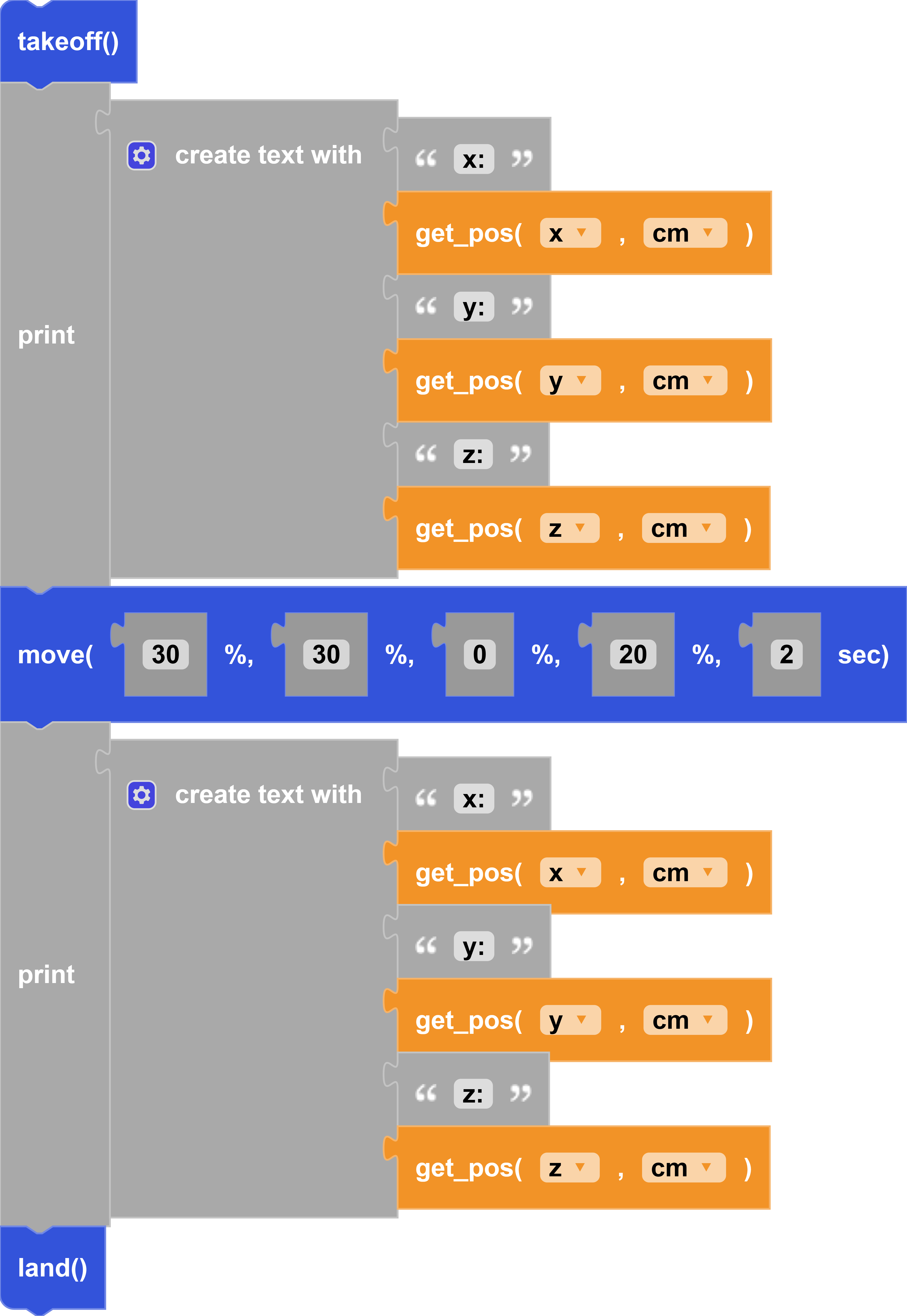
In this example, after takeoff, the console prints the x-y-z coordinates of the drone's position, in inches. Prints x-coordinate of the drone after moving right. Prints y-coordinate of the drone after moving forward. Prints z-coordinate of the drone after flying higher.

get_battery()
Block

Code
drone. get_battery()Description
This function returns the current battery percentage of the drone battery.
Parameters
None
Returns
integer battery percentage: the battery percentage from 0 to 100
Example
In this example, the program will check the drone's battery before takeoff and after landing.
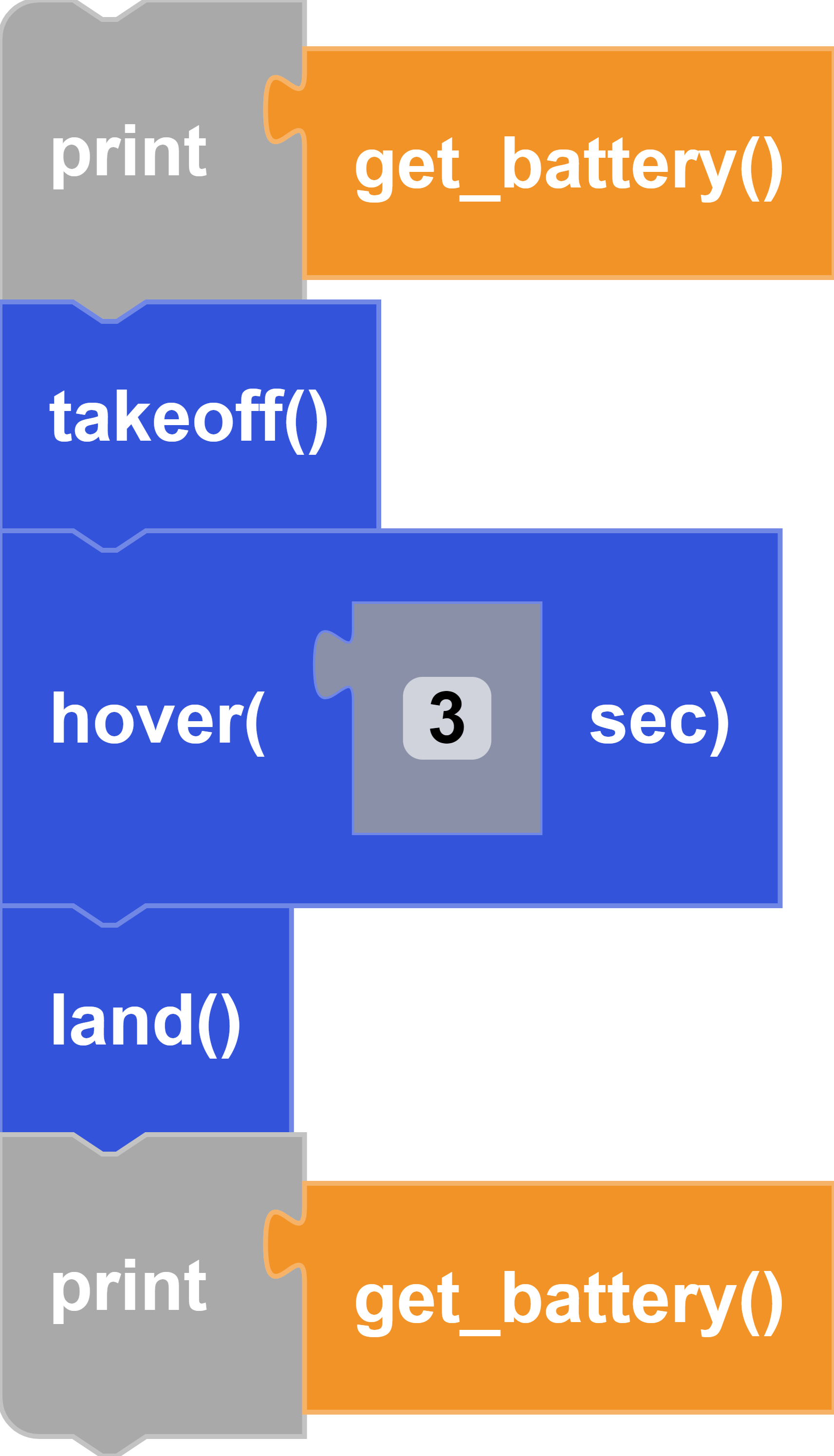
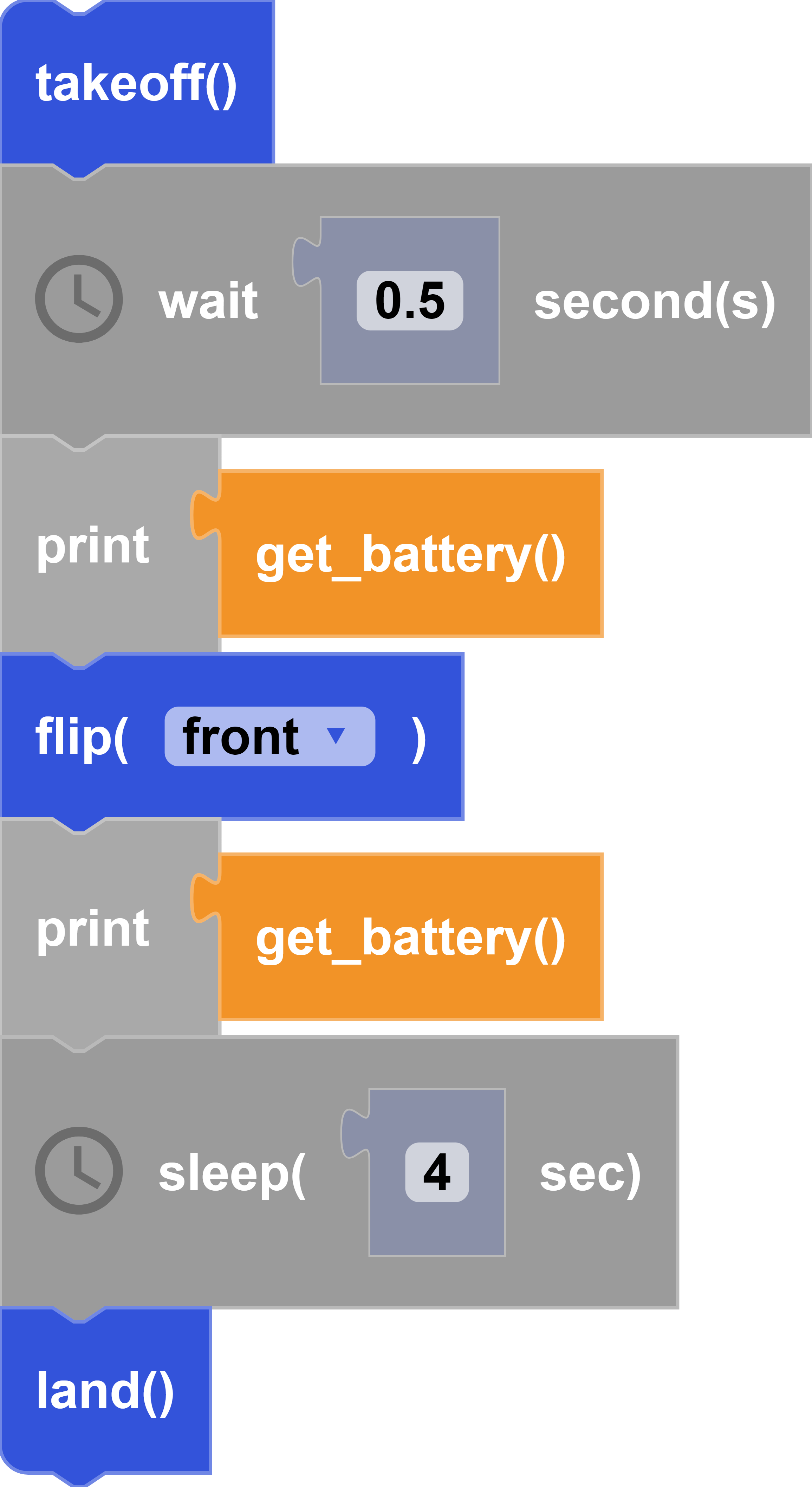
In the example below, the program will check the drone's battery before takeoff and after the front flip. The difference of battery percentage will be larger in this example than the previous one.
get_height()
Block

Code
drone. get_height()Description
Returns the calculated distance from the bottom infrared (IR) range sensor to the surface. The sensor range is up to 1.5m. This is another name for the get_range("bottom") function.
NOTE: The bottom range sensor will be able to get an exact reading of 0 if the drone is sitting on a surface. If the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range sensor turns off (causing a reading of 0), so that the color sensor can turn on and detect color without any interference. It is safe to assume that if the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range or height is 0.
Parameters
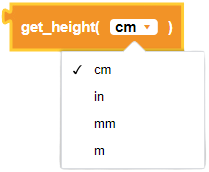
units: cm, in, mm, m
Returns
float height: float height value in the units selected
Example
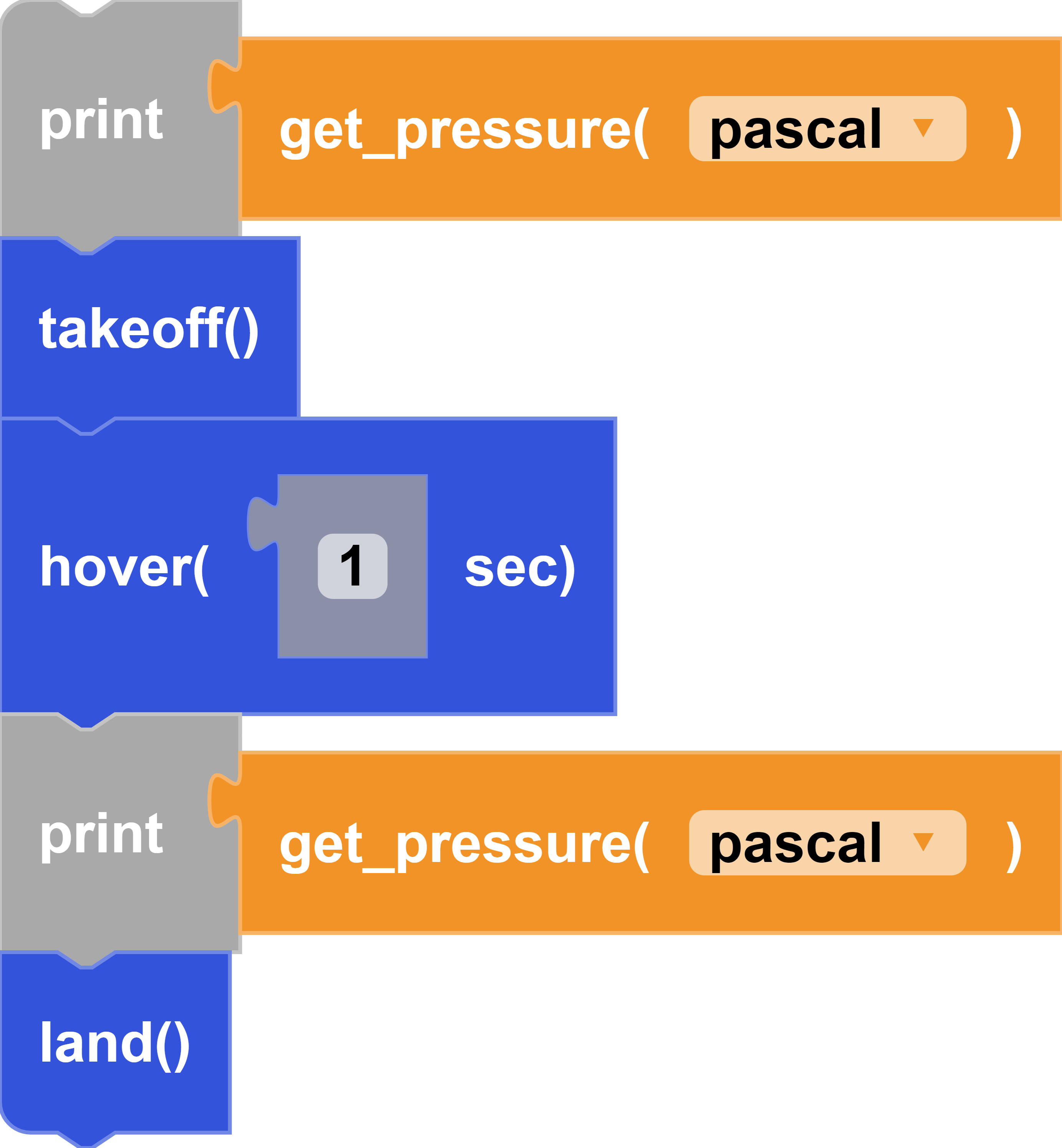
get_pressure()
Block

Code
drone. get_pressure()Description
This function returns barometer data in either pascals or millibars.
Note: 1 mbar = 100 Pa
Parameters

unit: pascal or millibar
Returns
float pressure: float value in either Pa or mbar
Example
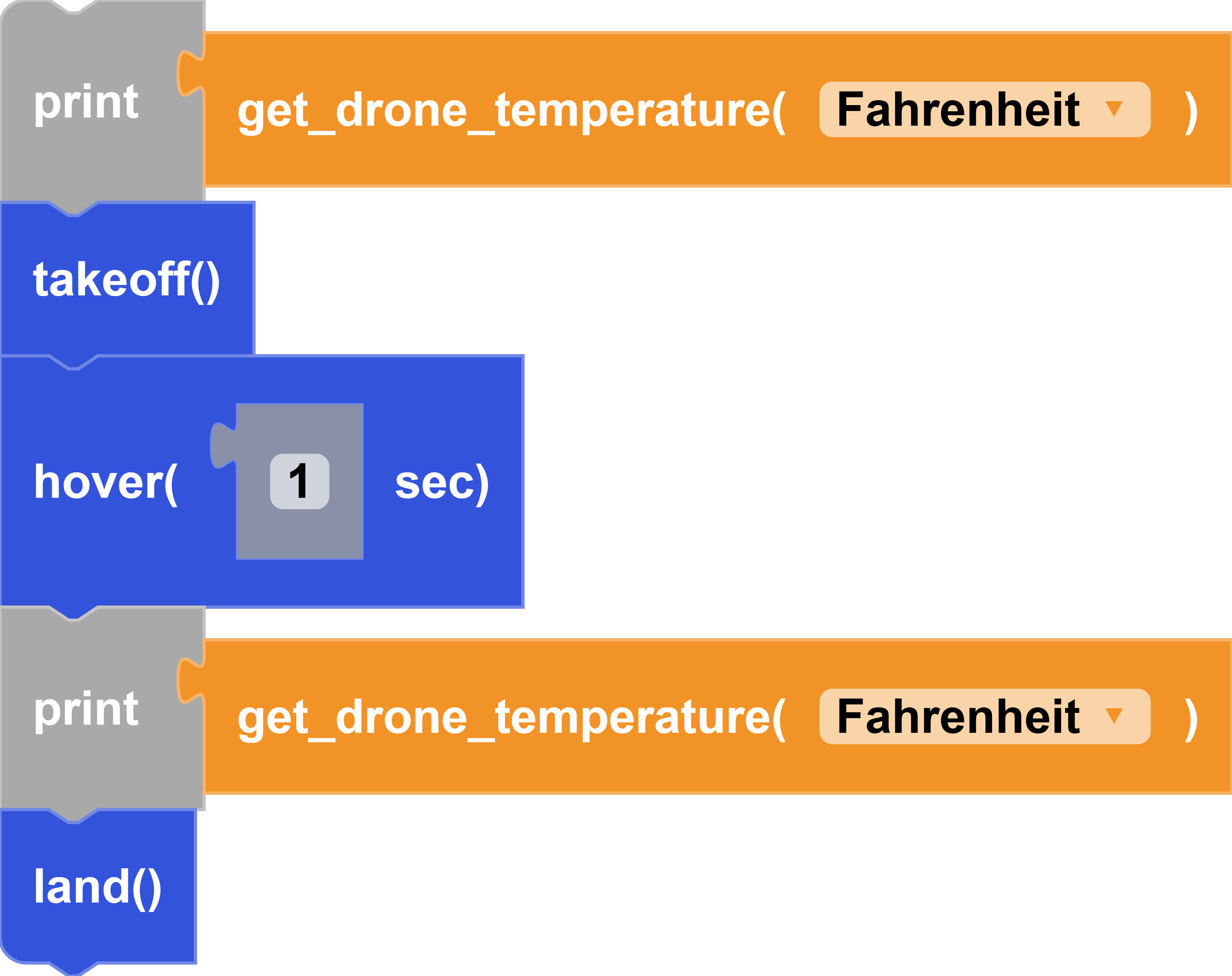
get_drone_temperature()
Block

Code
drone. get_drone_temperature()Description
This block returns the current temperature of the drone in either Celsius or Fahrenheit.
Parameters
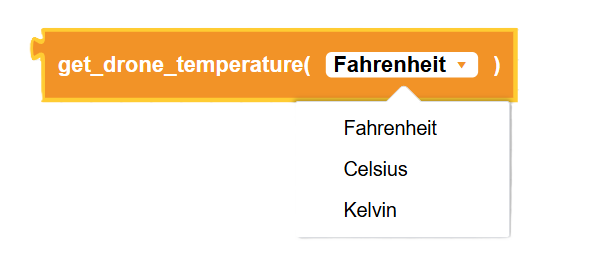
unit: Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin
Returns
float temperature: float value in degrees
Example
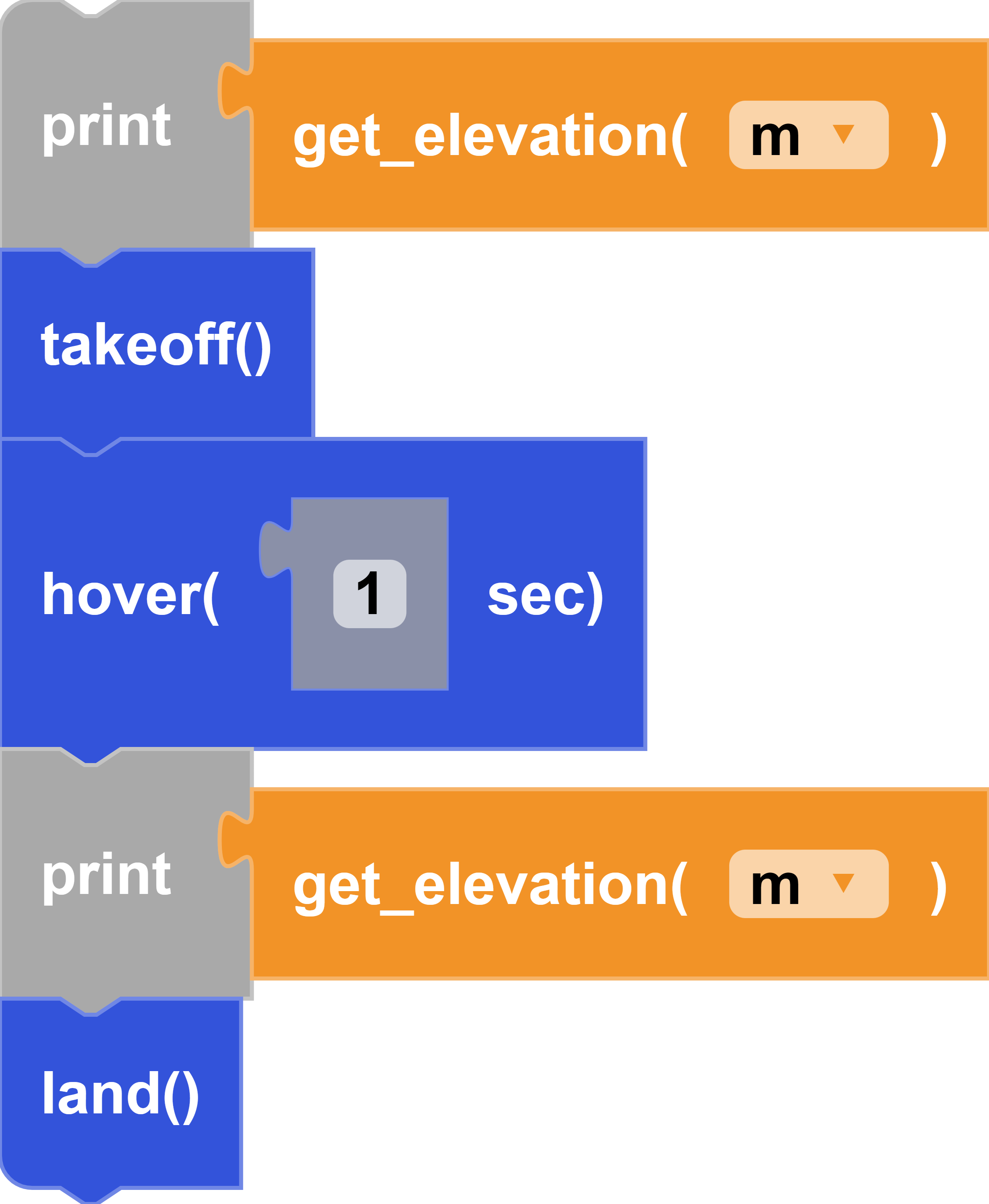
get_elevation()
Block

Code
drone. get_elevation()Description
Returns the estimated elevation data from the CoDrone EDU's barometer.
Parameters
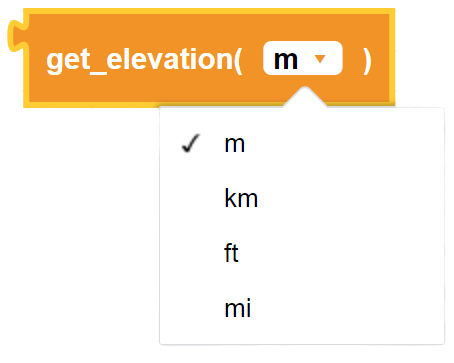
unit: m (meter), km (kilometer), ft (feet), mi (miles).
Returns
float elevation: float elevation value in units selected
Example
get_color()
Block

Code
front: drone.get_front_color()
back: drone.get_back_color()
Description
This functions reads the color data from either of the two bottom color sensors and returns one of the 8 pre-calibrated colors (provided in the color cards). The drone must be flat on a surface (not flying) for the color sensor to activate.
Parameters
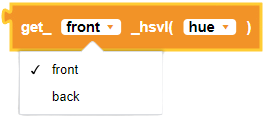
type: front, back
Returns
color: detected color as a string (Red, Green, Yellow, Blue, Cyan, Magenta, Black, White, Unknown)
Example
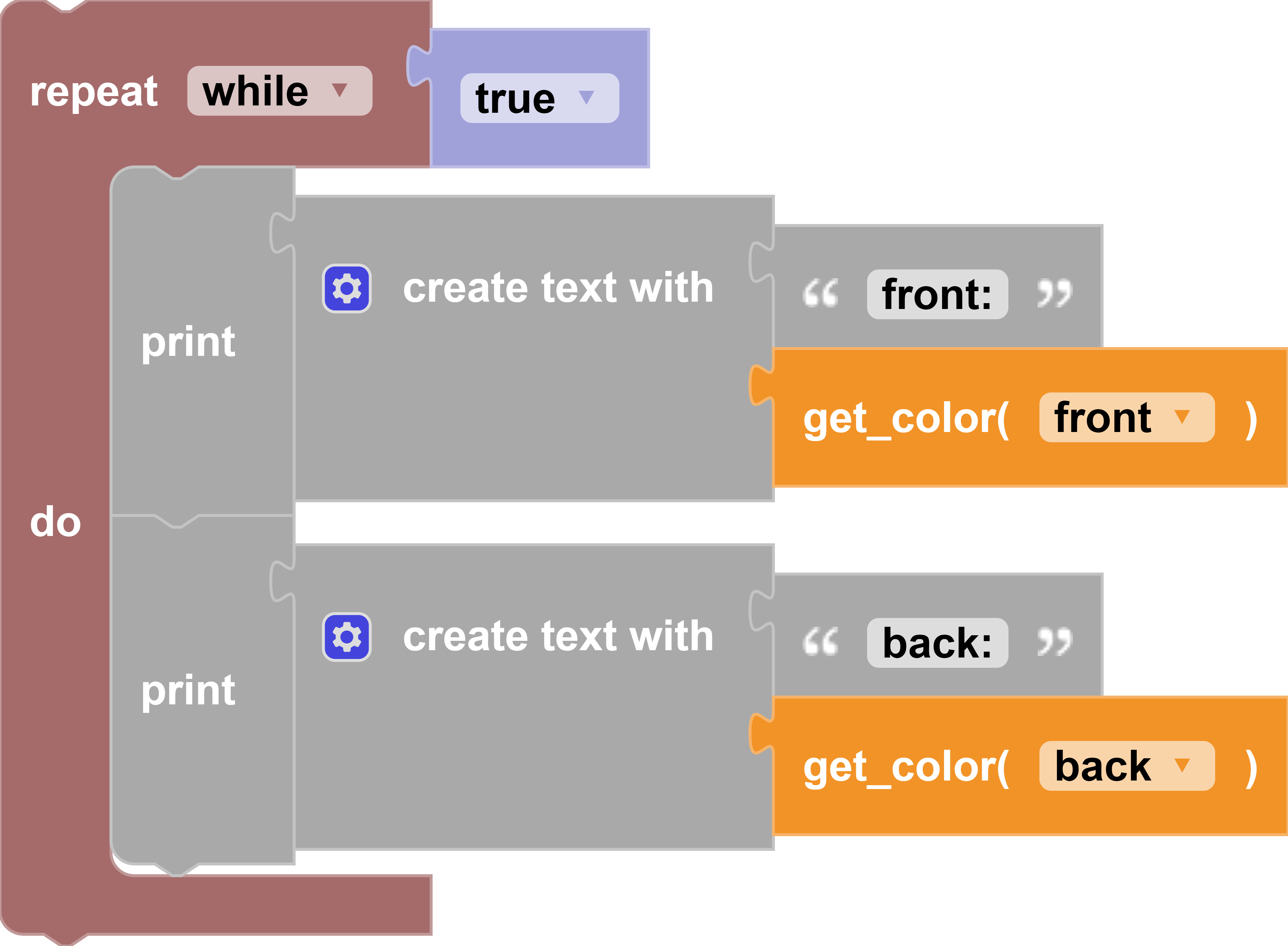
In this example, if the drone's front color detector detects the color green, the drone's LED will light up green; otherwise, the drone's LED will turn off.
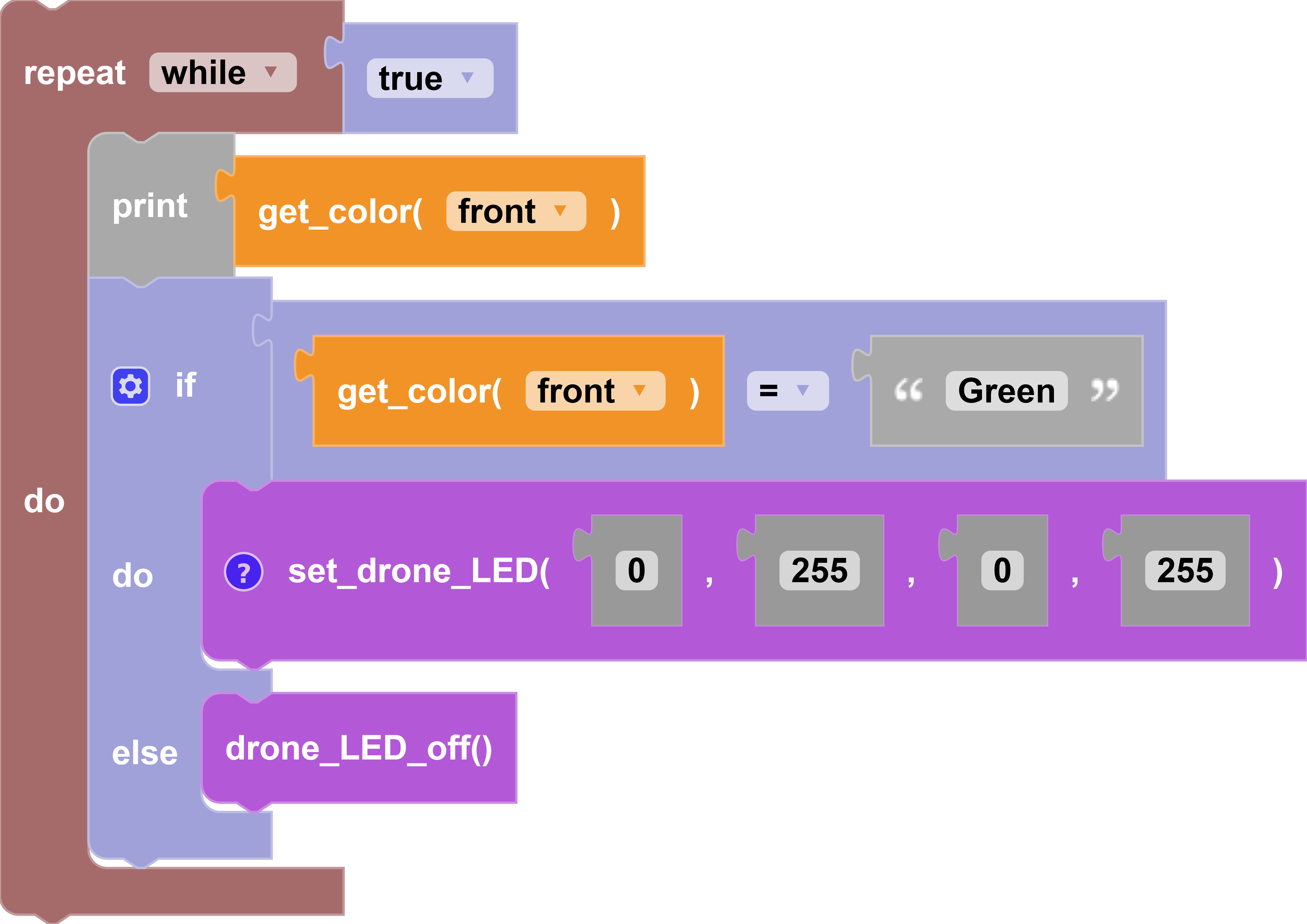
In the example below, place the drone under two different colored surfaces, so that the back and front sensor detector aren't detecting the same surface. The program will output different colors for the back and front sensor.
get_hsvl()
Block

Code
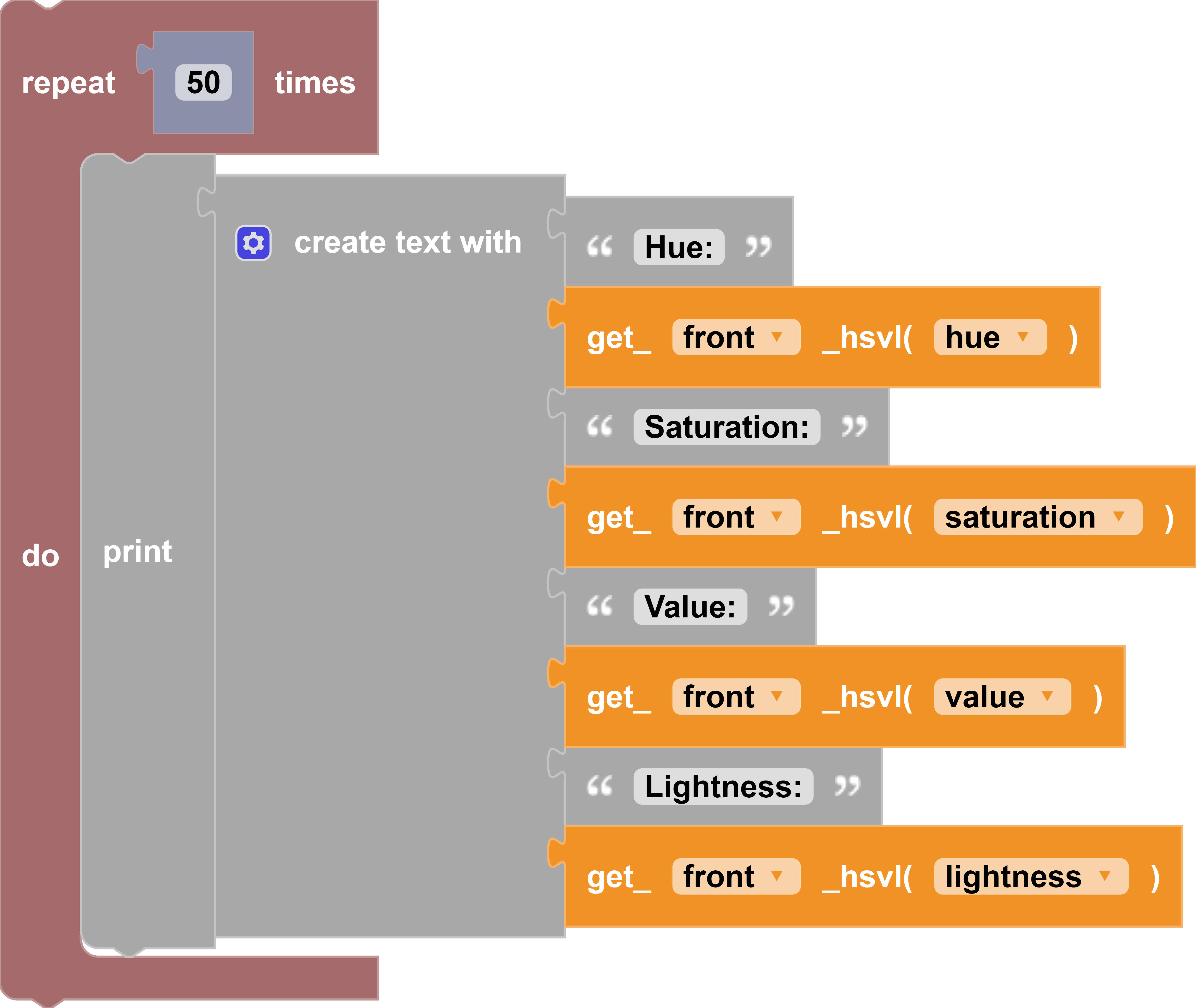
(front, hue): drone.get_color_data()[1]
(front, saturation): drone.get_color_data()[2]
(front, value): drone.get_color_data()[3]
(front, lightness): drone.get_color_data()[4]
(back, hue): drone.get_color_data()[5]
(back, saturation): drone.get_color_data()[6]
(back, value): drone.get_color_data()[7]
(back, lightness): drone.get_color_data()[8]
Description
Returns the HSVL (hue, saturation, value, lightness) data from either of the CoDrone EDU's bottom color sensors. The drone must be flat on a surface (not flying) for the color sensor to activate.
Parameters

type: front, back
unit: hue, saturation, value, lightness
Returns
hsvl value from sensor
Example
get_state_data()
Block

Code
modeFlight: drone.get_flight_state()
modeMovement: drone.get_movement_state()
Description
Returns the current state of the CoDrone EDU.
Parameters
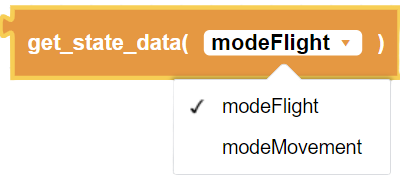
unit: modeFlight, modeMovement
Returns
state: name of flight/movement state
Example
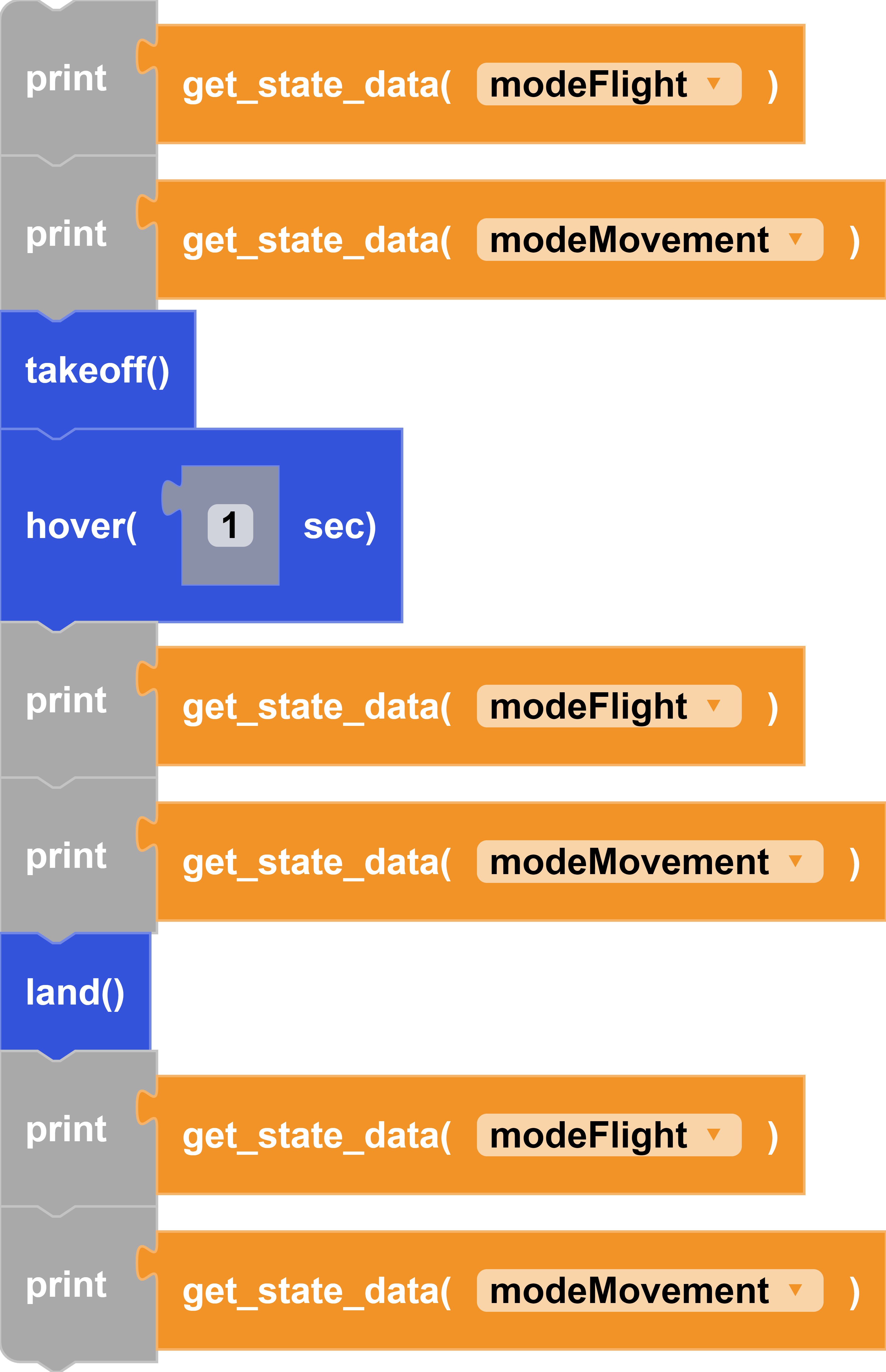
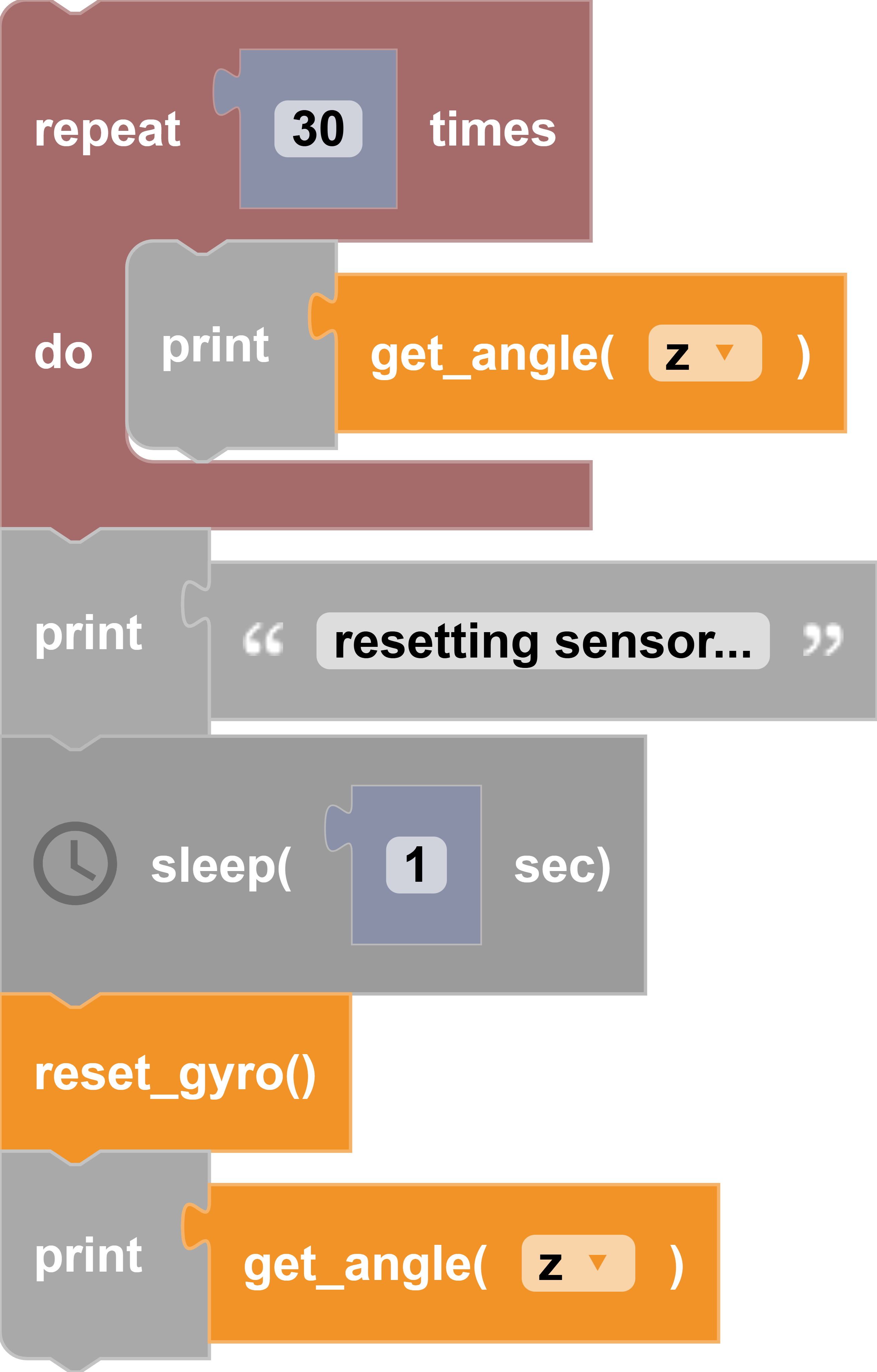
reset_gyro()
Block

Code
drone. reset_gyro()Description
Resets the gyroscope angles to 0. Make sure the drone is on a flat surface when running this block.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
To use this example file turn the drone manually with your hand and watch the Z angle change. Then, place the drone on a flat surface before the reset. You will see that the Z angle is reset to 0.
Sounds
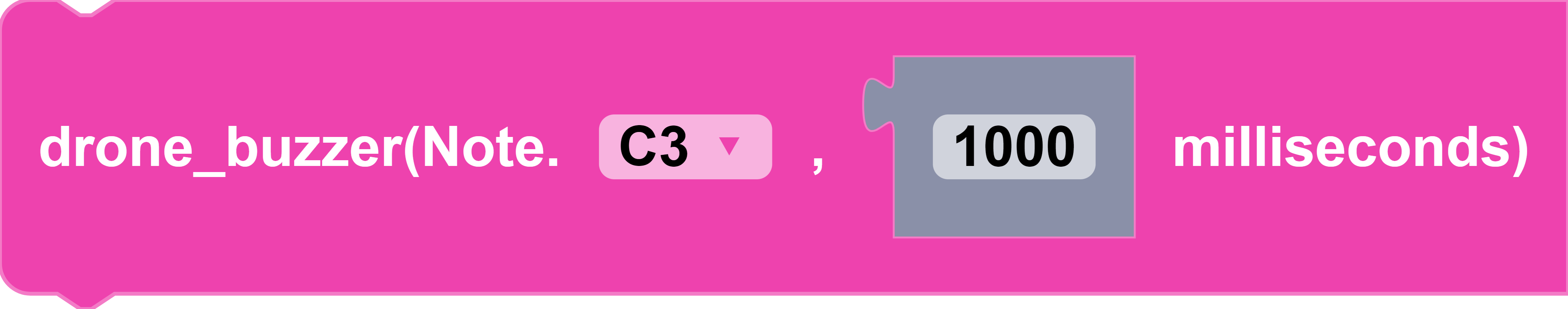
drone_buzzer()
Block
Code
drone. drone_buzzer()Description
Plays a note for a duration in milliseconds using the CoDrone EDU drone buzzer.
Parameters
note: note range from C3 to B7, Mute, Fin
integer duration: the duration of note played in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example

controller_buzzer()
Block

Code
drone. controller_buzzer()Description
Plays a note for a duration in milliseconds using the CoDrone EDU controller buzzer.
Parameters
note: note range from C3 to B7, Mute, Fin
integer duration: the duration of note played in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example

drone_buzzer_hertz()
Block

Code
drone. drone_buzzer()Description
Plays a sound frequency for a duration in milliseconds using the CoDrone EDU drone buzzer.
Parameters
integer hertz: the frequency of the buzzer, in Hertz
integer duration: the duration of the buzzer played, in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example
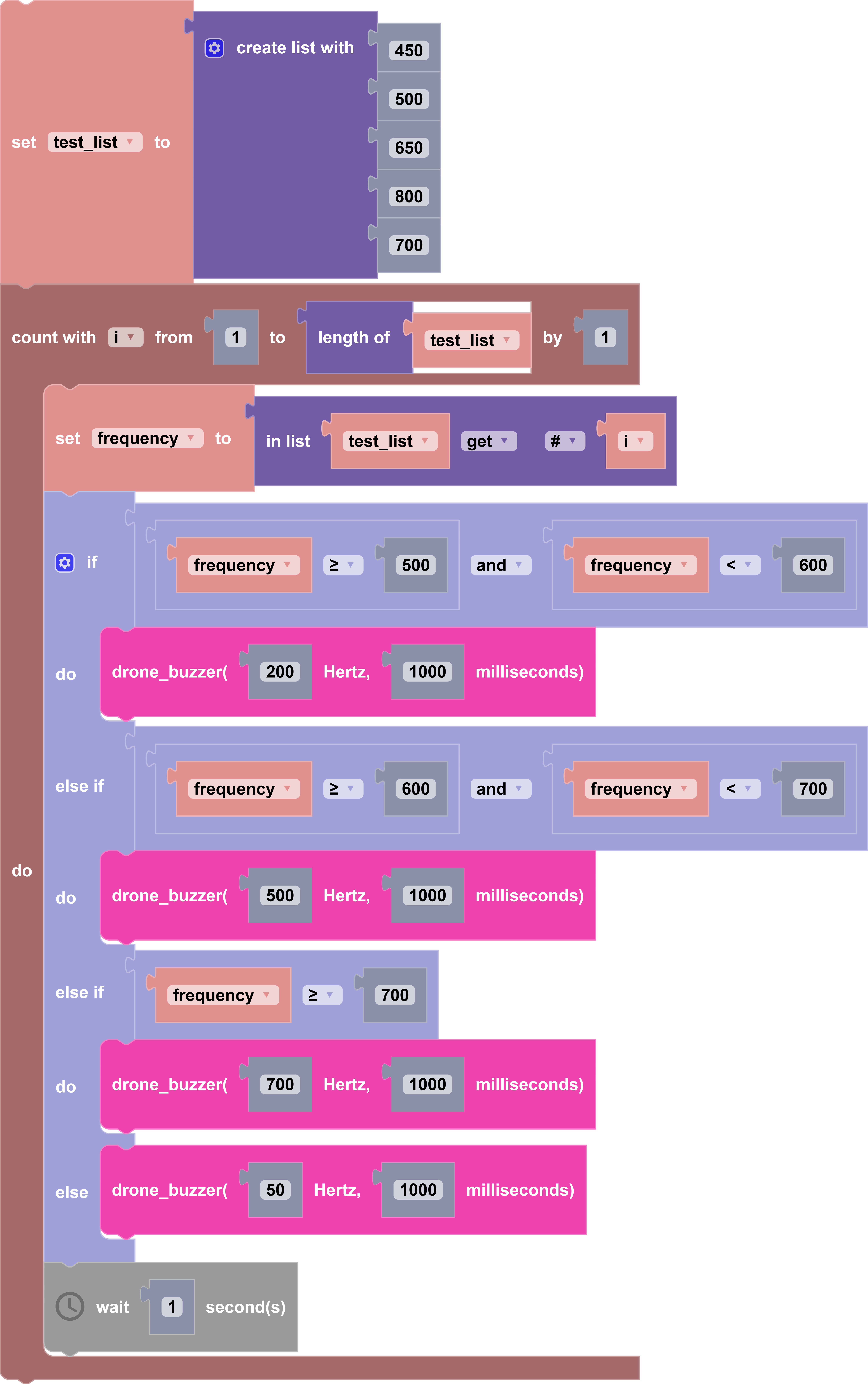
In this example, the drone will be buzzing a different frequency for half a second each.
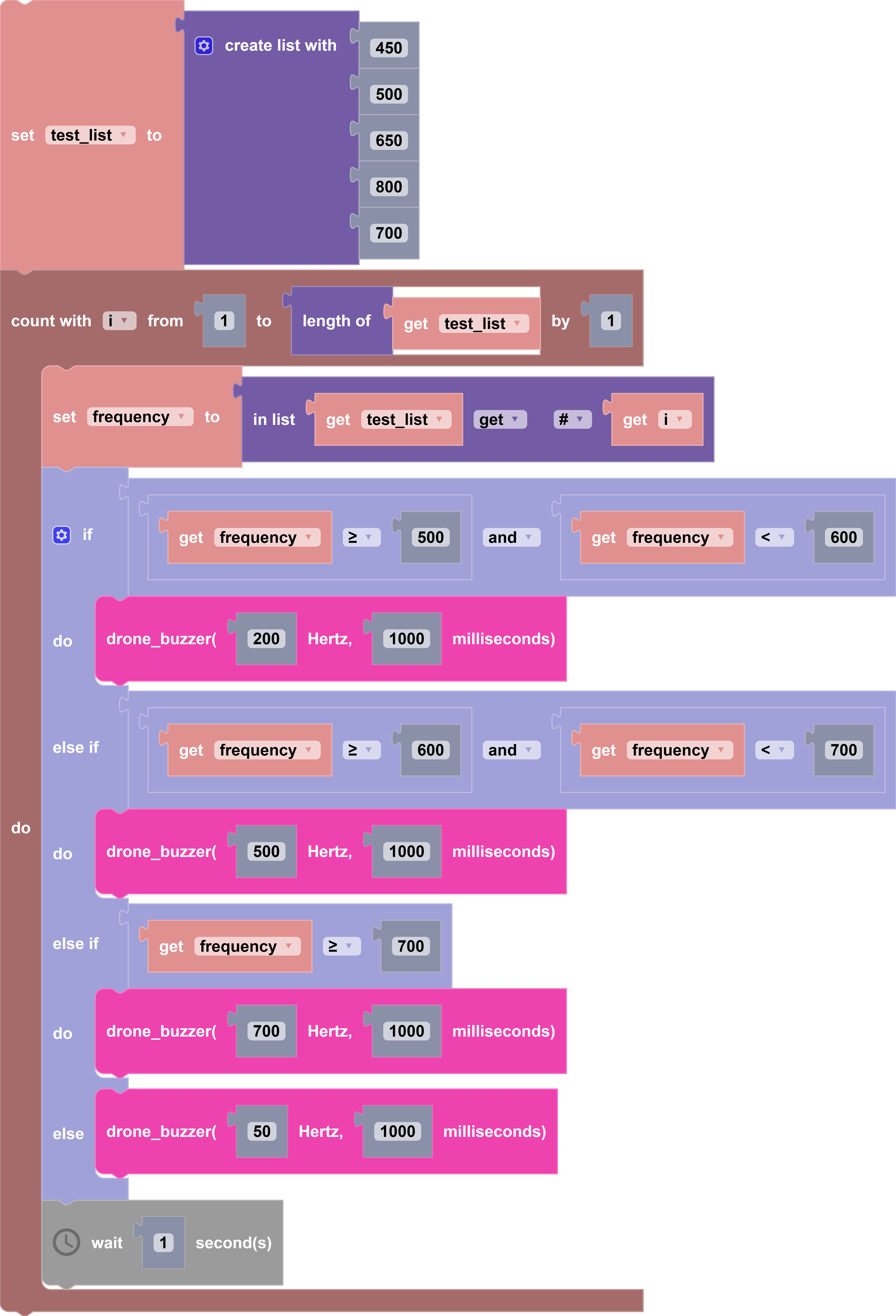
In the example below, a list variable test_list is created [450,500,650,800,700]. The loop iterates through the list using the "length of" block as the stop parameter of the loop block. The frequency variable is set a value from test_list at index "i" (the loop's index variable). Depending on which conditional statement frequency satisfies, the drone will buzz a specific frequency.
controller_buzzer_hertz()
Block

Code
drone. controller_buzzer()Description
Plays a sound frequency for a duration in milliseconds using the CoDrone EDU controller buzzer.
Parameters
integer hertz: the frequency of the buzzer, in Hertz
integer duration: the duration of the buzzer played, in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example

start_drone_buzzer()
Block

Code
drone. start_drone_buzzer()Description
Plays a note on the CoDrone until it is programmed to be stopped with stop_drone_buzzer().
Parameters
Note: note played on the drone
Returns
None
Example
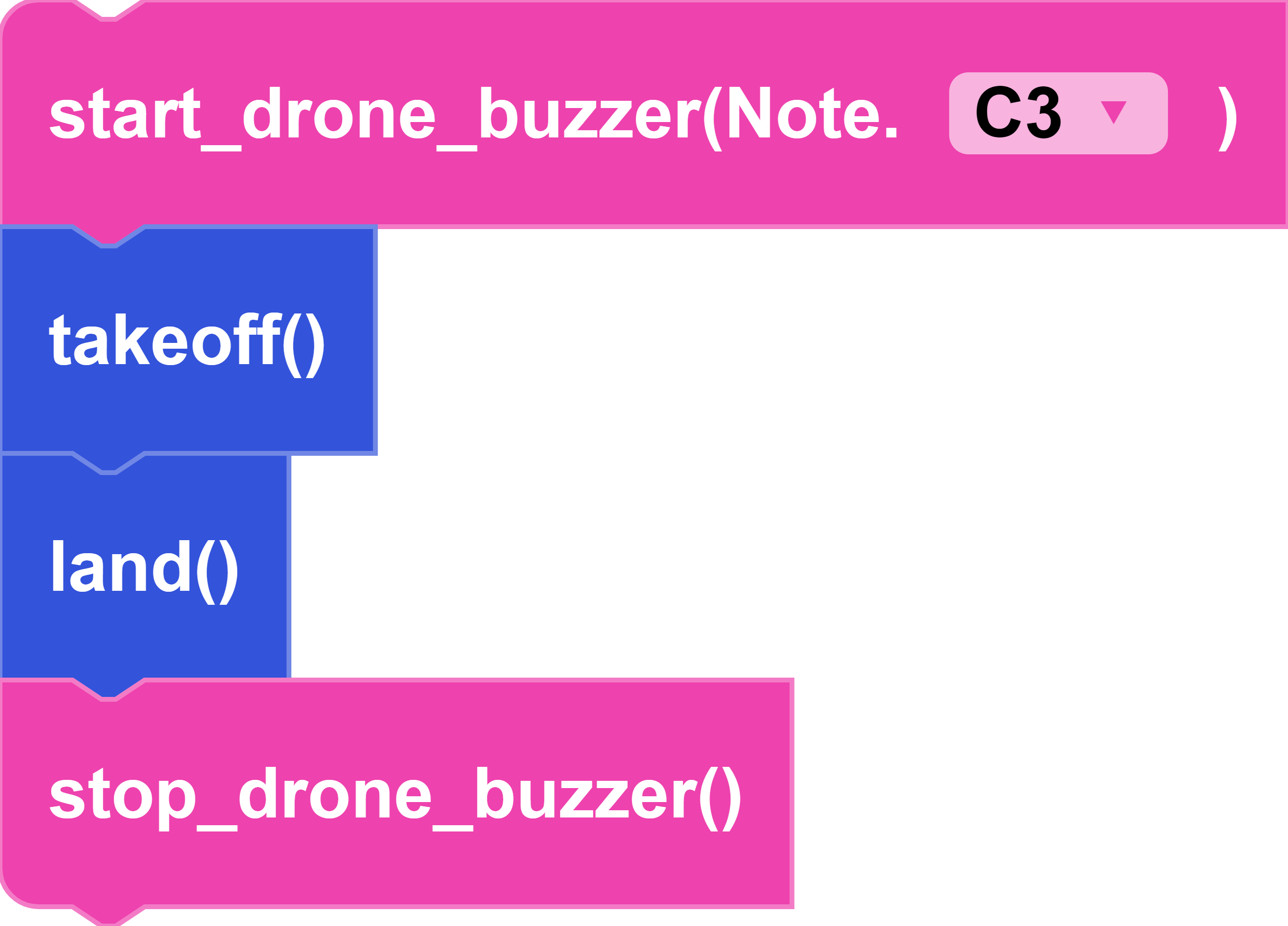
stop_drone_buzzer()
Block

Code
drone. stop_drone_buzzer()Description
Stops note played from the drone.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example

start_controller_buzzer()
Block

Code
drone. start_controller_buzzer()Description
Plays a note on the controller until it is programmed to be stopped with stop_controller_buzzer().
Parameters
Note: note played on the controller
Returns
None
Example
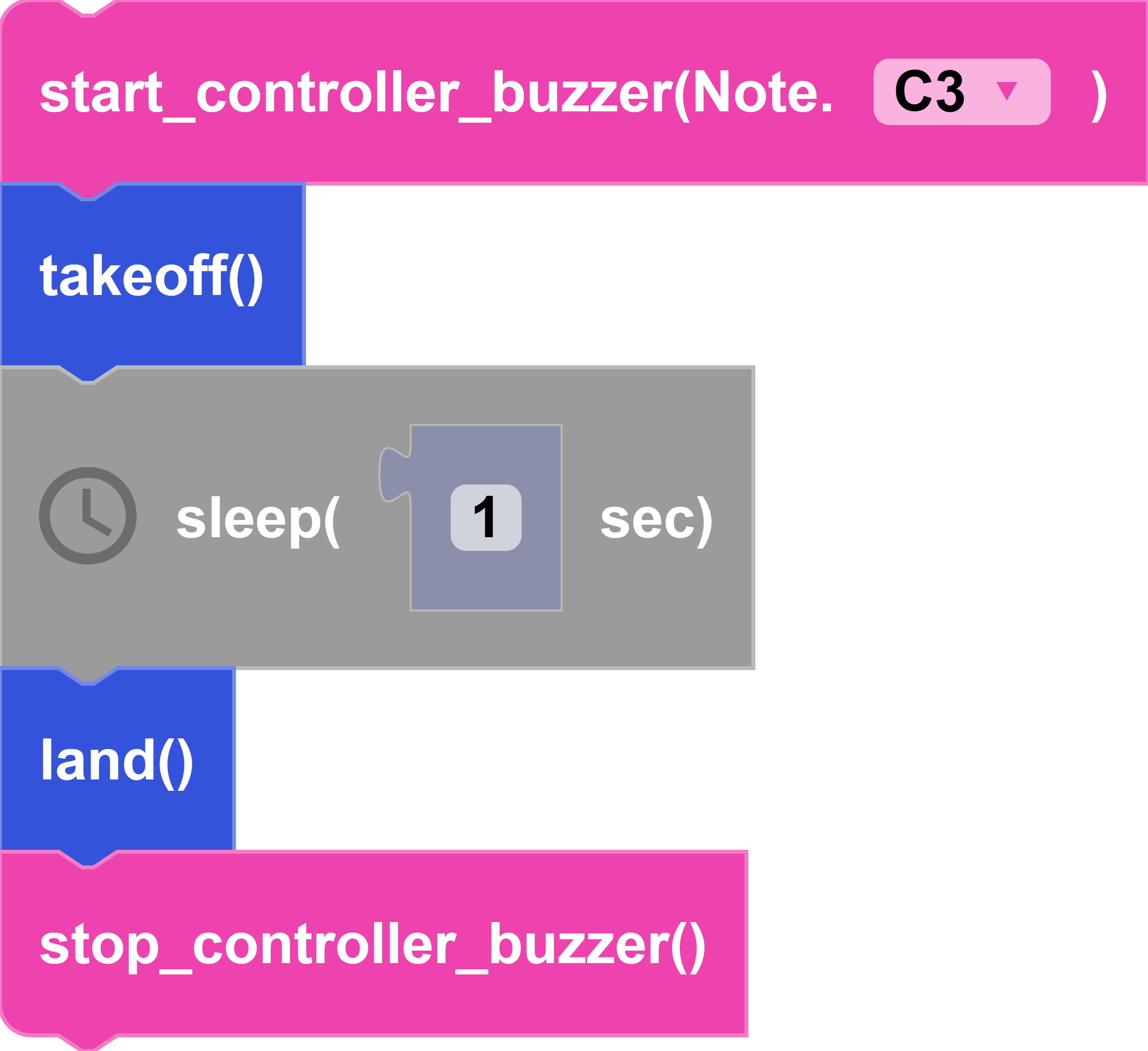
stop_controller_buzzer()
Block

Code
drone. stop_controller_buzzer()Description
Stops note played from the controller.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example

Colors
load_color_data()
Block

Code
drone. load_color_data()Description
Loads color data onto CoDrone EDU. The string inside the parameter is the name of your color set (name is set when creating the color set). predict_colors() block uses this color set to predict colors. To learn how to create a color set, visit our lesson on Color Sensors.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
To make this example work, your color set must be loaded into your Blockly workspace and code using the "load_color_data" block. The "predict_color" block will make a prediction of the color detected and return that color based on the color set that was loaded. Place the drone on different colored surfaces (red, yellow, or blue) to make the drone play a different note.
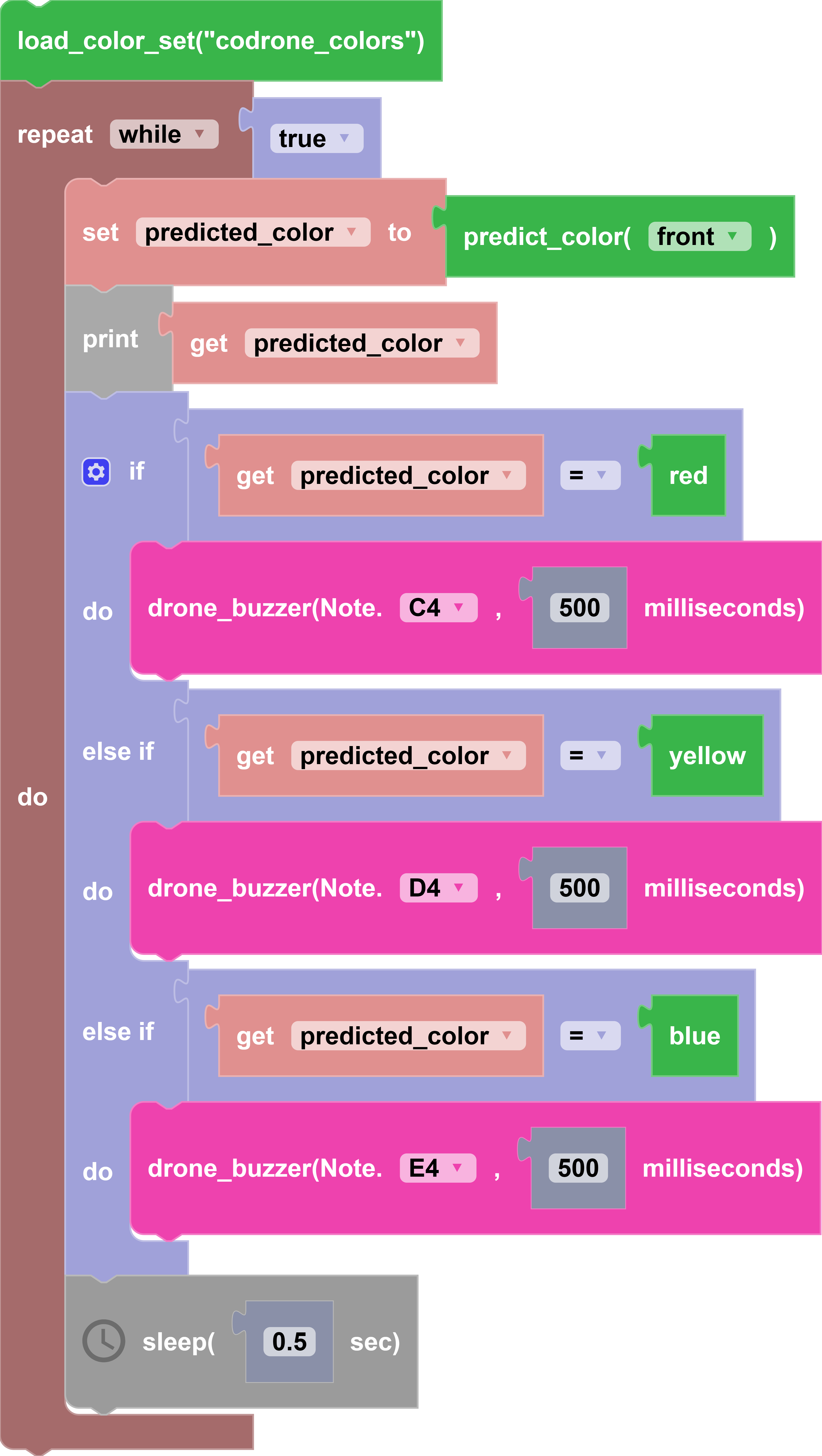
predict_color()
Block

Code
front: drone.predict_colors(drone.get_color_data())[0]
back: drone.predict_colors(drone.get_color_data())[1]
Description
Predicts what color the color sensors are currently seeing (front or back).
Parameters
sensor: the front or back sensor
Returns
string predicted color: The color that's predicted based off of what the front or back sensor detects.
Example
To make this example work, your color set must be loaded into your Blockly workspace and code using the "load_color_data" block. The "predict_color" block will make a prediction of the color detected and return that color based on the color set that was loaded. Place the drone on different colored surfaces (red, yellow, or blue) to make the drone play a different note.

Controller
controller_create_canvas()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block

Code
drone. controller_create_canvas()Description
Creates a canvas for drawing on the controller. This block is required for the other "controller_draw" blocks to work and must be placed before the other "controller_draw" blocks.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
controller_draw_canvas()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block

Code
drone. controller_draw_canvas()Description
Draws custom canvas onto the controller screen. This block is placed after placing the desired "controller_draw" blocks for the canvas (created by "controller_create_canvas").
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
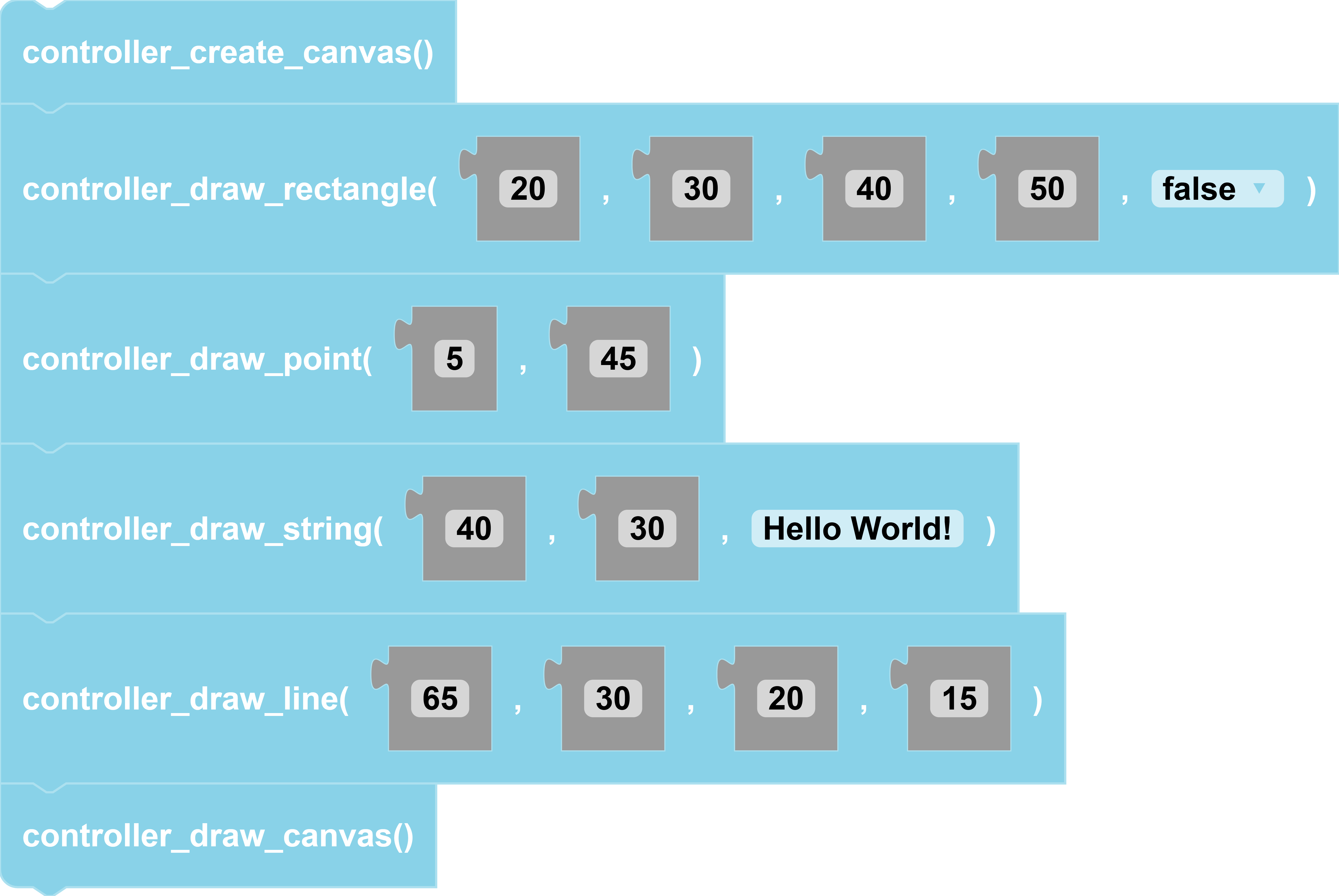
controller_draw_line()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block
Code
drone. controller_draw_line()Description
(x1,y1) \
\
\
\ (x2,y2)
Draws a line between points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) on canvas created by controller_create_canvas().
Parameters
integer x1: point 1 x coordinate
integer y1: point 1 y coordinate
integer x2: point 2 x coordinate
integer y2: point 2 y coordinate
Returns
None
Example
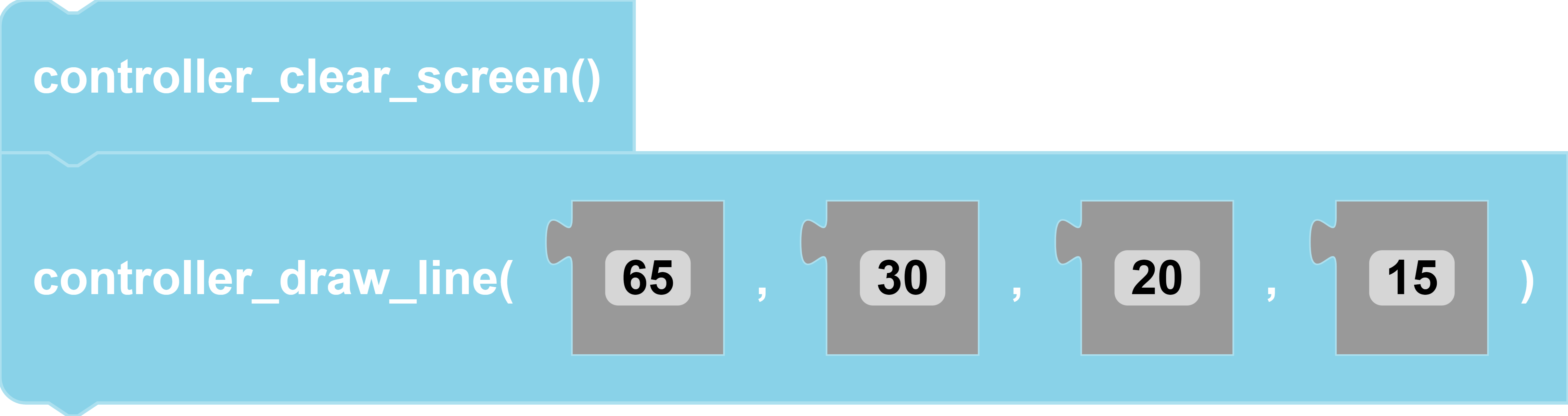
controller_draw_string()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block
Code
drone. controller_draw_string()Description
Draws a string from the given x_start, x_end and y positions on canvas created by controller_create_canvas(). The string can be aligned along the x_start and x_end positions
Parameters
integer xStart: starting x position
integer yStart: starting y position
text: any string input
Returns
None
Example
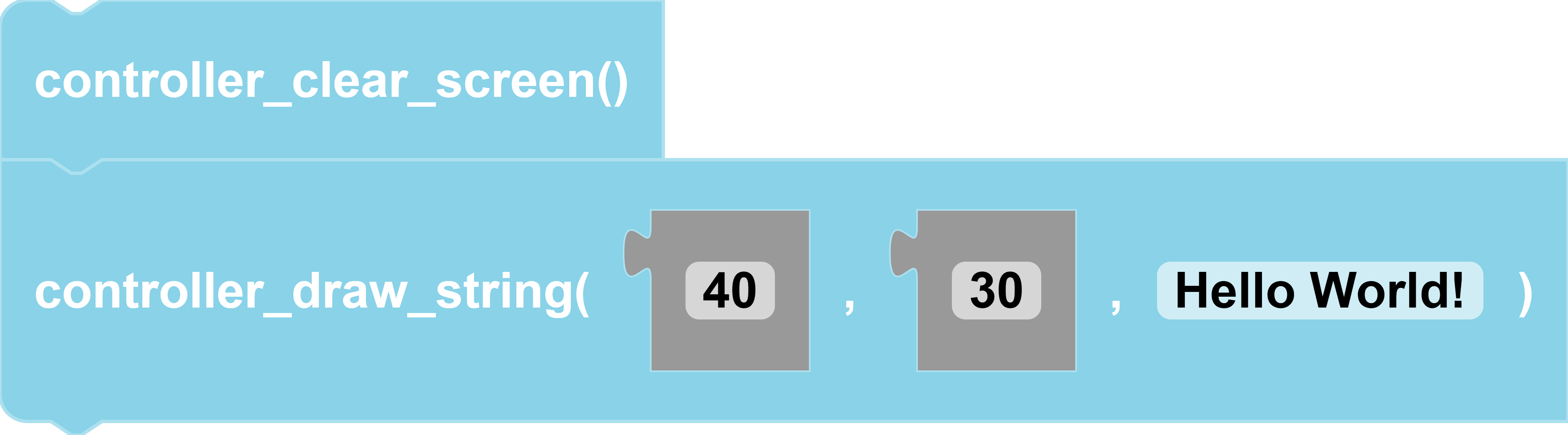
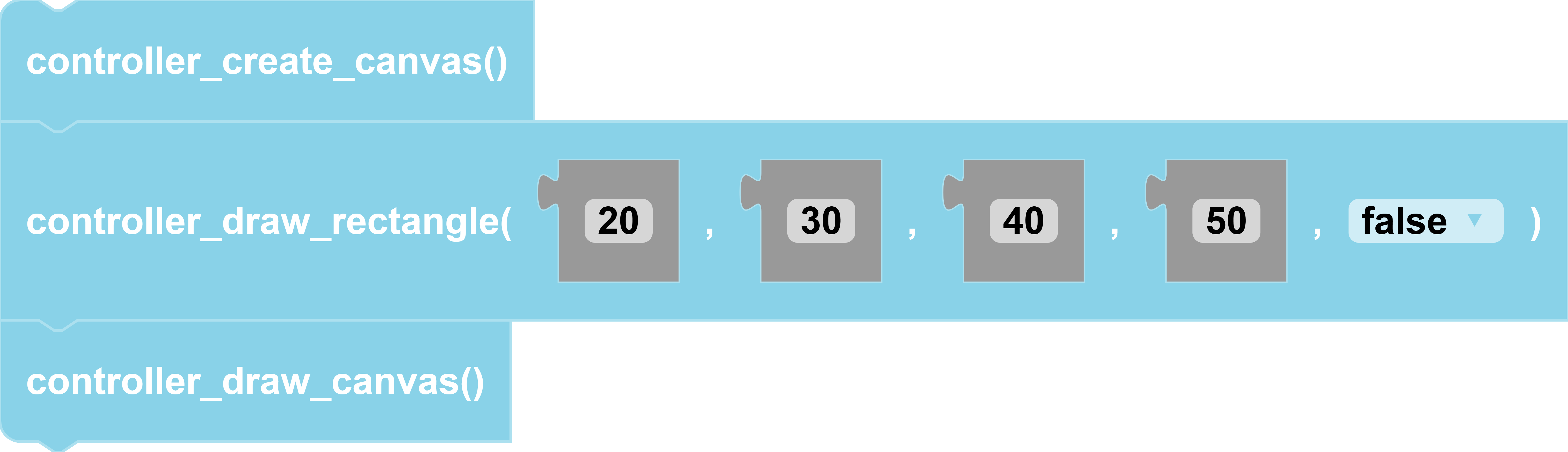
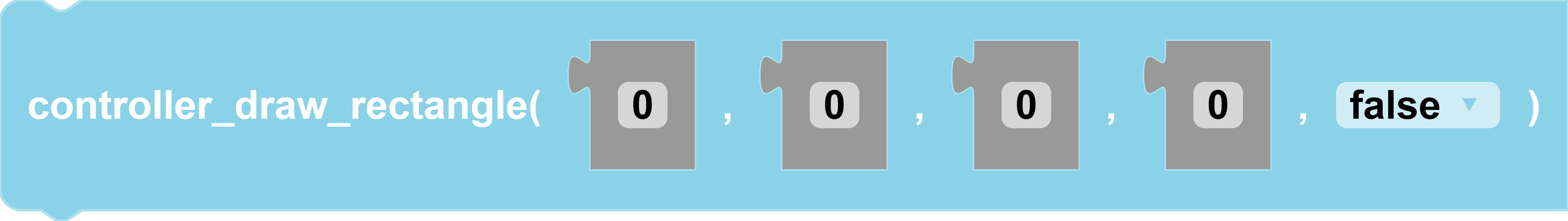
controller_draw_rectangle()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block
Code
drone. controller_draw_rectangle()Description
width
(x,y)|---------------|
| | height
|_______________|
Draws a rectangle on canvas created by controller_create_canvas(), starting from point (x,y) and extends to given height and width
Parameters
integer xStart: top left corner x coordinate
integer yStart: top left corner y coordinate
integer width: width of rectangle
integer height: height of rectangle
boolean flagFill: optional parameter to fill in the rectangle or not. default value is False
Returns
None
Example
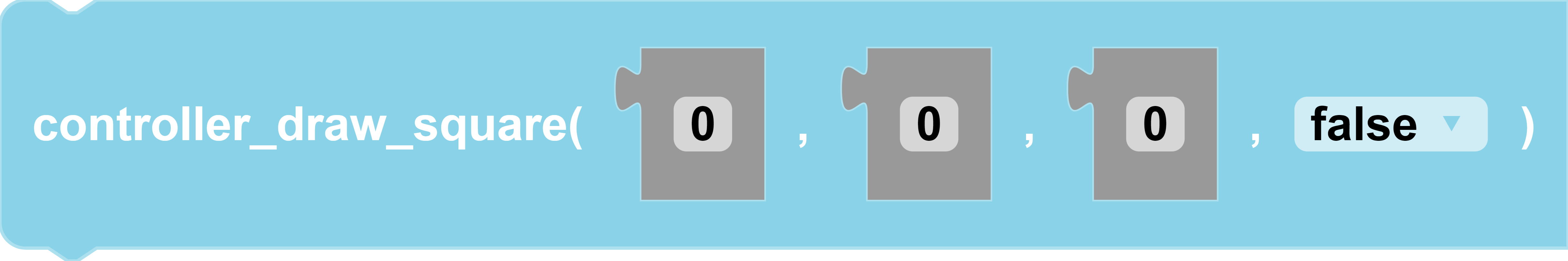
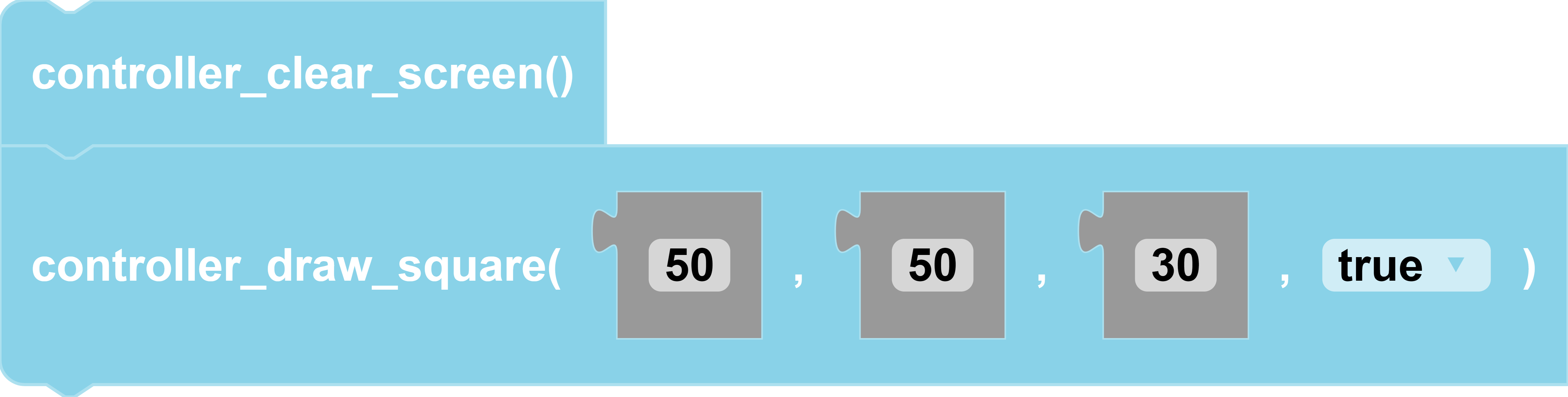
controller_draw_square()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block
Code
drone. controller_draw_square()Description
width
(x,y)|------|
| | width
|______|
Draws a square on canvas created by controller_create_canvas(), starting from point (x,y) and will extend to the given width
Parameters
integer xStart: top left corner x coordinate
integer yStart: top left corner y coordinate
integer width: width of square
boolean flagFill: optional parameter to fill in the square or not. default value is False
Returns
None
Example
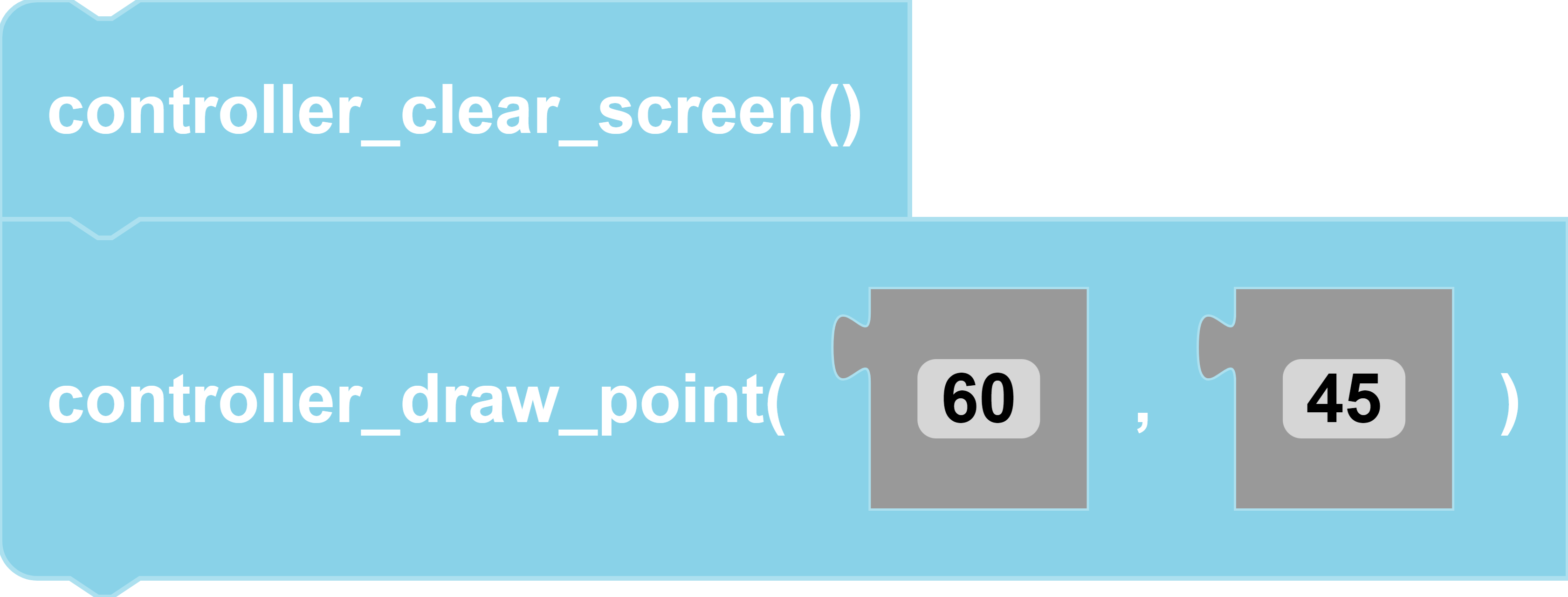
controller_draw_point()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block
Code
drone. controller_draw_point()Description
Draws a point on canvas created by controller_create_canvas(), at point (x, y).
Parameters

integer x: x coordinate
integer y: y coordinate
Returns
None
Example
controller_clear_screen()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Block

Code
drone. controller_clear_screen()Description
Clears the CoDrone EDU controller screen.
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example
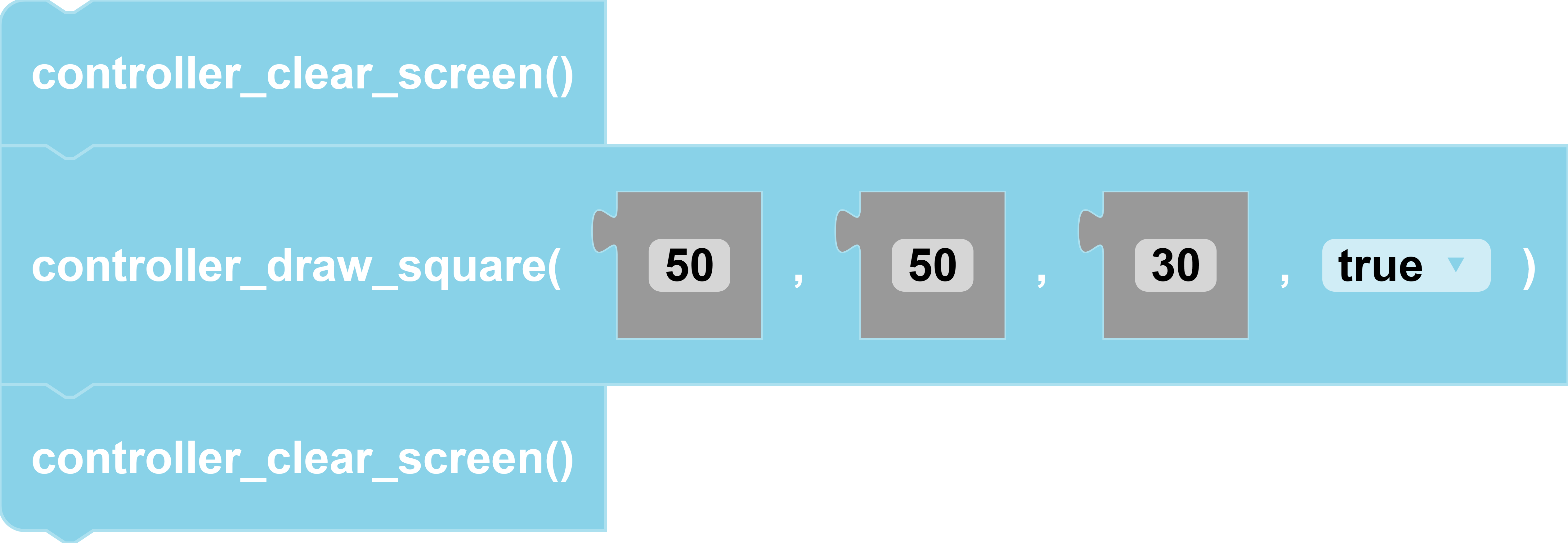
[button]_pressed()
Block

Code
L1: drone.l1_pressed()
L2: drone.l2_pressed()
L1: drone.r1_pressed()
L1: drone.r2_pressed()
h: drone.h_pressed()
power: drone.power_pressed()
up arrow: drone.up_arrow_pressed()
left arrow: drone.left_arrow_pressed()
right arrow: drone.right_arrow_pressed()
down arrow: drone.down_arrow_pressed()
s: drone.s_pressed()
p: drone.p_pressed()
Description
This command determines if the controller's desired button has been pressed or held down.
Parameters

button: The controller button to retrieve data from.
Returns
Boolean is pressed: True if the button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return False.
Example
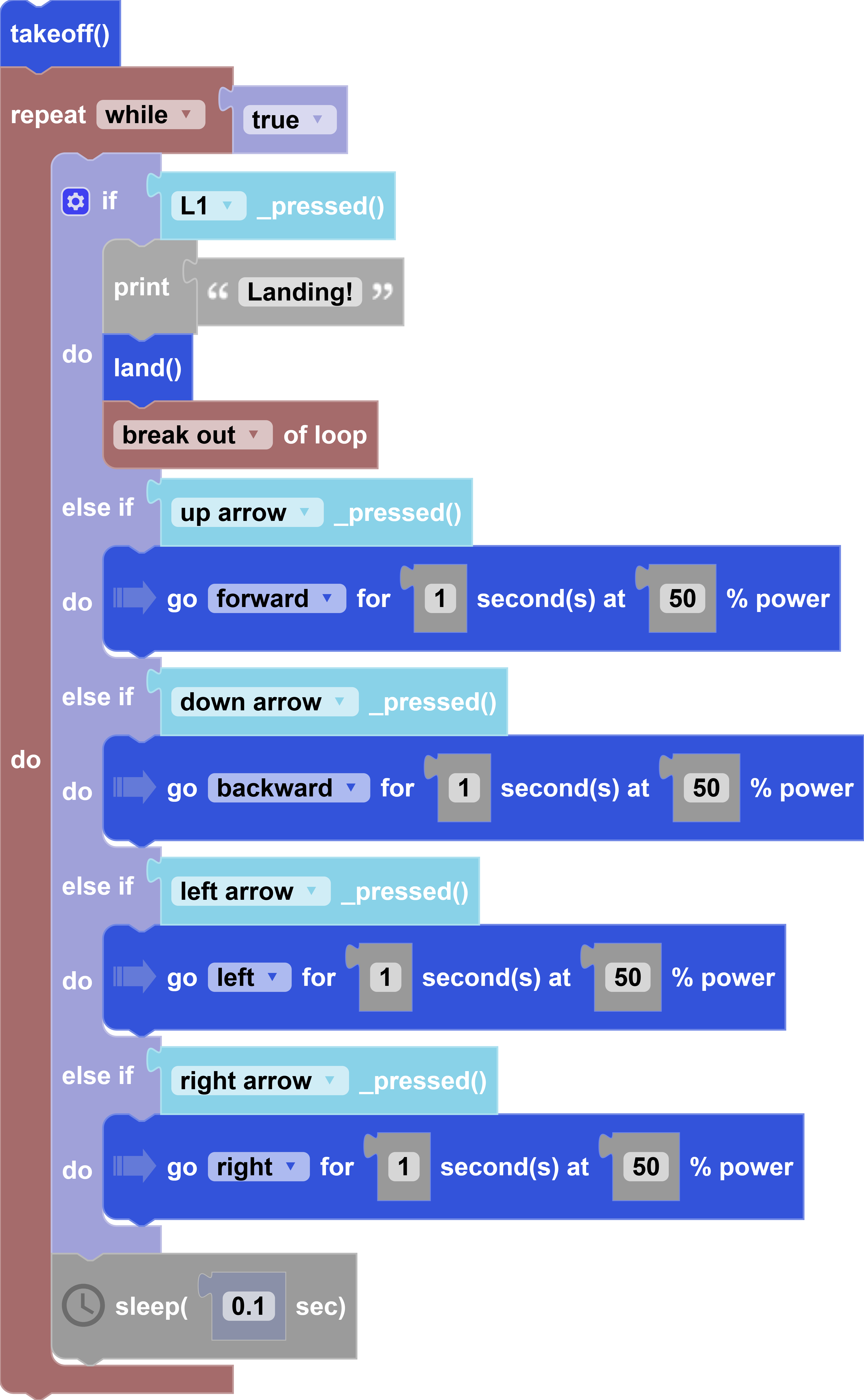
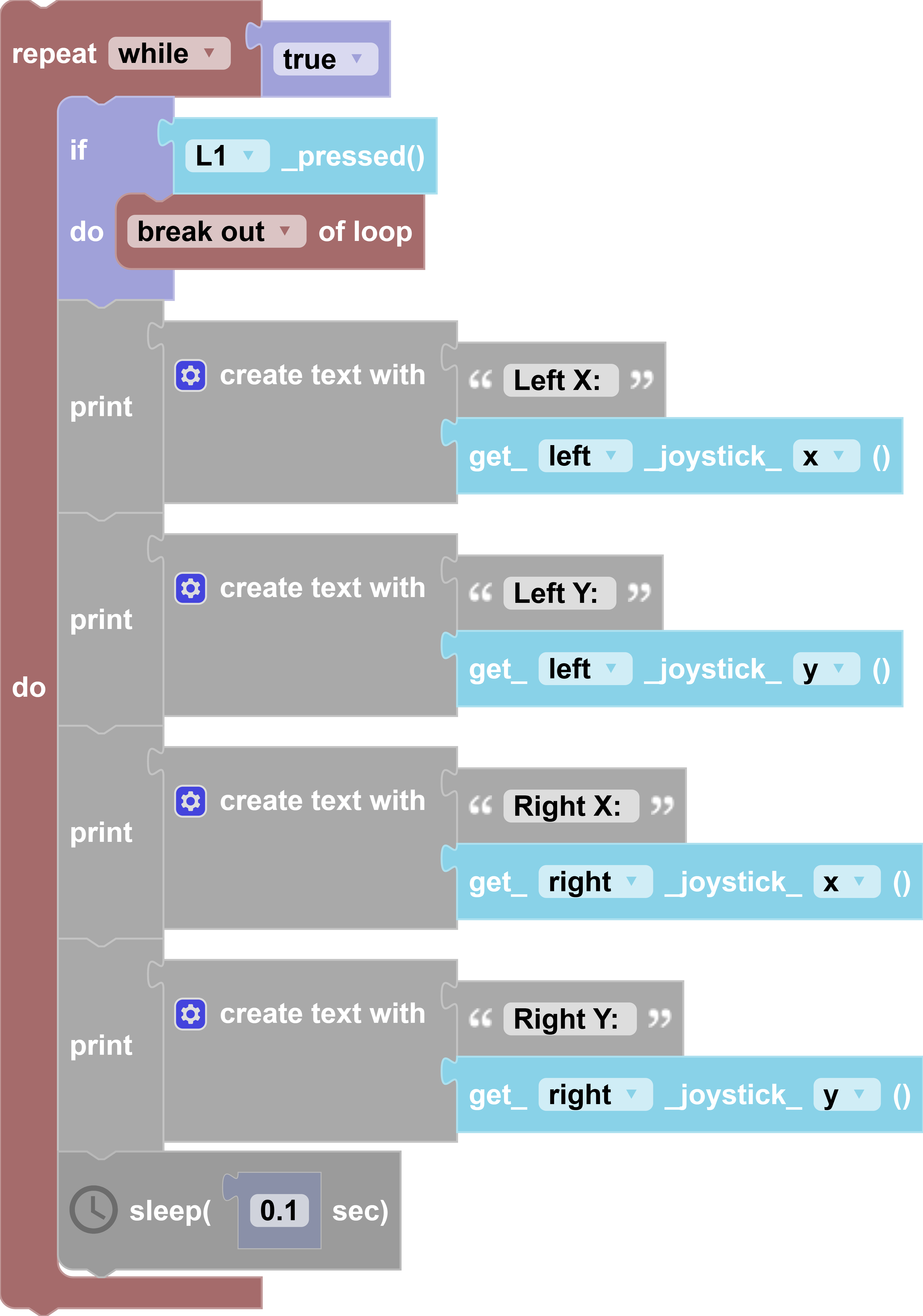
get_[type]_joystick_[axis]()
Block

Code
(left, x): drone.get_left_joystick_x()
(left, y): drone.get_left_joystick_y()
(right, x): drone.get_right_joystick_x()
(right, y): drone.get_right_joystick_y()
Description
This command gets the position of the desired, left or right, joystick's x or y position. The x-position represents left (negative x) or right (positive x) position of the joystick, and the y-position represents down (negative y) or up (positive y) position of the joystick.
Parameters
type: The controller joystick to retrieve data from.
axis: The controller joystick's axis.
Returns
integer position: The position of the desired joystick on the desired axis, ranging from -100 to 100.
Example
Lists
create empty list
Block

Description
Creates an empty list (a list with no items).
Parameters
None
Returns
list: An empty list []
Example
create list with
Block

Description
Creates a list based on given values attached to the "create list with" block. The list could contain values with different data types: strings, integers, floats.
Parameters
Clicking on the gear icon will give you the option to manually add or reduce the number of items.
Returns
list: A list with values attached onto the "create list with" block
Example
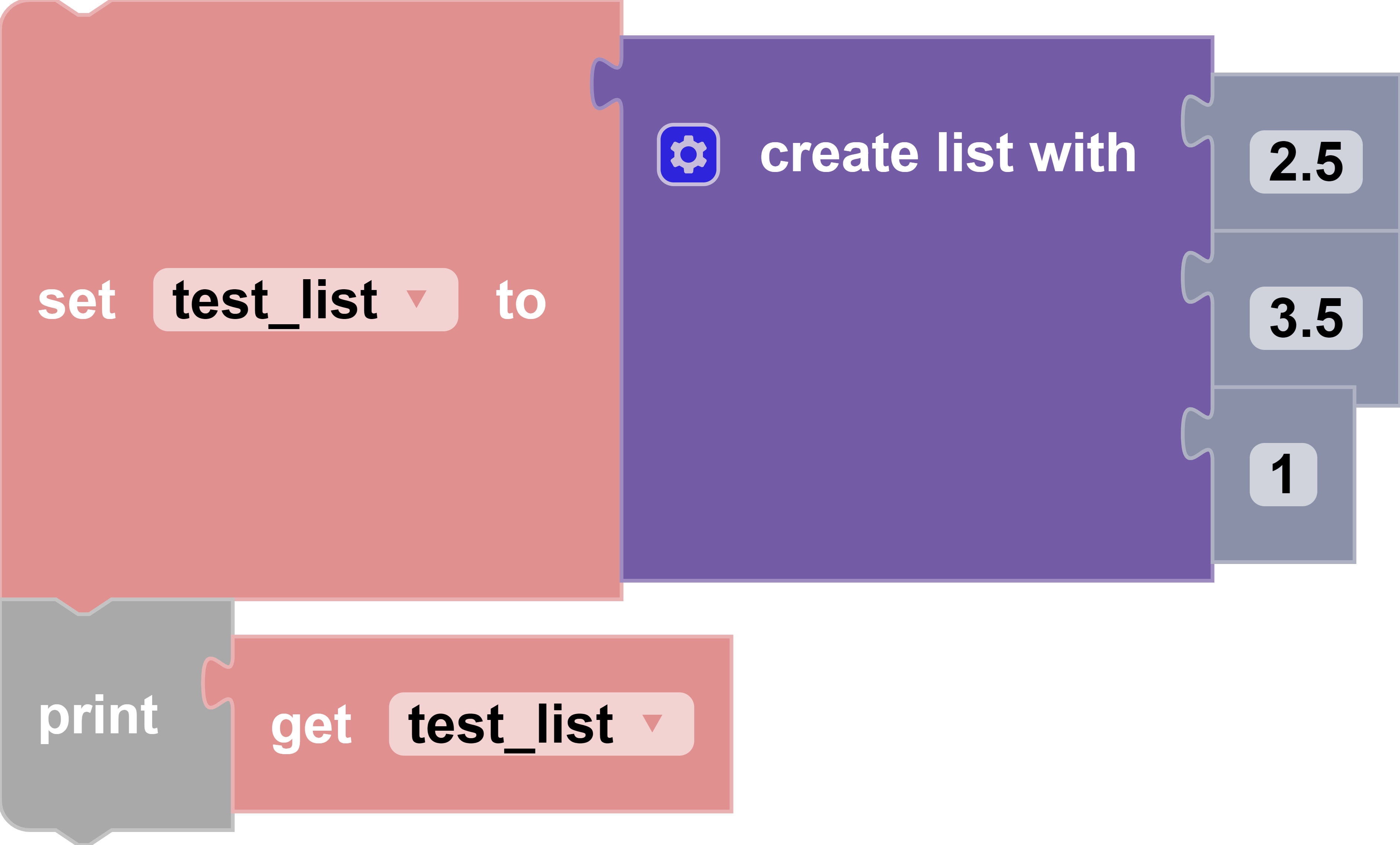
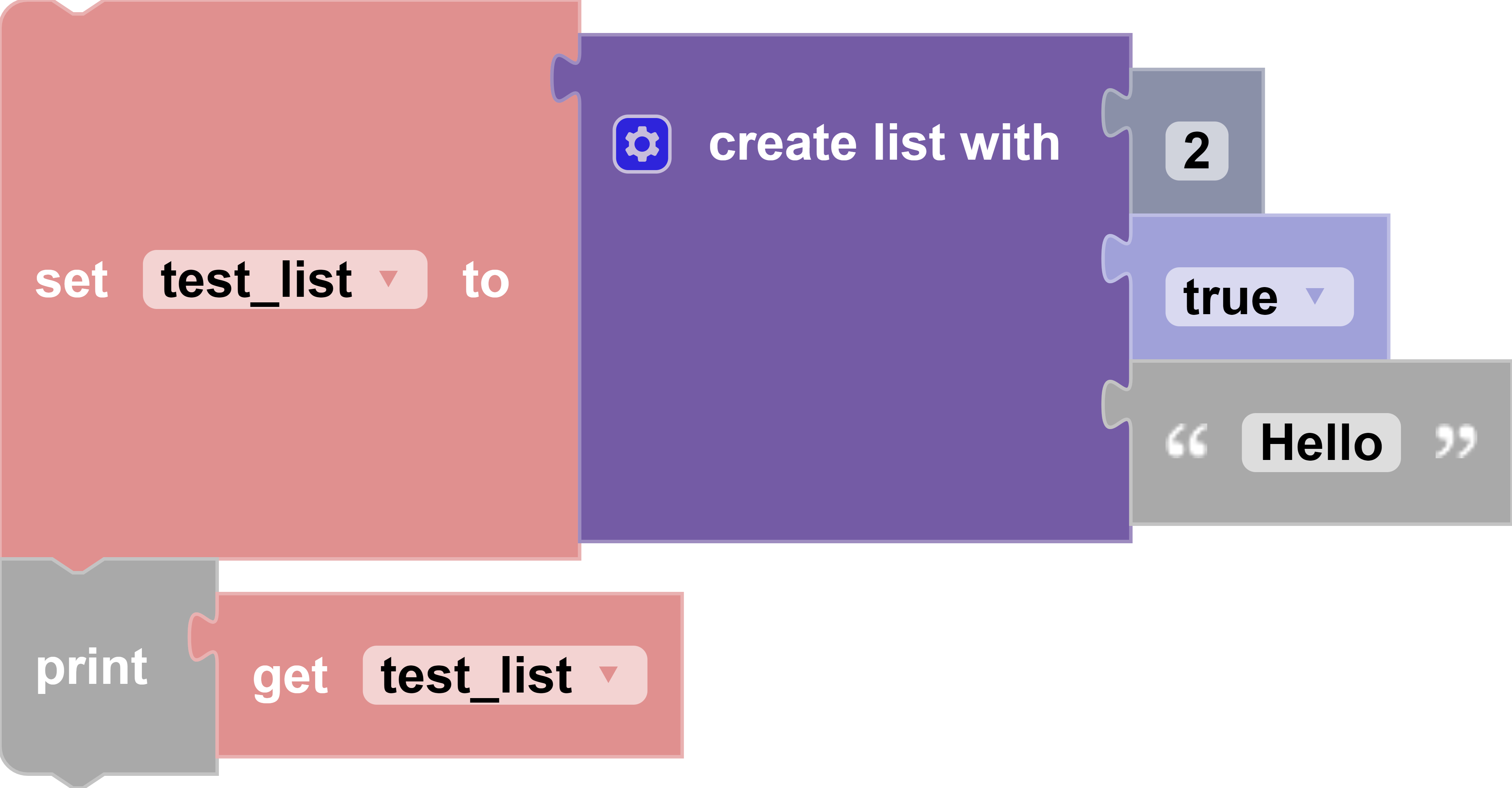
In this example, a list variable was created with a value of the same data type. The test_list variable is assigned the value of [2.5,3.5,1]
In this example, a list variable was created with a value of different data types. The test_list variable is assigned the value of [2,True,"Hello"]
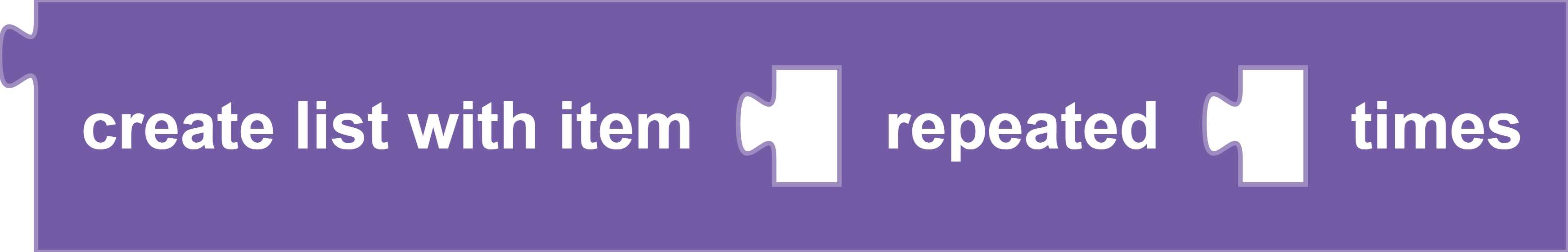
create list with item [item] repeated [number] times
Block
Description
Creates a list with a given value, repeated for a given number of times. The both parameters could contain an operation like "1+1", as long as it returns a value—integer or float. The first parameter can be a string value as well.
Parameters
integer/float/string value repeated: value that will be repeated in the list
integer repeats: the number of times the given value will be in the list.
Returns
list: A list containing the given value repeated a given number of times.
Example
In this example, instead of simply putting a number block, the first parameter contains an operation block that will return a number, which is 2. The second parameter contains a number block of 3. Printing test_list will result in [2,2,2].

length of
Block

Description
Returns the length of the list, which is the number of items that are inside the list.
Parameters
None
Returns
int length: The length (number of items in the list) of the list.
Example
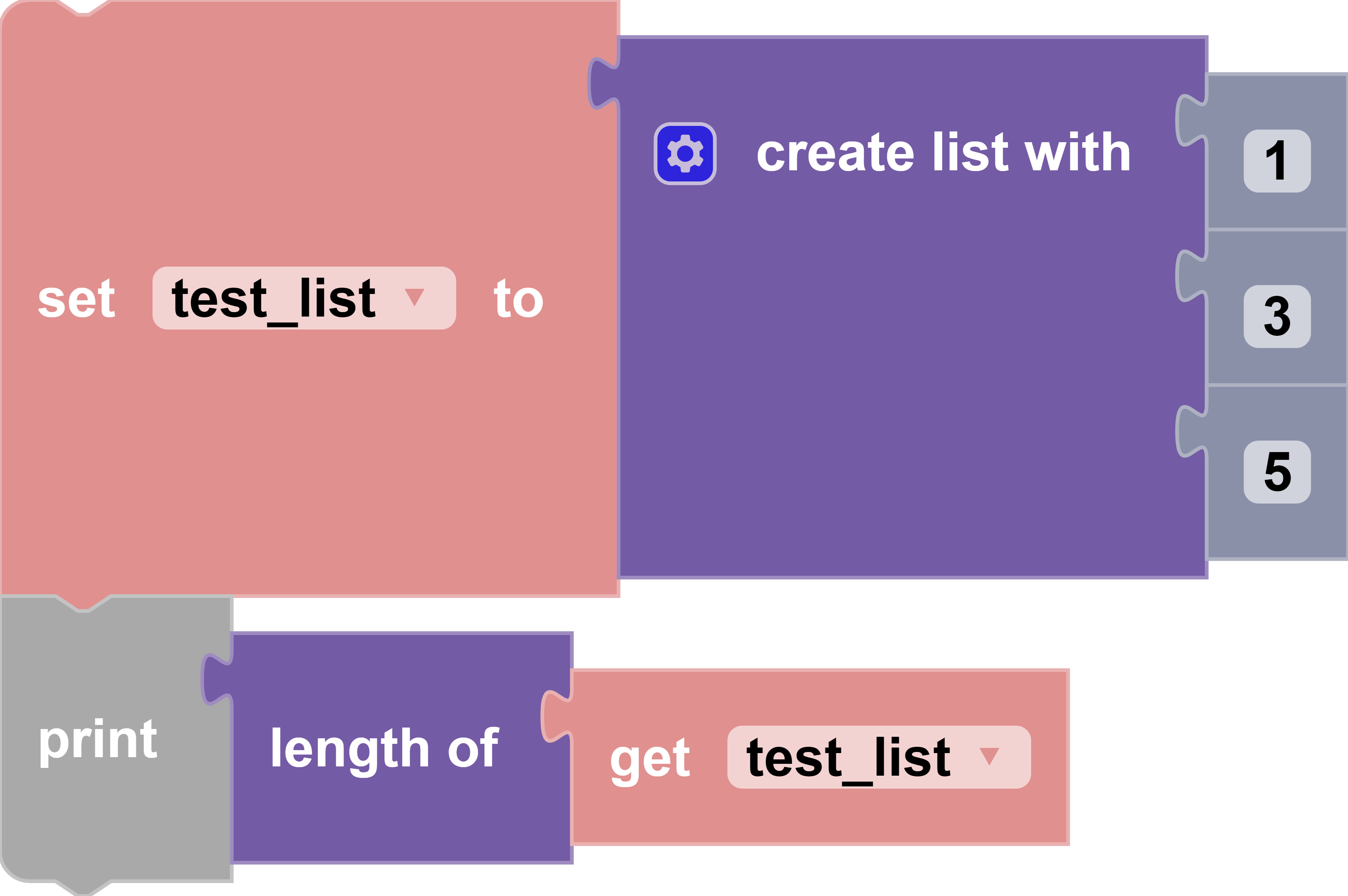
After creating the list [1,2,3] and assigning it to the variable test_list, the console will print the length of test_list, which is 3 (three items in the list).
[list] is empty
Block

Description
Returns a boolean value indicating if the list is empty or not (if the list has no items or not).
Parameters
list list variable: a variable that's a list
Returns
boolean is empty: True if there are items in the list. Otherwise, returns False
Example
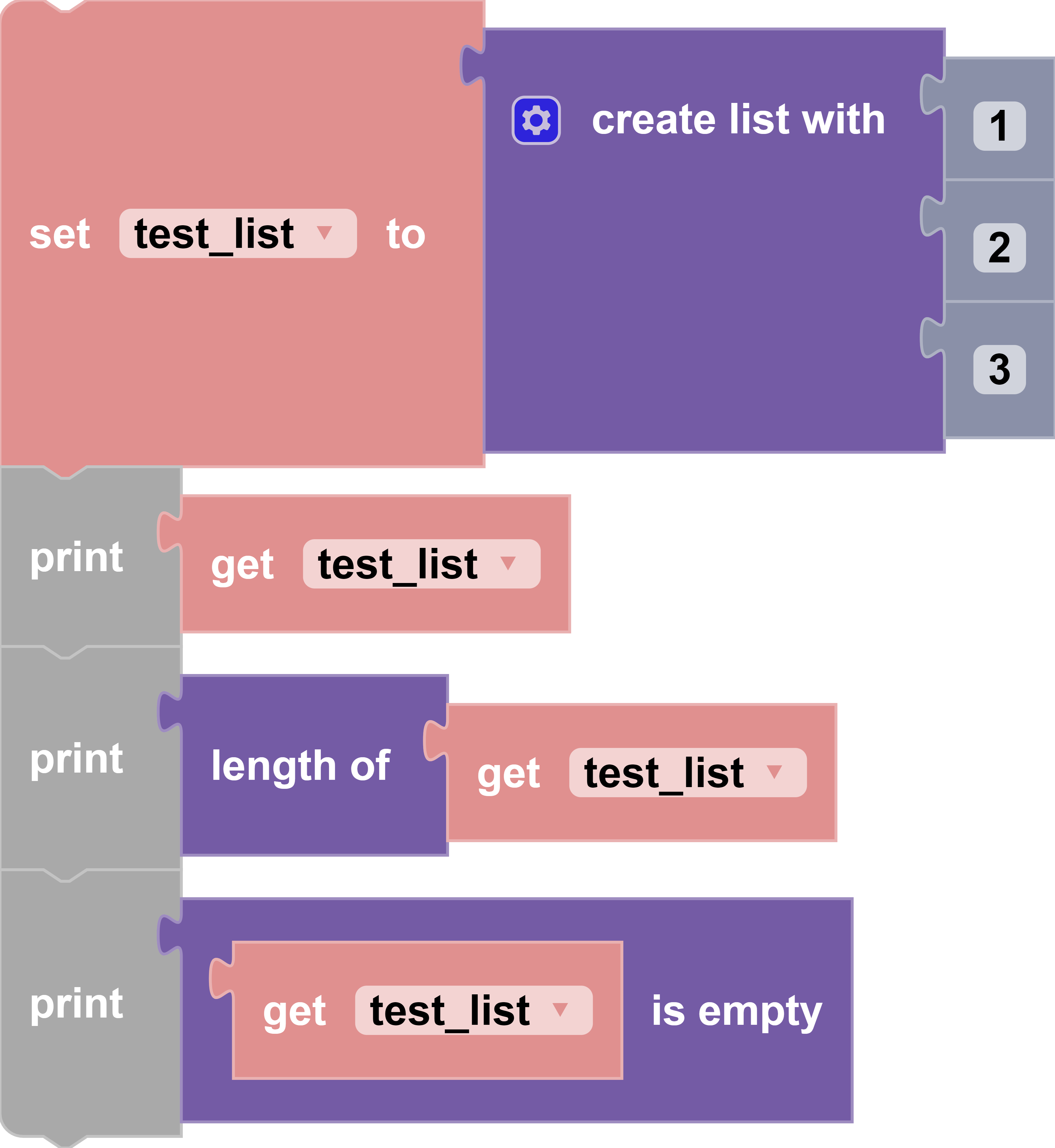
In this example, test_list block is attached to the "create empty list" block. The console prints test_list, which is []. Then, the console prints the length of test_list, which is 0. Finally, the console prints whether or not test_list is empty, which is True. These 3 printing statements are ways to verify if the list is indeed empty or not. "is empty" is useful when applying if-statements to it.
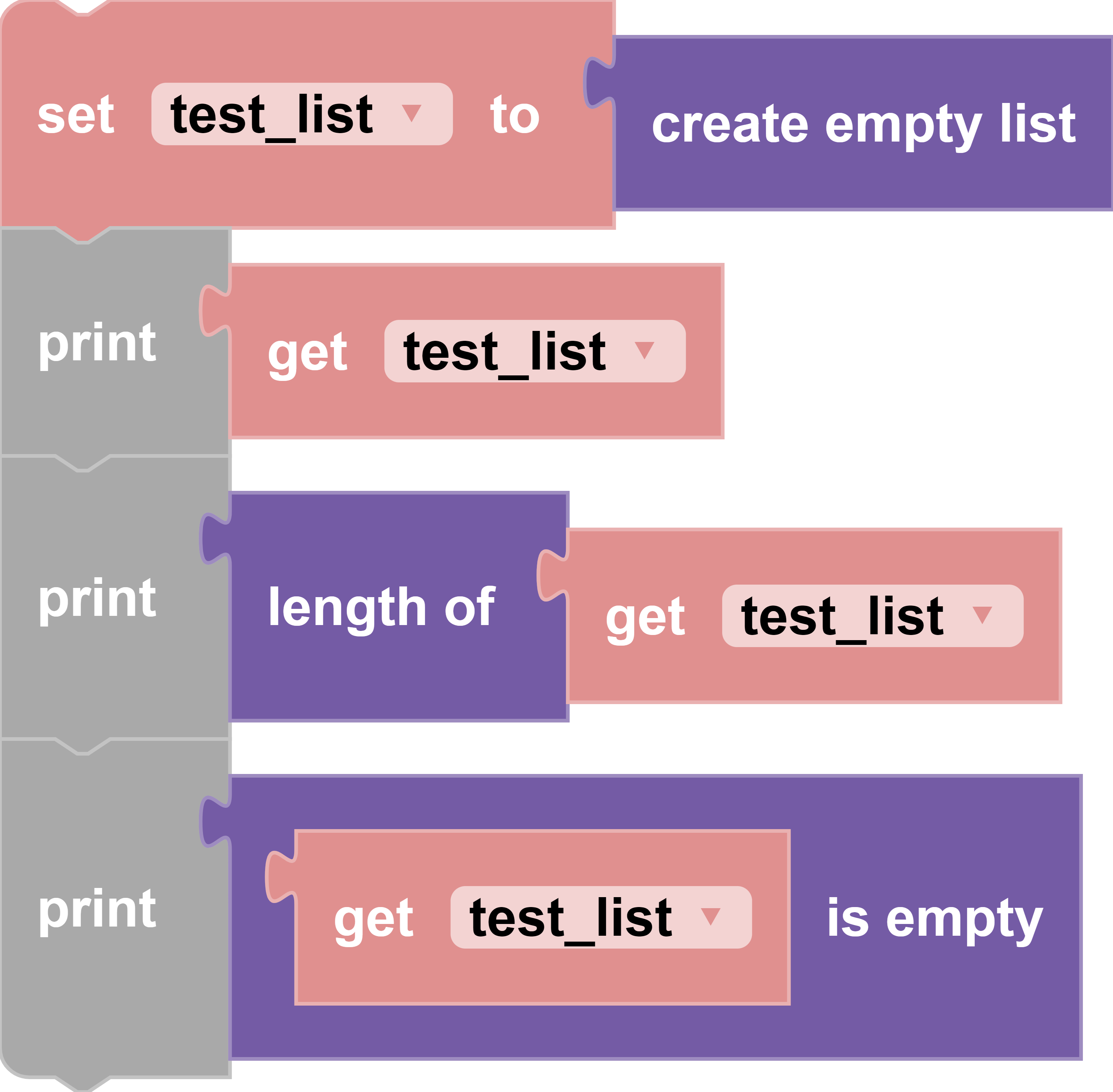
In this example, the console prints whether or not test_list is empty, which is False. test_list indeed is not empty since there are items in it.
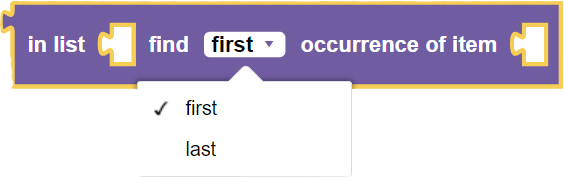
in list [list] find [occurrence] occurrence of item [item]
Block

Description
Returns the position number (index) of the first/last occurrence of the given item in the given list variable.
Parameters
list list variable: a variable that is a list
occurrence: the first or last occurrence of the item
integer/float/string item: value of the item
Returns
integer index: The position number of the item in the list
Example
In this example, the test_list variable is assigned the value of [1,2,3]. The console prints 1 as the first occurrence of the item "2" in test_list since it is the second item in test_list.
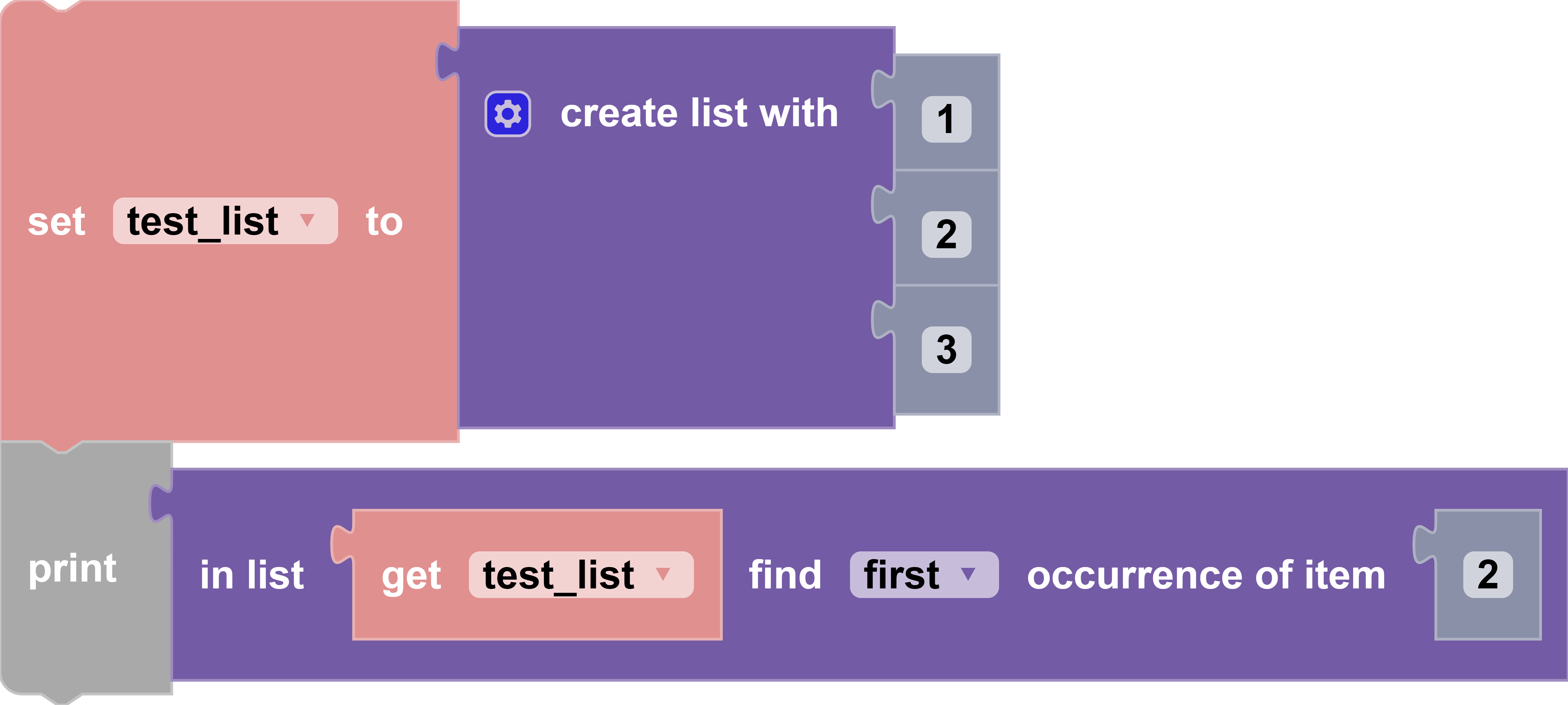
in list [list] get/remove [occurrence]
Block

Description
If choosing the "get" option, it returns the value of the item in a given index of the list. If choosing the "remove" option, it removes the item in a given index of the list. If choosing the "get and remove" option, it returns the value of the item and removes the item in a given index of the list.
Parameters
list list variable: A variable that is a list
command: option to whether to get, get and remove, or remove an item from the list
index: The position number of the item. (Some options require an integer input like the "#" and "# from end").
Returns
integer/float/string item: If choosing "get" or "get and remove", the value of the item is returned. If choosing "remove", returns None
Example
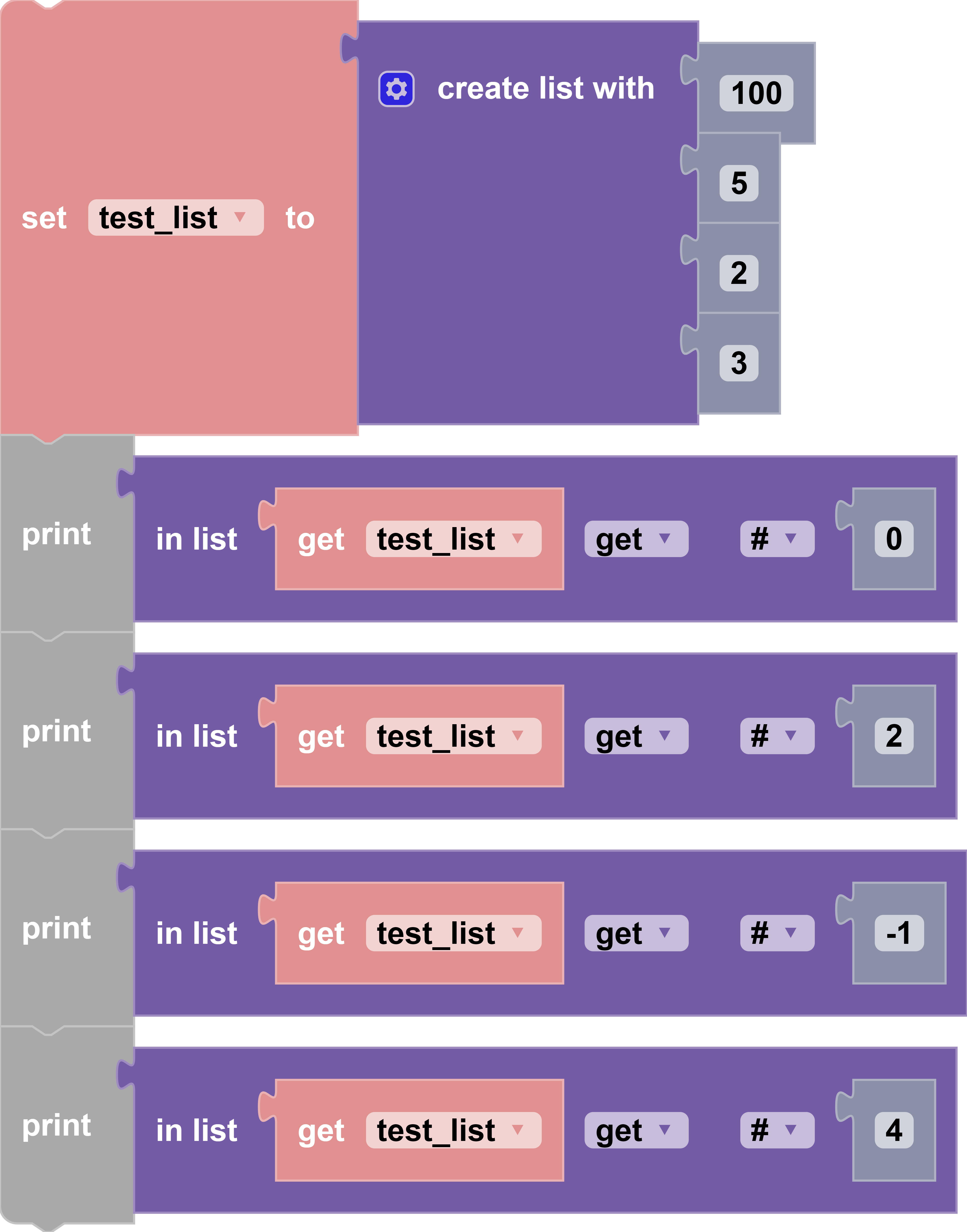
In this example, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [100,5,2,3]. The list blocks use 0-based indexing, which means that the first item in a list is index 0, the second item in a list is index 1, and so on. If an index is negative, the last item of the list is index -1, the second-to-last item of the list is index -2, and so on. The first print statement outputs 100 since #0 indicates the first item of the list. The second print statement outputs 2 since #2 indicates the 3rd item of the list. The third print statement outputs 3 because, in Python, index #-1 indicates the last item of the list. The fourth print statement outputs 3 because #3 indicates 4th item of the list.
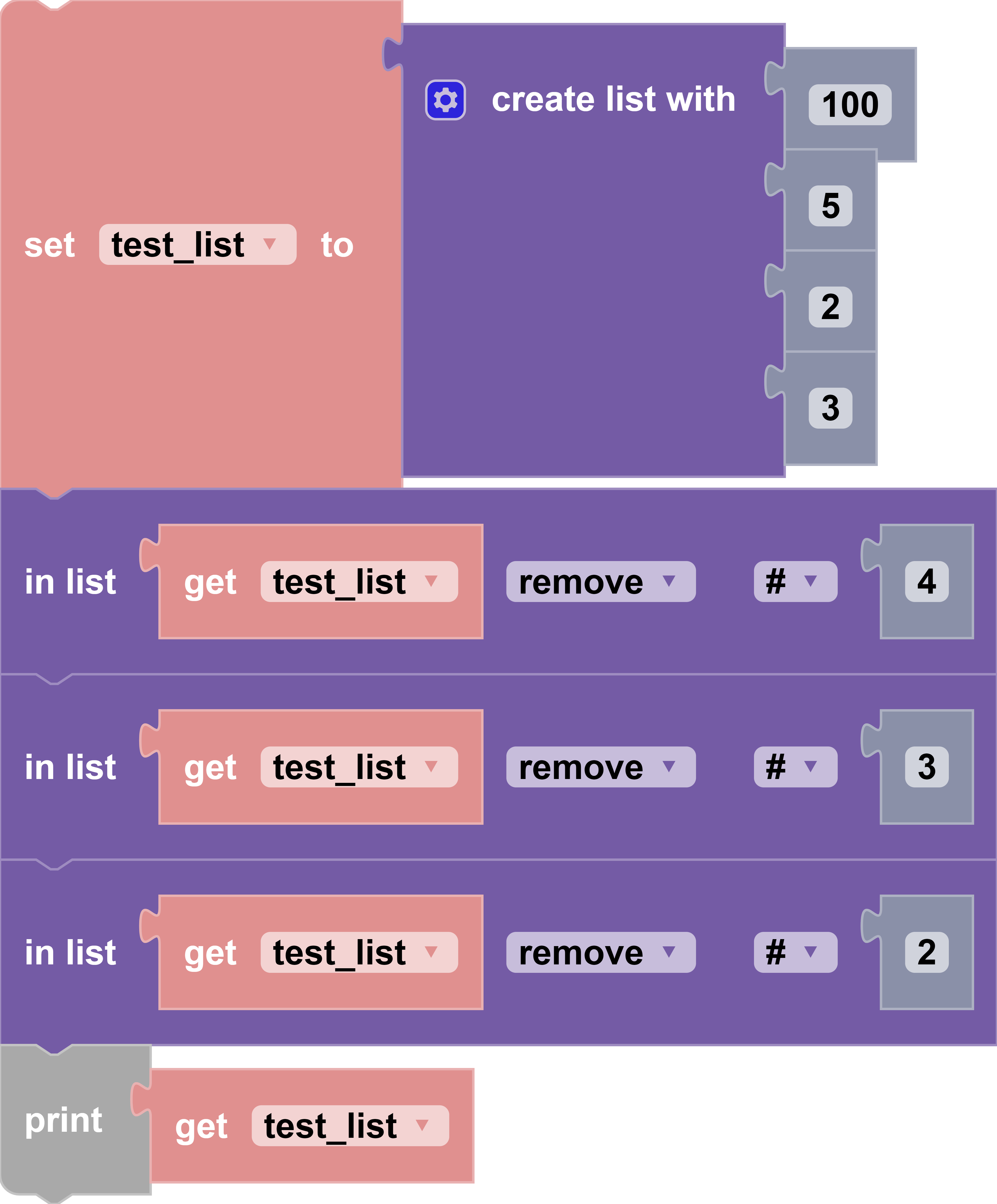
In the example below, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [100,5,2,3]. Then, in order, the items at index 3, index 2, and index 1 are removed from test_list. The console prints test_list, which outputs [100].
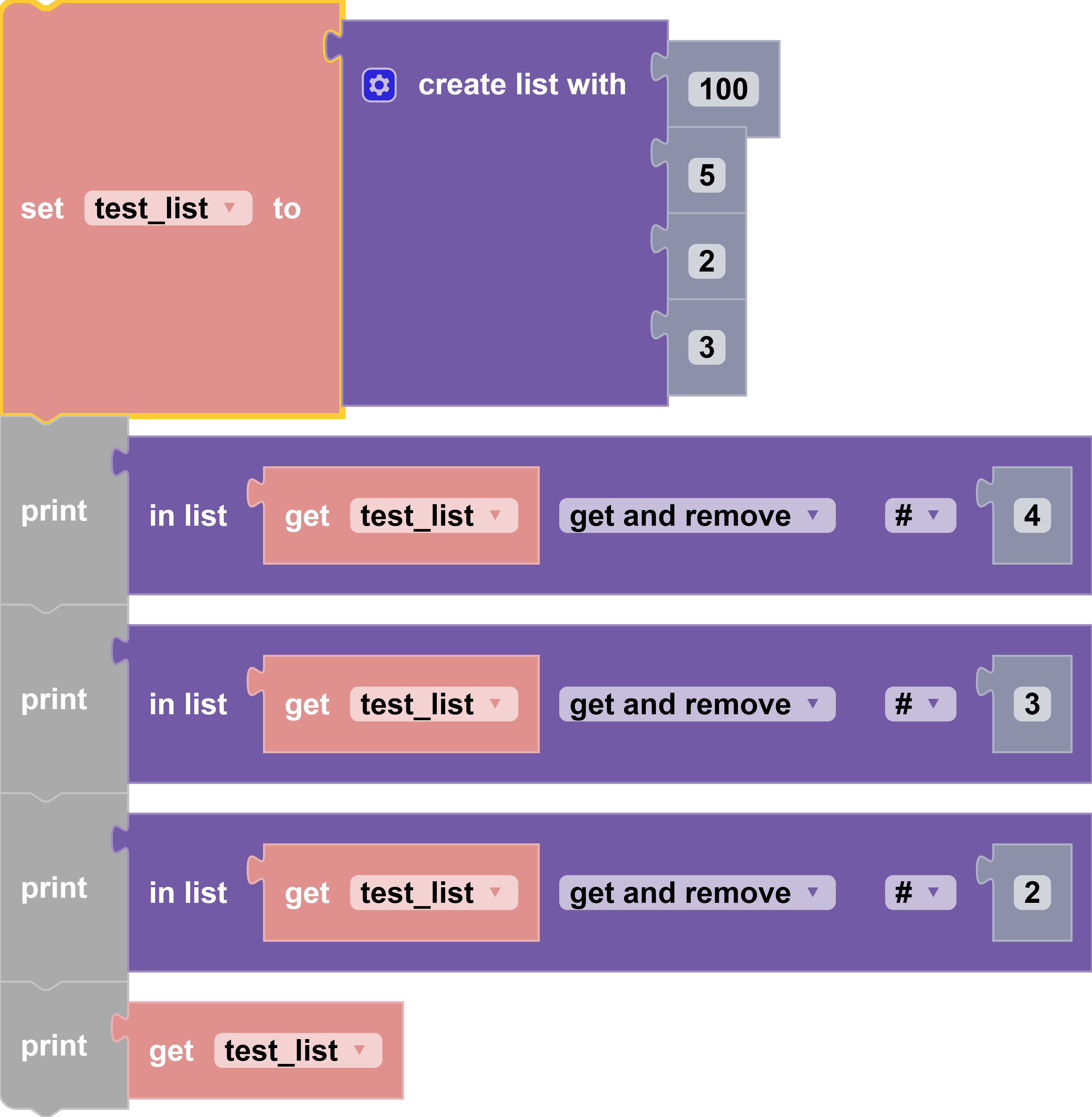
In the example below, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [100,5,2,3]. Then, in order, the items at index 3, index 2, and index 1 are printed on the console and removed from test_list. The console prints test_list, which outputs [100]. NOTE: "get and removed" option makes the block capable to be attached to a variable block as well.
in list [list] set/insert [occurence] as [value]
Block

Description
If choosing the "set" option, the block will set an existing item at a given index to a given value. If choosing the "insert at" option, the block insert/add a new item a given value into a given index in the list.
Parameters
list: list variable: a variable that is a list that you'll be modifying
command: option to whether set an existing item to a value or insert a new item into the list.
index: The position number of the item. (Some options require an integer input like the "#" and "# from end").
integer/float/string value: The value that the updated or new item will be.
Returns
None
Example
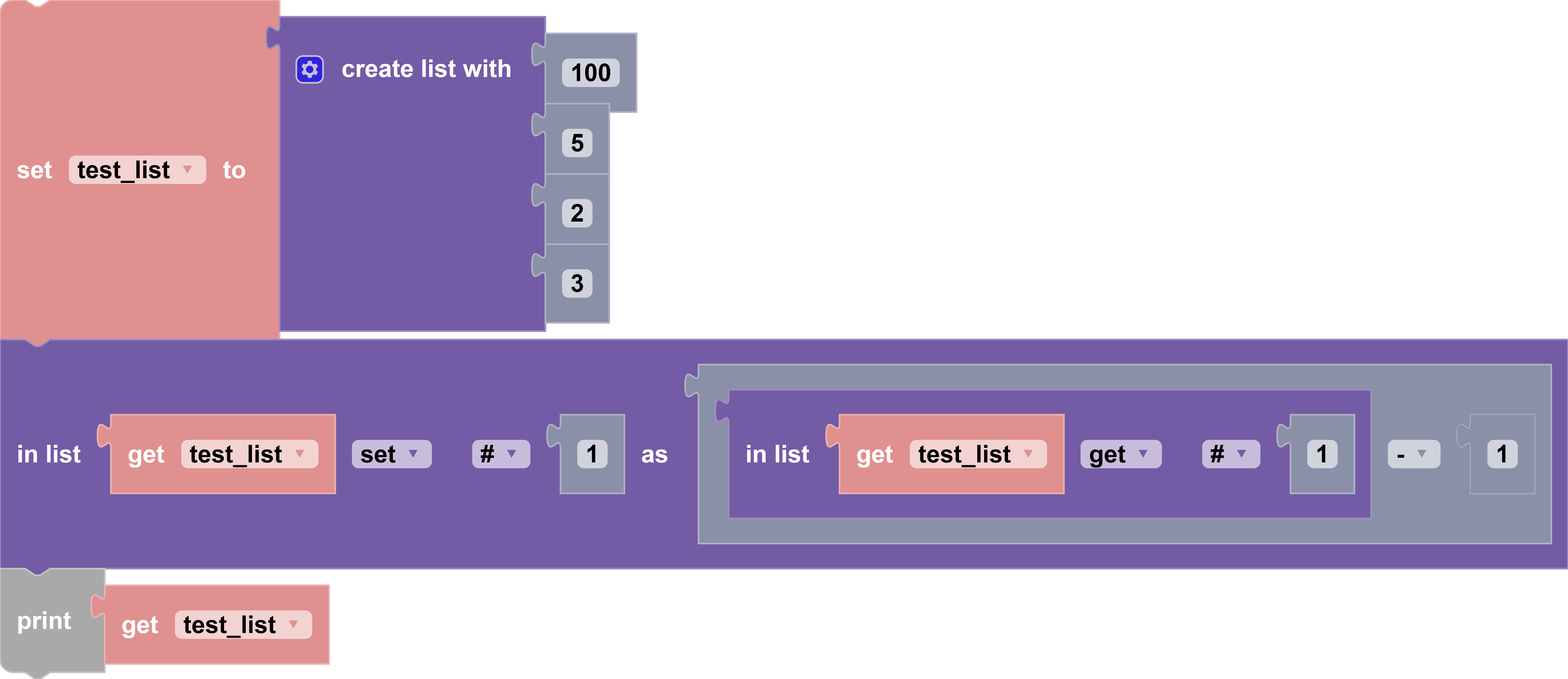
In this example, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [100,5,2,3]. On the next block, the item at index 0 (100) will be a set with a new value given by the value parameter. The new value is equal to the current value of the item at index 0 (represented by the "get" block inside) subtracted by 1 (99). Finally, printing test_list will result this output: [99,5,2,3].
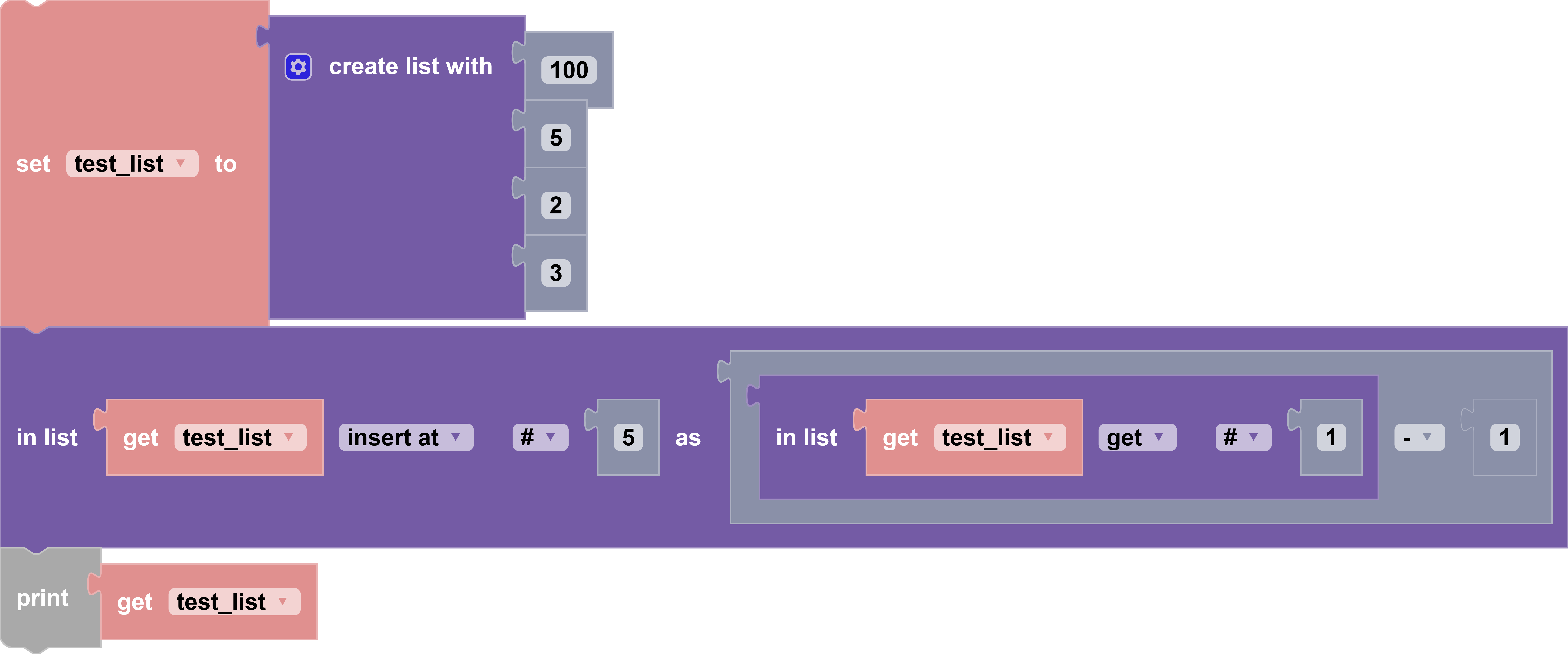
In this example, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [100,5,2,3]. On the next block, a new item will be inserted/at index 4 with a value given by the value parameter. The new item's value is equal to the value of the item at index 0 (represented by the "get" block inside) subtracted by 1 (99). Finally, printing test_list will result this output: [100,5,2,3,99].
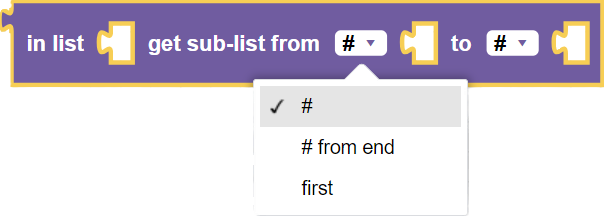
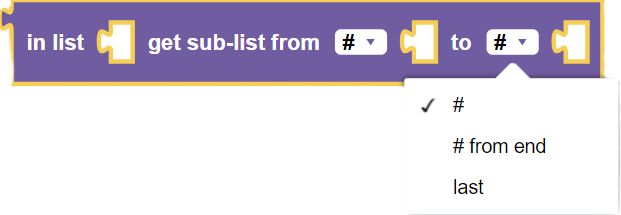
in list [list] get sub-list from [index1] to [index2]
Block

Description
Returns a list that is a sub-list of a given list from a given starting index (inclusive) to a given ending index (non-inclusive). It does not modify the given list.
Parameters
list list: a list block or a variable that is a list
starting index: The index on the list where the sub-list will start at. (Some options require an integer input like the "#" and "# from end").
ending index: The index on the list where the sub-list will end at, which is not included into the sub-list. (Some options require an integer input like the "#" and "# from end").
Returns
list sub-list: The sub-list from the given list
Example
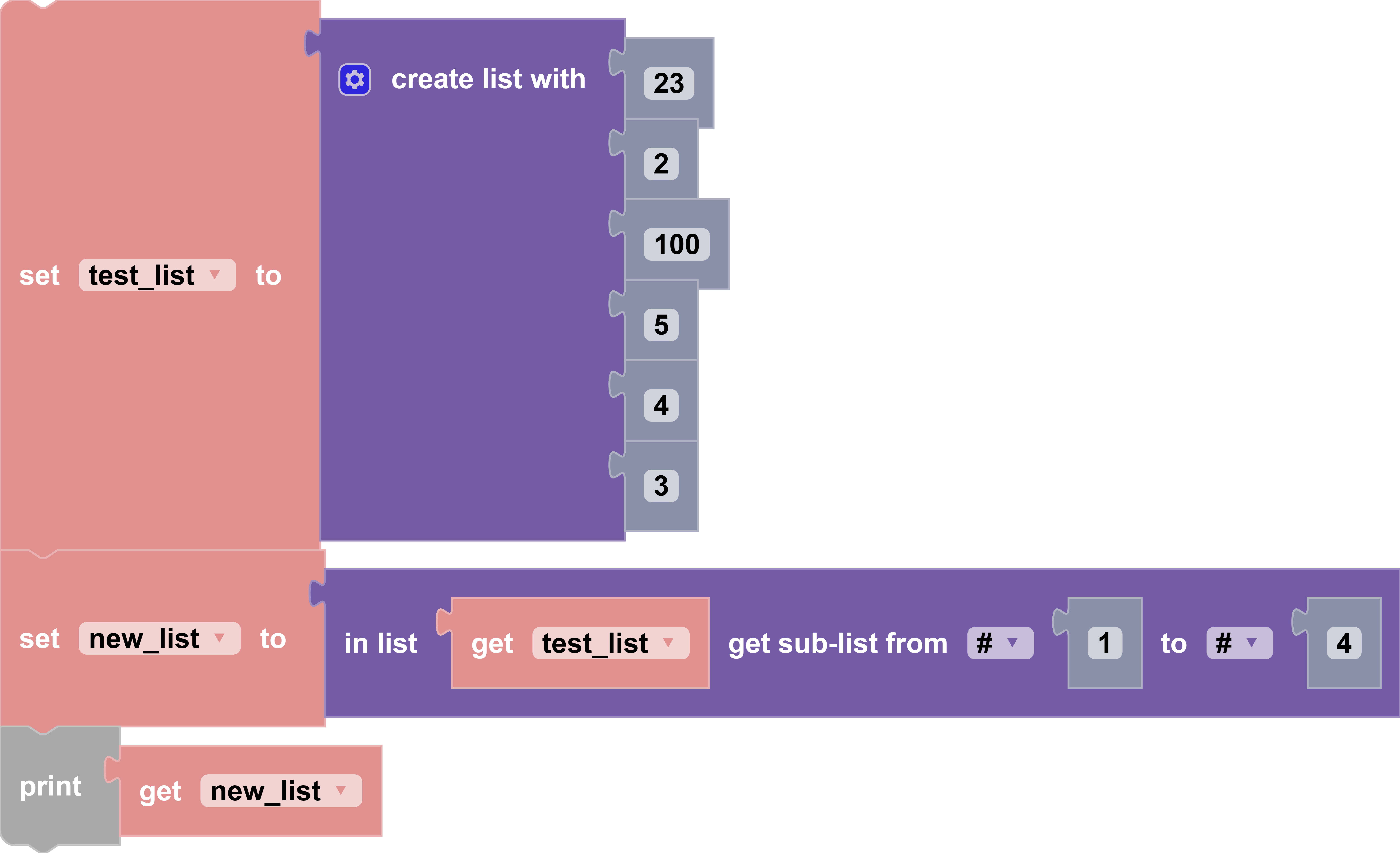
In this example, the list variable test_list is created with a value of [23,2,100,5,4,3]. The list variable new_list is created with a value of [23,2,100]. This is because the "get sub-list" block gets a portion of test_list from index 0 (23) to index 3 (5), which is not included into the sub-list.
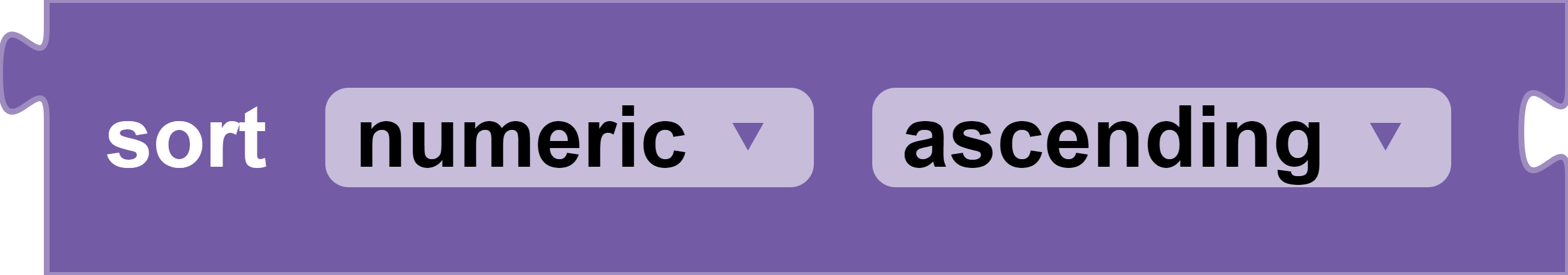
sort numeric/alphabetic ascending/descending
Block
Description
Returns sorted list based on numerical/alphaetical order and ascending/descending order. This could be attached to a "print" block or a "set variable" block.
NOTE: alphabetical ordering, in programming, is done using the strings' letters' ASCII codes. The uppercase alphabet (A-Z) has ASCII values between 65 and 90, and the lowercase alphabet (a-z) has ASCII values between 97 and 122. This means lowercase alphabet has higher ASCII values than the uppercase alphabet.
Parameters
order type: The way the list is sorted, by alphabetical or numerical order
order: ascending (A-z or smallest to biggest) or descending (z-A or biggest to smallest)
Returns
list sorted list: a sorted list
Example
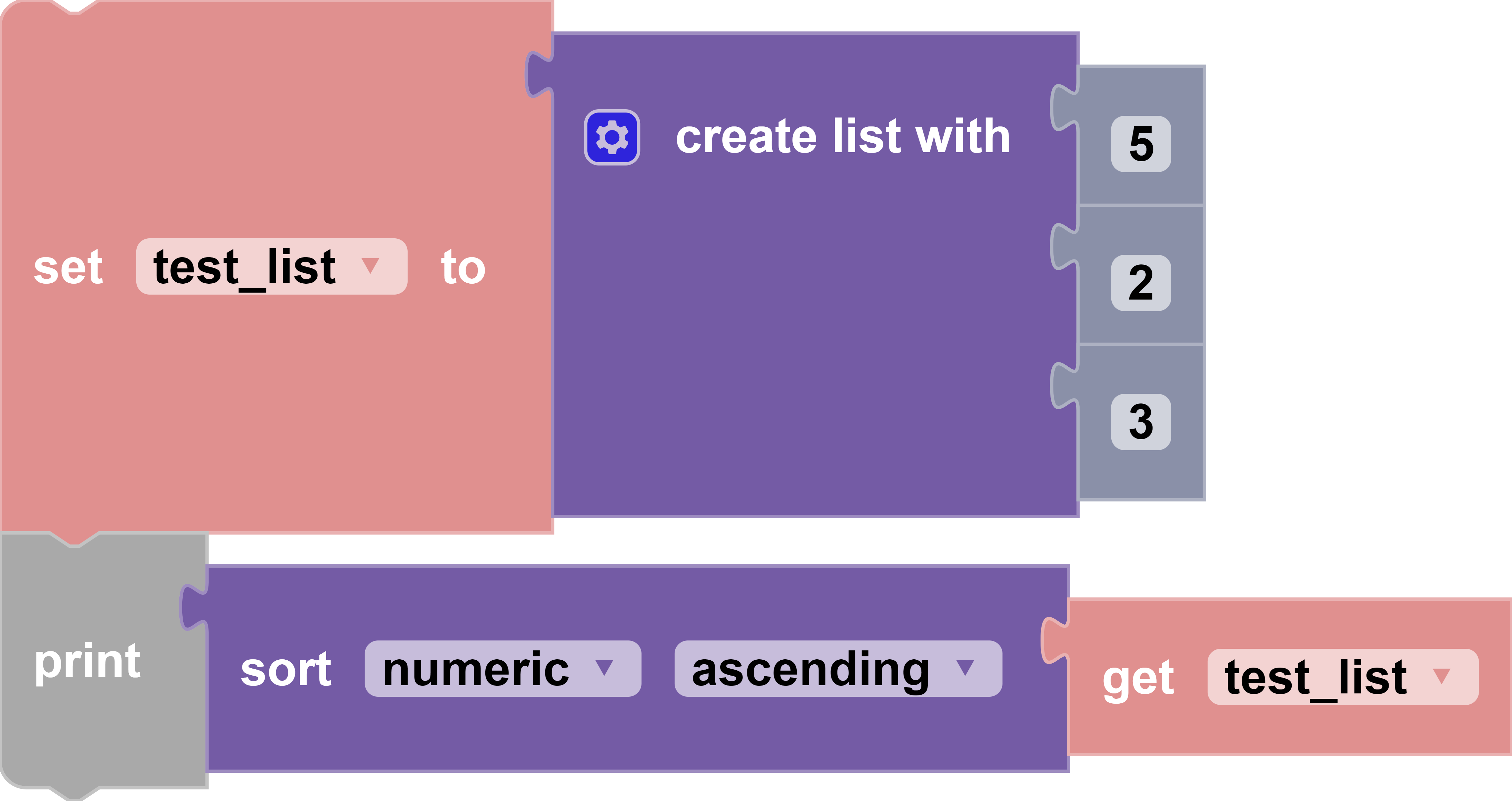
In this example, a list variable test_list is created with a value of [5,2,3]. The console prints the output of the sorted list from test_list in ascending, numerical order [2,3,5].
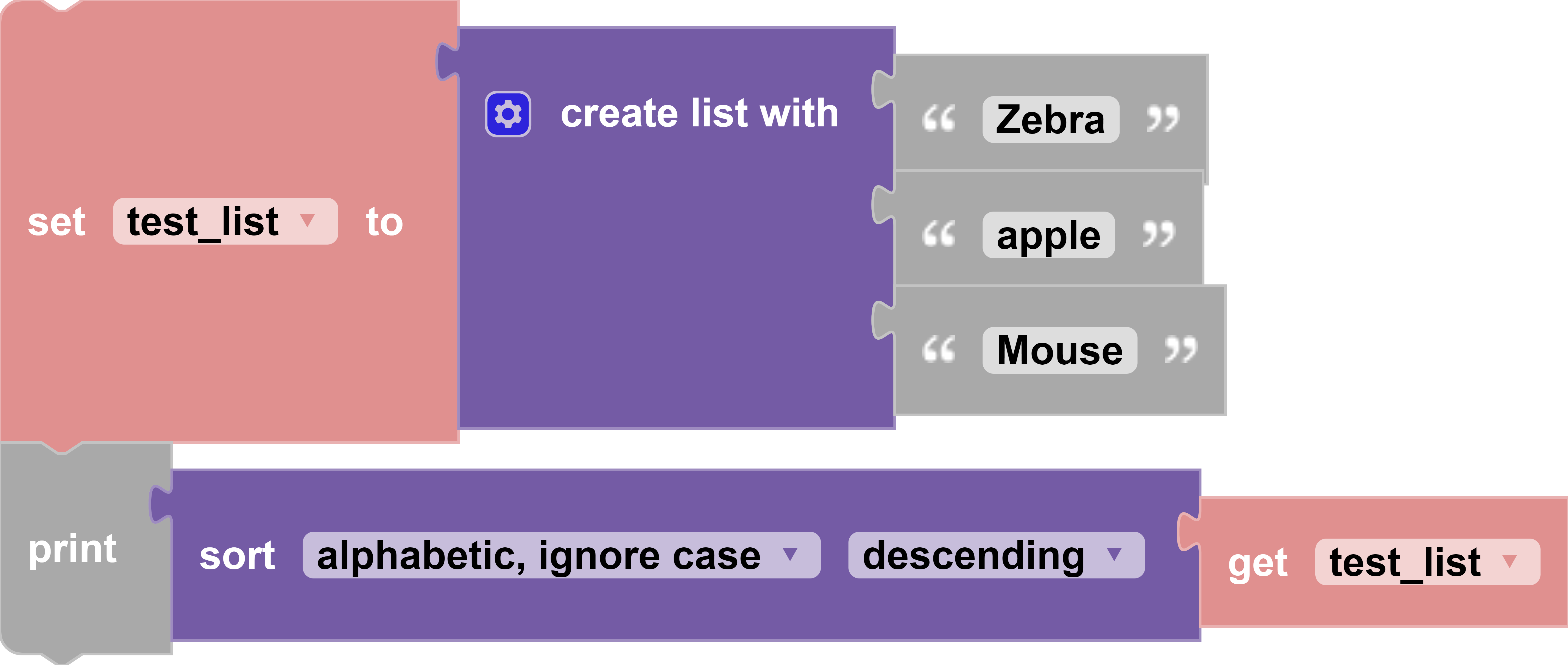
In the example below, a list variable test_list is created with a value of ["Zebra","apple","Mouse"]. The console prints the sorted list from test_list in descending alphabetical order, which is ["apple", "Zebra", "Mouse"].
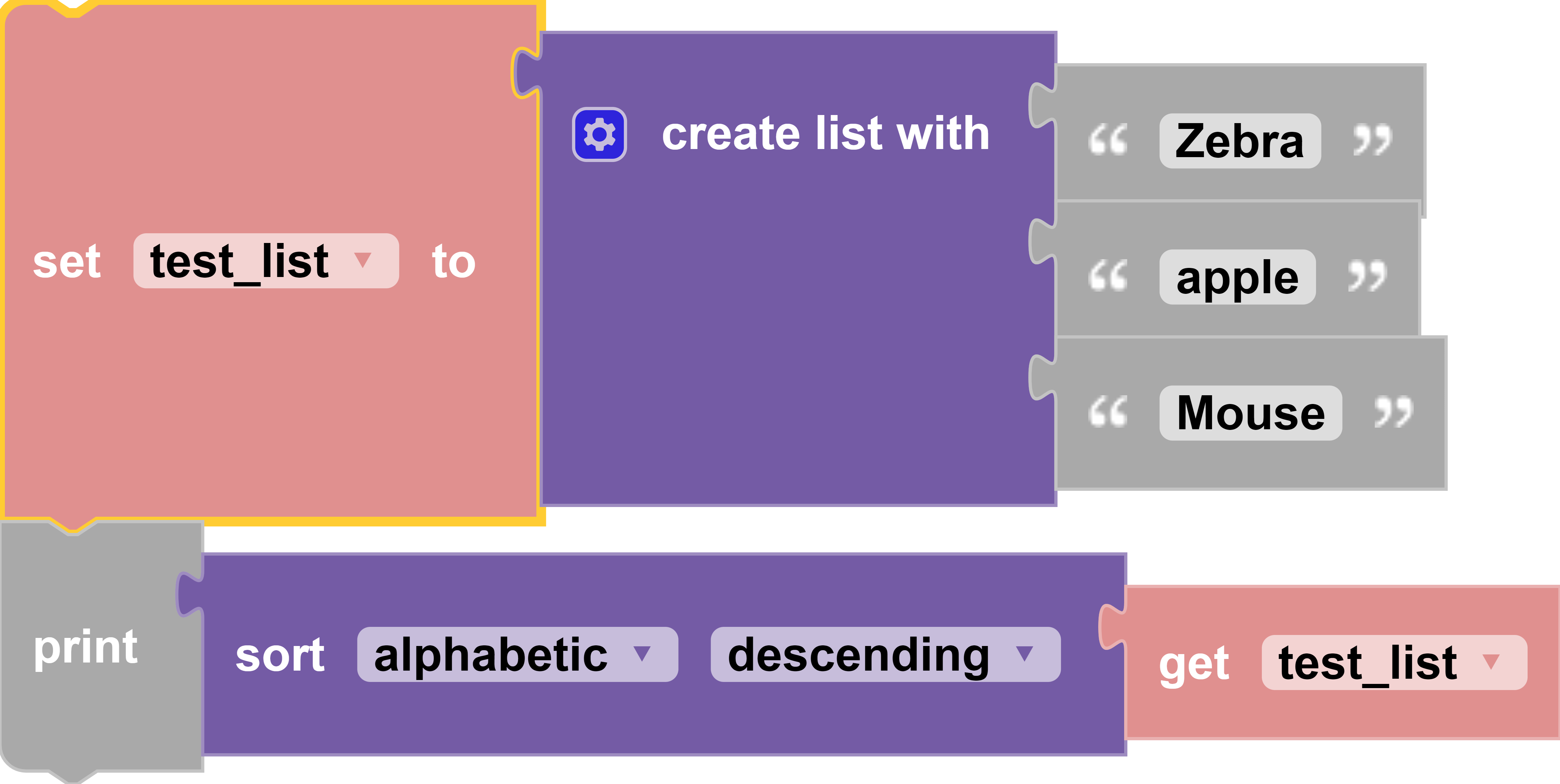
In the example below, a list variable test_list is created with a value of ["Zebra","apple","Mouse"]. The console prints the sorted list from test_list in descending alphabetical order (ignoring case), which is ["Zebra", "Mouse", "apple"]. Ignoring case essentially reads the uppercase letters as lowercase letters, so a lowercase "z" has a greater ASCII value than a lowercase "m" (and lowercase "m" greater than lowercase "a").
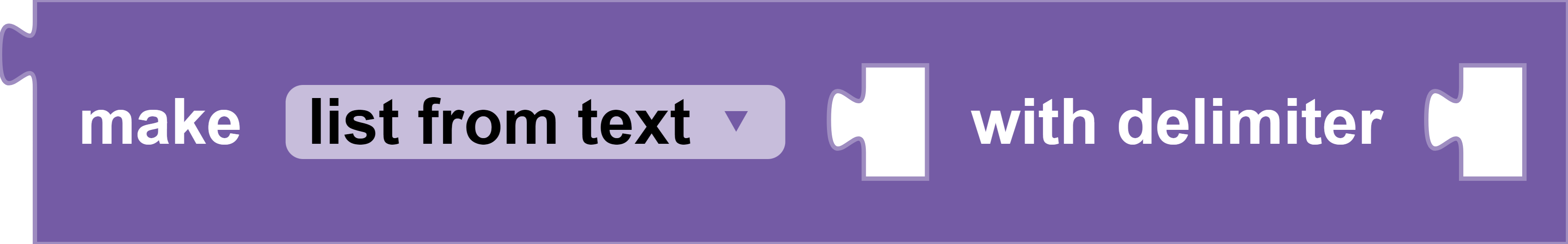
make [list from text/text from list] [text/list] with delimiter [value]
Block
Description
If choosing the "list from text" option, the block internally splits the given text into parts based on the given delimiter and returns a list. For example, the string "12!23!5!" with a delimiter of "!" will be converted to [12,23,5]. If choosing the "text from list" option, the block internally joins the given list's items based on the given delimiter and returns a string. For example, the list [12,3,5] with a delimiter of "--" will be converted to "12--3--5".
Parameters
string/list string/list variable: the variable, which is a list or text, that will be converted into a string or list.
string delimiter: a string of characters that will join a list's items or split the text's contents.
Returns
string/list converted string or list: a list (or string) that is the result of the conversion of the given string (or list) with the given delimiter.
Example
In this example, the string "14,2,1" will be converted into a list with the "," delimiter. The list variable test_list will be set to this conversion. The console will print test_list, which is [14,2,1].

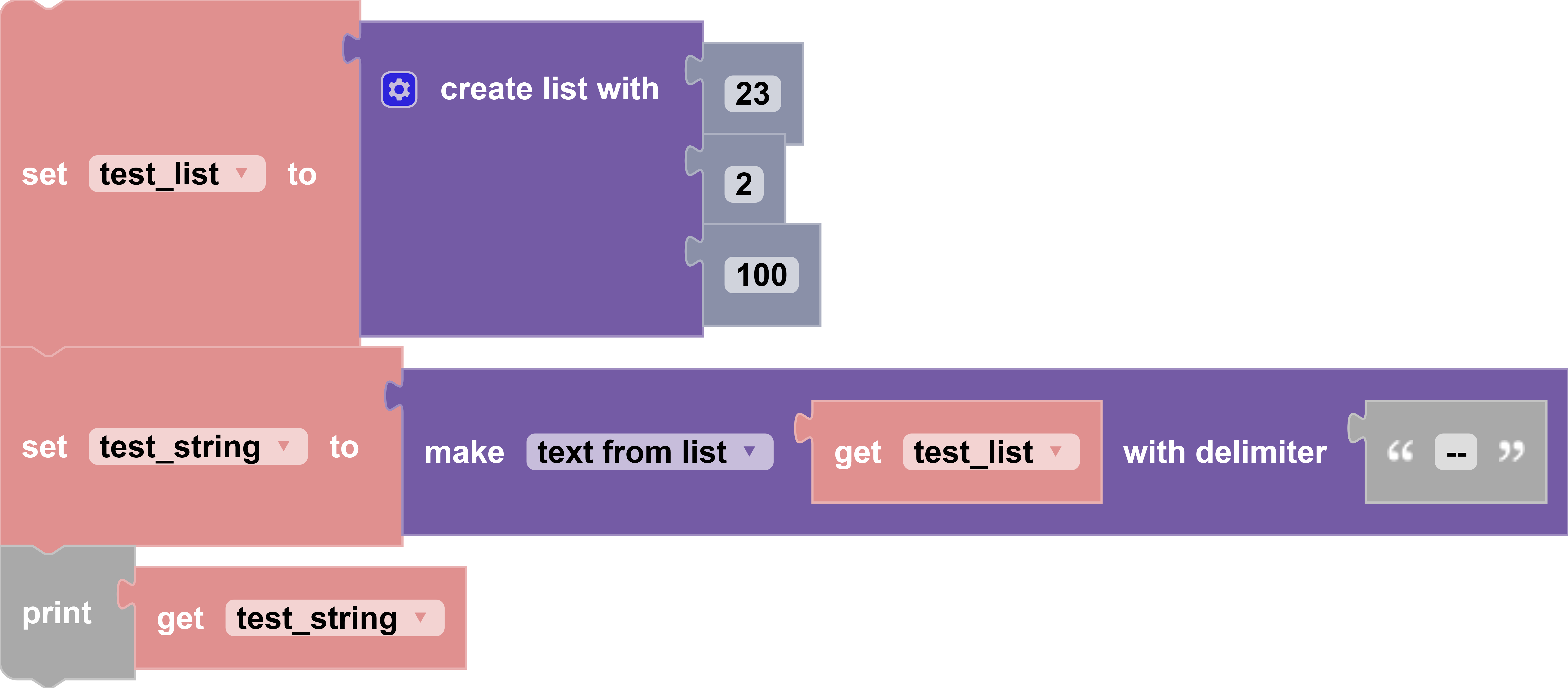
In this example, the list variable test_list will have value of [23,2,100]. The string variable test_string will have the value of "23--2--100" since it's set to the value of the converted list of test_list with the -- delimiter.
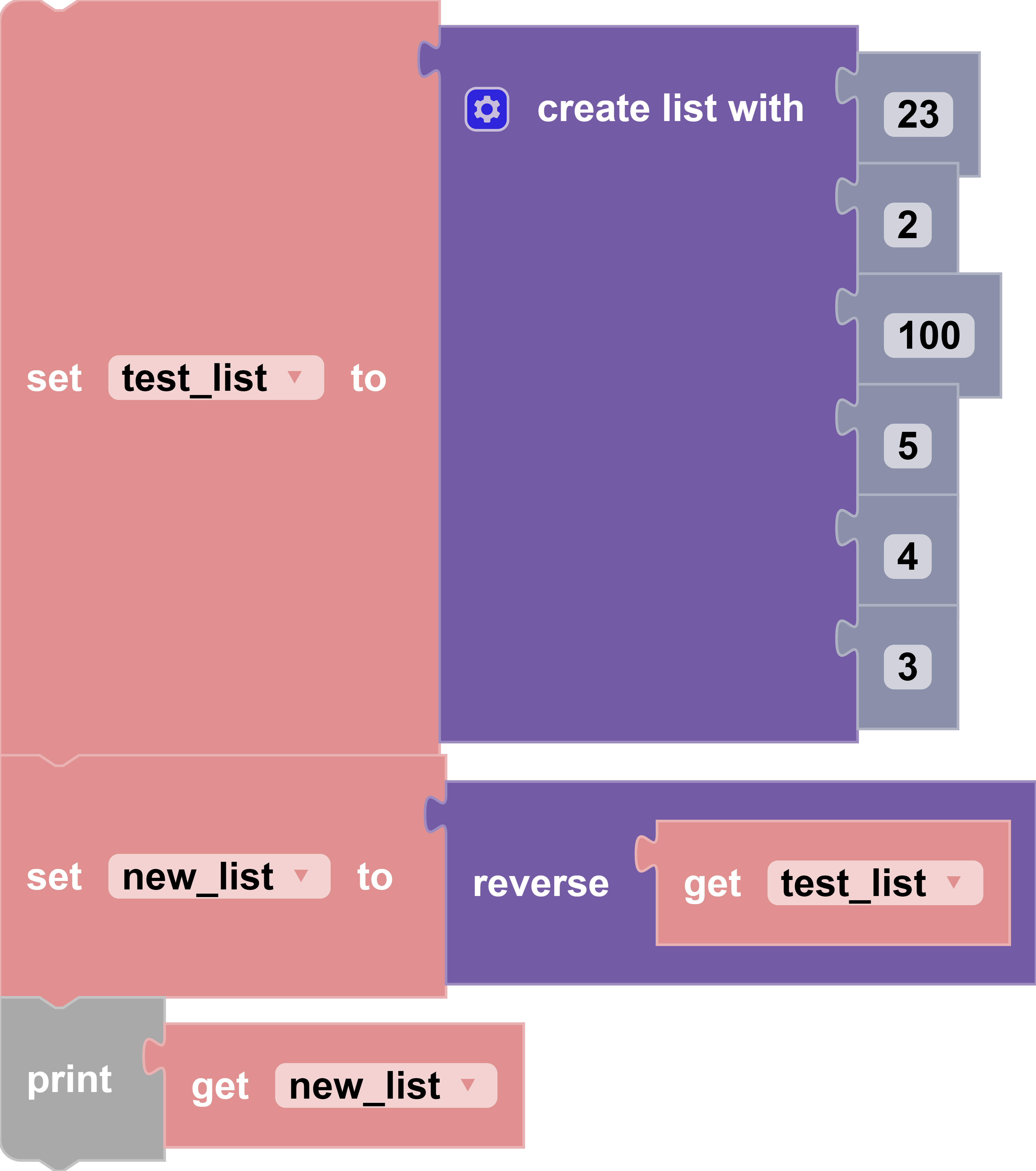
reverse [list]
Block

Description
Returns a list with the reversed order of the given list.
Parameters
list list variable: the list variable that will its order reversed
Returns
list reversed list: a reversed list of the given list
Example
In this example, the list variable test_list has a value of [23,2,100,5,4,3]. Then, the list variable new_list is set to the value of a reversed list of test_list. The console will print [3,4,5,100,2,23].