Drone Function Documentation
version 2.6 (Changelog)
Connection
pair()
Description
This function connects your controller with the program. You can also set the specific USB port name.
Syntax
pair()
pair(portname)
Parameters
string portname: A string containing the port name or number.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair() # pair automatically, may not always work
# drone.pair(port_name = 'COM3') # pair with a specific port
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
close()
Description
This function closes the connection of your controller with the program.
Syntax
close()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(1)
drone.land()
drone.close() # closes connection between controller and program
Flight Commands
takeoff()
Description
This function makes the drone takeoff at an average height of 80 centimeters and hover. The drone will always hover for 1 second in order to stabilize before it executes the next command. NOTE: The takeoff parameters or height cannot be modified.
Syntax
takeoff()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3)
drone.land()
drone.close()
land()
Description
This function makes the drone stop all commands, hover, and make a soft landing where it is. The function will also reset the flight motion variables to 0. NOTE: If you want to take off and immediately land, it is recommended to run a hover() or time.sleep() in between the takeoff() and land(), because the CoDrone EDU may miss the land command otherwise.
Syntax
land()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3) # include a hover() or time.sleep() to prevent land() from skipping
drone.land()
drone.close()
emergency_stop()
Description
This function immediately stops all commands and motors, so the drone will stop flying immediately. The function will also reset the flight motion variables to 0. NOTE: If you want to take off and emergency stop, it is recommended to run a hover() or time.sleep() in between the takeoff() and emergency_stop(), because the CoDrone EDU might miss the emergency_stop() command.
Syntax
emergency_stop()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3) #Recommended to have a hover() or time.sleep(1) before landing
drone.emergency_stop()
drone.close()
hover()
Description
This function makes the drone hover for a given amount of time. If given no parameters, it will hover indefinitely until given a another command.
Syntax
hover(duration)
Parameters
integer duration: Duration of the hovering in seconds
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3)
drone.land()
drone.close()
go()
Description
A beginner-friendly function that allows the drone to move the drone at a given direction, power, and duration.
Syntax
go(direction, power=50, duration=1)
Parameters
string direction: The direction of the movement
int power: The power at which the drone flies (0-100). Defaults to 50% if not defined.
float duration: The duration of the movement. Defaults to 1 second if not defined.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.go("forward", 30, 1) # move forward at 30% power for 1 second
drone.go("backward", 30, 1) # move backward at 30% power for 1 second
drone.go("right", 30, 1) # move right at 30% power for 1 second
drone.go("left", 30, 1) # move left at 30% power for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
avoid_wall()
Description
A looped method that makes the drone fly forward until it reaches a desired distance based on the front range sensor. The range of front sensor is from 0cm-100cm
Syntax
avoid_wall()
avoid_wall(timeout)
avoid_wall(distance)
avoid_wall(timeout, distance)
Parameters
integer timeout: timeout is an optional parameter that is the duration in seconds that the function will run. the default value is 2
integer distance: distance is an optional parameter that is the distance in centimeters the drone will stop at in front of an object. the default value is 70
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# fly forward until a wall is found 50 cm away. run this loop for 10 seconds.
drone.avoid_wall(10, 50)
drone.land()
drone.close()
keep_distance()
Description
A looped method that makes the drone fly forward until it reaches a desired distance. Once the desired distance in reached the drone will maintain that distance. The sensor range is up to 150 cm.
Syntax
keep_distance()
keep_distance(timeout)
keep_distance(distance)
keep_distance(timeout, distance)
Parameters
integer timeout: the duration in seconds that the function will execute. The default value is 2 seconds.
integer distance: the distance in centimeters the drone will stop and maintain distance in front of an object. The default value is 50 centimeters.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# maintain a distance of 60cm from an object once detected for 10 seconds
drone.keep_distance(10, 60)
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_trim()
Description
This function gets the current trim values of the drone.
Syntax
get_trim()
Parameters
None
Returns
list trim data: A list of trim data — [0] for roll trim and [1] for pitch trim
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# print the trim values
trim = drone.get_trim()
print(trim)
print(trim[0])
print(trim[1])
drone.close()
reset_trim()
Description
You can reset the roll and pitch trim of the drone in case your drone is drifting. This function will reset the roll and pitch trim values back to zero.
Syntax
reset_trim()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_trim(5,0)
print(drone.get_trim())
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3)
drone.land()
drone.reset_trim()
print(drone.get_trim())
drone.close()
set_trim()
Description
You can set the roll and pitch trim of the drone in case your drone is drifting. For example, if the drone is drifting to its right, you may want to set the roll to a small negative value. This trim will remain saved, even after powering off until you've changed the trim either programmatically, or done a reset with the remote. NOTE: If you're setting the trim right before a takeoff, make sure to add a time.sleep(1) before the takeoff(), otherwise the takeoff commmand might be skipped.
Syntax
set_trim(roll, pitch)
Parameters
integer roll: the power of the roll (-100 - 100)
integer pitch: the power of the pitch (-100 - 100)
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_trim(-5, 0) # example: drone is drifting right, so trim to roll left a little bit
time.sleep(1) # Add a time.sleep(1) before takeoff if you're planning to set the trim before takeoff
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3)
drone.land()
drone.close()
move_forward()
Description
Moves the drone forward for a given distance. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
Syntax
move_forward(distance)
move_forward(distance, unit, speed)
Parameters
float distance: the distance to travel.
string unit: The unit of measurement for the distance flown. Available units are "cm" (centimeter), "ft" (feet), "in" (inches), "m" (meter).
float speed: The drone's speed, in meters per second. The default speed is 1.0 meter per second. Max is 2.0 meters per second.
Returns
None
Example Code
The drone will take off, move forward 50cm at 1m/s, and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_forward(distance=50, units="cm", speed=1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
move_backward()
Description
Moves the drone backward for a given distance. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
Syntax
move_backward(distance)
move_backward(distance, unit, speed)
Parameters
float distance: the distance to travel.
string unit: The unit of measurement for the distance flown. Available units are "cm" (centimeter), "ft" (feet), "in" (inches), "m" (meter).
float speed: The drone's speed, in meters per second. The default speed is 1.0 meter per second. Max is 2.0 meters per second.
Returns
None
Example Code
The drone will take off, move backward 50cm at 1m/s, and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_backward(distance=50, units="cm", speed=1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
move_left()
Description
Moves the drone left for a given distance. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
Syntax
move_left(distance)
move_left(distance, unit, speed)
Parameters
float distance: the distance to travel.
string unit: The unit of measurement for the distance flown. Available units are "cm" (centimeter), "ft" (feet), "in" (inches), "m" (meter).
float speed: The drone's speed, in meters per second. The default speed is 1.0 meter per second. Max is 2.0 meters per second.
Returns
None
Example Code
The drone will take off, move left 50cm at 1m/s, and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_left(distance=50, units="cm", speed=1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
move_right()
Description
Moves the drone right for a given distance. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
Syntax
move_right(distance)
move_right(distance, unit, speed)
Parameters
float distance: the distance to travel.
string unit: The unit of measurement for the distance flown. Available units are "cm" (centimeter), "ft" (feet), "in" (inches), "m" (meter).
float speed: The drone's speed, in meters per second. The default speed is 1.0 meter per second. Max is 2.0 meters per second.
Returns
None
Example Code
The drone will take off, move right 50cm at 1m/s, and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_right(distance=50, units="cm", speed=1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
move_distance()
Description
Moves the drone by the specified distances along the x, y, and z axes, relative to its current position and heading. If two or more distances have non-zero values, the function will move the drone by these distances simultaneously. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
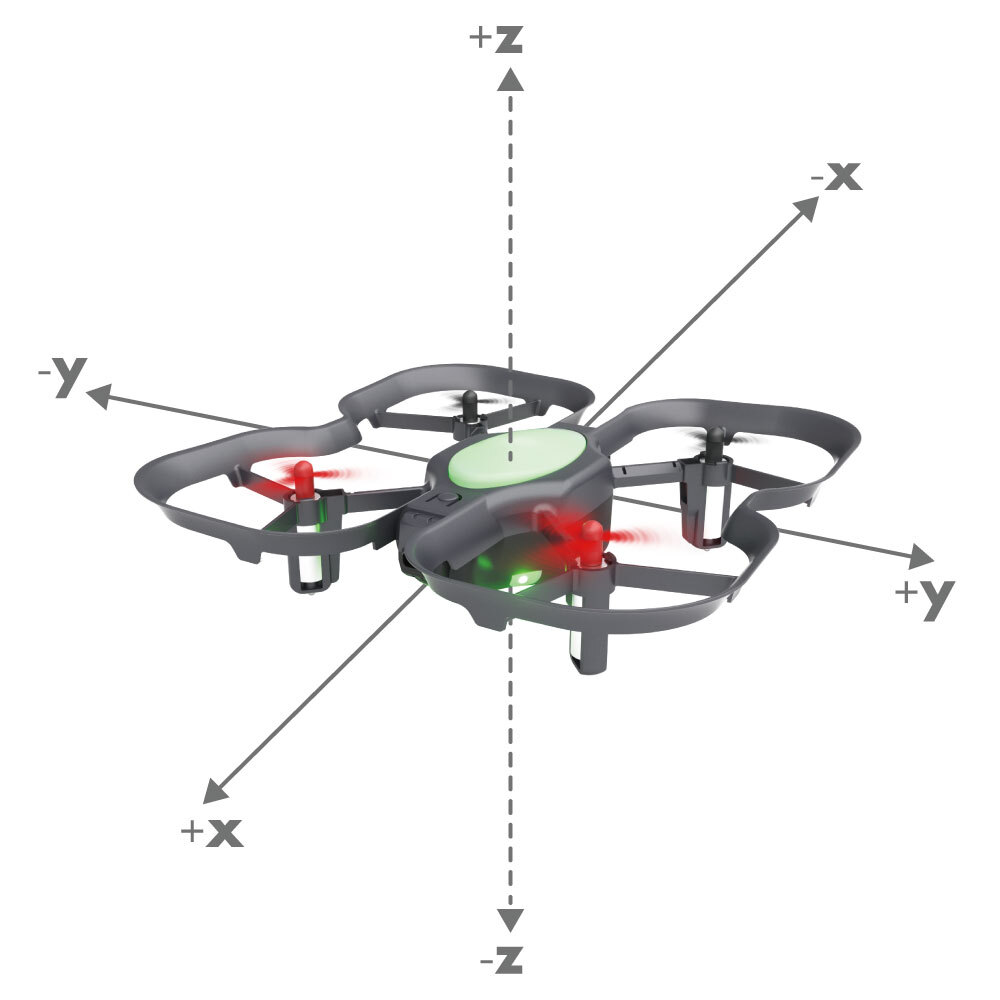
Syntax
move_distance(positionX, positionY, positionZ, velocity)
Parameters
float positionX: The distance to travel in the x-direction, in meters. This corresponds to forward/backward movement.
float positionY: The distance to travel in the y-direction, in meters. This corresponds to left/right movement.
float positionZ: The distance to travel in the z-direction, in meters. This corresponds to vertical movement.
float velocity: The drone's velocity, in meters per second. The default velocity is 1.0 meter per second. Max is 2.0 meters per second.
Returns
None
Example Code 1
The drone will take off, simultaneously move forward 0.5m, left 0.5m, and upward 0.25m at 1m/s (relative to its current position and heading), move back 0.75cm at 0.75m/s (relative to its current position and heading), and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_distance(0.5, 0.5, 0.25, 1) # move forward 0.5m, left 0.5m, and upward 0.25m simultaneously at 1m/s
drone.move_distance(-0.75, 0, 0, 0.75) # move back 0.75m at 0.75m/s
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 2
The drone will take off, move upward 0.50m at 0.50m/s, move right 0.50m at 0.50m/s, move downward 0.50m at 0.50m/s, move left 0.50m at 0.50m/s, and land.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.move_distance(0, 0, 0.5, 0.50) # move up 0.50m at 0.50m/s
drone.move_distance(0, -0.5, 0, 0.50) # move right 0.50m at 0.50m/s
drone.move_distance(0, 0, -0.5, 0.50) # move down 0.50m at 0.50m/s
drone.move_distance(0, 0.5, 0, 0.50) # move left 0.50m at 0.50m/s
drone.land()
drone.close()
send_absolute_position()
Description
Sends a movement command to the drone based on its absolute position from its first takeoff location. For the best performance, please make sure your drone is flying over a well-lit, patterned surface.
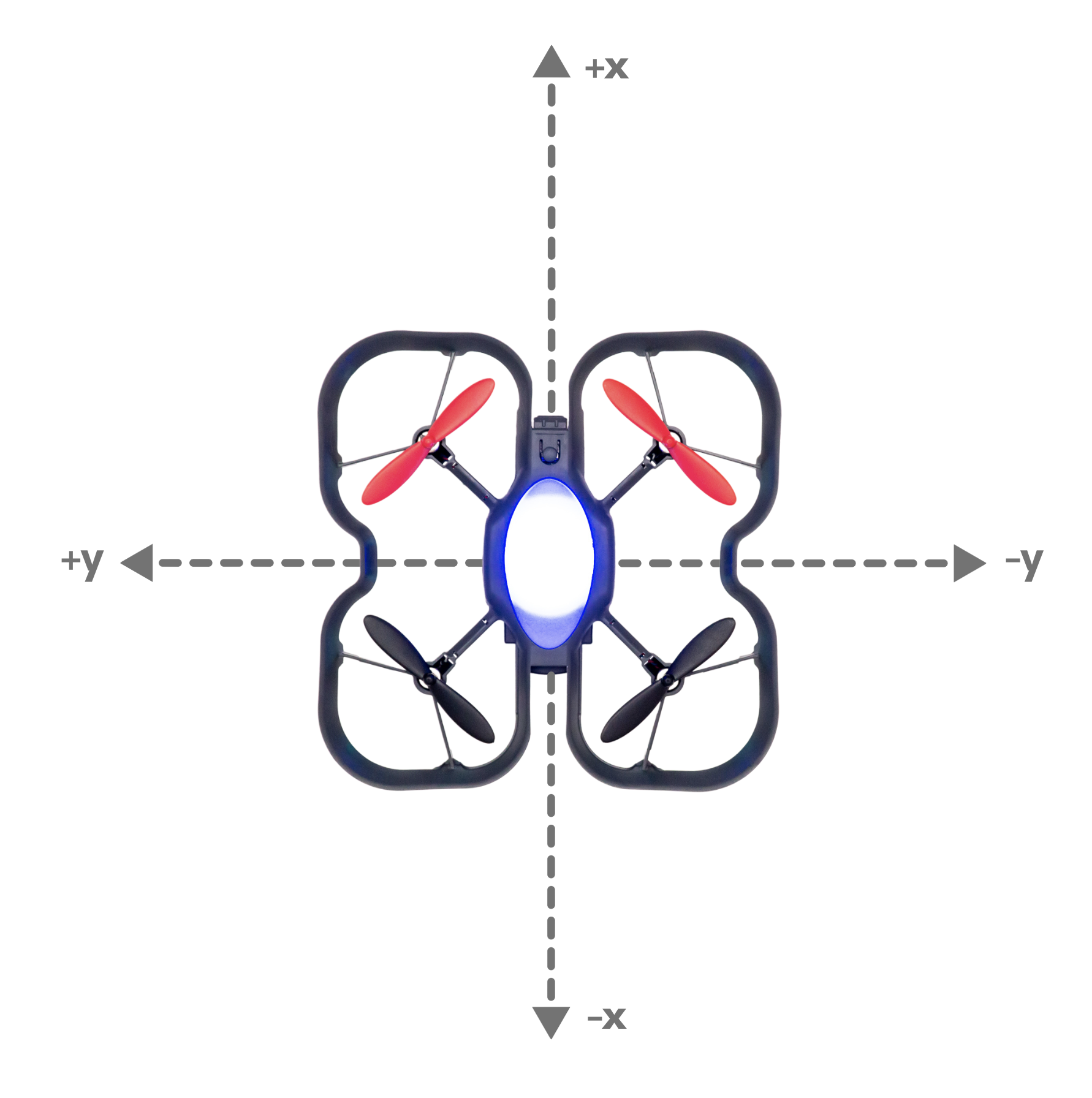

Syntax
send_absolute_position(positionX, positionY, positionZ, velocity, heading, rotationalVelocity)
Parameters
float positionX: The X position of the drone (-10m ~ 10m).
float positionY: The Y position of the drone (-10m ~ 10m).
float positionZ: The Z position of the drone (0m ~ 1.5m).
float velocity: The velocity of the drone in meters per second (0.5 ~ 2). The movement speed of the drone.
integer heading: Heading value in degrees. The heading is the z-angle of the drone.
integer rotationalVelocity: The rotational velocity of the drone in degrees per second (0 - 360). Left and right rotation speed of the drone.
Returns
None
Example Code 1
The drone takes off, moves to (0.5m, 0, 1m) at 0.5m/s, hovers at (0.5m, 0, 1m) since the drone is already in that position, and then lands.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Sending the drone forward from its takeoff location 0.5 meters moving at 0.5 m/s
drone.send_absolute_position(0.5, 0, 1, 0.5, 0, 0)
# Sending the same command will cause the drone to hover around
# the same area since this command uses absolute positioning from the takeoff location
drone.send_absolute_position(0.5, 0, 1, 0.5, 0, 0)
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 2
The drone takes off, moves to (0.5m, 0, 0.8m) at 0.5m/s, moves to (0.5m, 0.5m, 0.8m) at 0.5m/s, moves to (0, 0.5m, 0.8m) at 0.5m/s, moves to (0, 0, 0.8m) at 0.5m/s, and finally lands.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone will move to (0.5m, 0, 0.8m) with 0 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0.5, 0, 0.8, 0.5, 0, 0)
# Drone will move to (0.5m, 0.5m, 0.8m) with 0 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0.5, 0.5, 0.8, 0.5, 0, 0)
# Drone will move to (0, 0.5m, 0.8m) with 0 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0, 0.5, 0.8, 0.5, 0, 0)
# Drone will move to (0, 0, 0.8m) with 0 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0, 0, 0.8, 0.5, 0, 0)
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 3
The drone takes off, hovers at (0, 0, 0.8m) and rotates to 180 degree heading at 180 degrees/second, hovers at (0, 0, 0.8m) and rotates to 270 degree heading at 90 degrees/second, hovers at (0, 0, 0.8m) and rotates to 360 degree heading at 90 degrees/second, hovers at (0, 0, 0.8m) and rotates to 450 degree heading at 90 degrees/second, and finally lands.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone will move to (0, 0, 0.8m) with 180 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0,0,0.8,0,180,180)
# Drone will move to (0, 0, 0.8m) with 270 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0,0,0.8,0,270,90)
# Drone will move to (0, 0, 0.8m) with 360 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0,0,0.8,0,360,90)
# Drone will move to (0, 0, 0.8m) with 450 degree heading.
drone.send_absolute_position(0,0,0.8,0,450,90)
drone.land()
drone.close()
turn()
Description
This function turns the drone to the left or right, based on the given power value (-100 - 100), for a given number of seconds.
Syntax
turn()
turn(power=50, seconds=None)
Parameters
integer power: The number represents the direction and power of the turn. Negative power turns the drone to the right, and positive power turns the drone to the left.
float seconds: The duration of the turn
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.turn(50, 2) # drone will turn left at 50% power for 2 seconds
drone.turn(-20,5) # drone will turn right 20% power for 5 seconds
drone.land()
drone.close()
turn_degree()
Description
Turns right or left to a specified heading, in degrees, with respect to drone's initial heading. The initial heading is defined by the heading right after takeoff. The function will calculate the shortest path to the specified heading and turn in that direction.
Syntax
turn_degree(degree, timeout, p_value)
Parameters
integer degree: angle of turn in degrees. This function allows values more than 360, but the drone will not do more than a full rotation. To go to degree=450, it will not calculate the difference from starting heading (0) and turn for 1.25 revolutions. It will calculate the equivalent angle (90) and take the shortest rotation.
integer timeout: optional parameter that is duration in seconds that drone will try to turn. default value is 3.
integer p_value: optional parameter that is the gain of the proportional controller, if this increased CDE will turn quicker, the smaller the slower. default value is 10.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.turn_degree(90) # drone will turn left 90 degrees
drone.land()
drone.close()
turn_left()
Description
Turns the drone left using the built in gyroscope. The default degree is 90.
Syntax
turn_left()
turn_left(degree)
Parameters
integer degree: optional parameter that turns the drone in the given degree, ranging from 0 - 360. default value is 90.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.turn_left() # make a 90 degree left turn.
drone.hover(1) # wait for 1 second in the air
drone.turn_left(30) # make a 30 degree left turn
drone.land()
drone.close()
turn_right()
Description
Turns the drone right using the built in gyroscope. The default degree is 90.
Syntax
turn_right()
turn_right(degree)
Parameters
integer degree: optional parameter that turns the drone in the given degree, ranging from 0 - 360. default value is 90.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.turn_right() # make a 90 degree right turn.
drone.hover(1) # wait for 1 second in the air
drone.turn_right(30) # make a 30 degree right turn
drone.land()
drone.close()
Flight Sequences
circle()
Description
Flies the drone in the shape of a circle. The speed of the drone will only determine the forward speed and turning speed of the drone, not the size of the circle. The size of the circle, at any power, is roughly the same, with a diameter of 4-5ft.
Syntax
circle()
circle(speed, direction)
Parameters
integer speed: optional parameter that is the speed the drone will move and rotate(0 - 100). default value is 75.
integer direction: optional parameter that determines the direction of the circle. 1 is right, -1 is left. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# default circle parameters (75, 1)
drone.circle()
drone.land()
drone.close()
flip()
Description
This functions makes the drone flip backward, forward, right, or left. Make sure your battery percentage is over 50% for the flip to execute.
Syntax
flip()
flip(direction)
Parameters
string direction: optional parameter that is the direction the drone will flip. default is "back"
Returns
None
Example Code
Add a hover or delay after the flip if you need to stabilize before your next command. The drone takes 3-4 seconds after a flip before it can do another flight command.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(3)
drone.flip("back") # send flip command
time.sleep(4) # wait for flip to complete
drone.set_pitch(30) # move forward for 1 second
drone.move(1)
drone.set_pitch(-30) # move backward for 1 second
drone.move(1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
spiral()
Description
Flies the drone in the shape of a downward spiral.
Syntax
spiral()
spiral(speed, seconds, direction)
Parameters
integer speed: optional parameter that is the speed the drone will move (0 - 100). default value is 50.
integer seconds: optional parameter that is the duration in seconds the drone flies in a downward spiral. default value is 5.
integer direction: optional parameter that determines the direction of the spiral. 1 is right, -1 is left. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# default spiral parameters (50, 5, 1)
drone.spiral()
drone.land()
drone.close()
square()
Description
Flies the drone in the shape of a square.
Syntax
square()
square(speed, seconds, direction)
Parameters
integer speed: optional parameter that is the speed the drone will move (0 - 100). default value is 50.
integer seconds: optional parameter that is the duration in seconds the drone flies for each side of the square. default value is 5.
integer direction: optional parameter that determines the direction of the square. 1 is right, -1 is left. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# default square parameters (60, 1, 1)
drone.square()
drone.land()
drone.close()
sway()
Description
Flies the drone in a swaying motion.
Syntax
sway()
sway(speed, seconds, direction)
Parameters
integer speed: optional parameter that is the speed the drone will move (0 - 100). default value is 30.
integer seconds: optional parameter that is the duration in seconds the drone will fly in each "sway" motion. default value is 2.
integer direction: optional parameter that determines the direction of the sway. 1 is left, -1 is right. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# default sway parameters (30, 2, 1)
drone.sway()
drone.land()
drone.close()
triangle()
Description
Flies the drone in the shape of a triangle.
Syntax
triangle()
triangle(speed, seconds, direction)
Parameters
integer speed: optional parameter that is the speed the drone will move (0 - 100). default value is 60.
integer seconds: optional parameter that is the duration in seconds the drone flies for each side of the triangle. default value is 1.
integer direction: optional parameter that determines the direction of the triangle. 1 is right, -1 is left. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# default triangle parameters (60, 1, 1)
drone.triangle()
drone.land()
drone.close()
Flight Variables
get_move_values()
Description
Previously named print_move_values(). Returns the current values of roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle flight variables.
Syntax
get_move_values()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
# Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_roll(30)
drone.set_pitch(40)
drone.set_yaw(50)
drone.set_throttle(60)
move_list = drone.get_move_values() # get_move_values() returns list of flight variables
print("roll:", move_list[0])
print("pitch:", move_list[1])
print("yaw:", move_list[2])
print("throttle:", move_list[3])
drone.close()
move()
Description
The move command will move the drone based on the set flight variables (set_pitch, set_roll, etc). If given a parameter the move command will execute the movement for the given amount of seconds. If given no parameter then the drone will execute the move command indefinitley. You must takeoff() first to use a move() function.
Syntax
move(duration)
Parameters
integer duration: Duration of the movement in seconds
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone goes up for 1 second with 50 power
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.move(1) # move command executes the movement for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
print_move_values()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_move_values() instead, which returns move values (roll, pitch, yaw, throttle) that can be printed as needed.
Description
Prints the current values of roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle flight variables.
Syntax
print_move_values()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.print_move_values() # will print pitch and roll at 50 and throttle and yaw at 0
drone.land()
drone.close()
reset_move()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use reset_move_values() instead.
Description
The reset_move command will reset the values of roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle to 0.
Syntax
reset_move()
reset_move(attempts)
Parameters
integer attempts: Optional parameter that sends the reset_move command multiple times.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.move(2)
drone.reset_move() # reset the pitch and roll to 0.
drone.move(2) # after resetting flight variables, move(2) won't move the drone
drone.land()
drone.close()
reset_move_values()
Description
The reset_move_values command will reset the values of roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle to 0.
Syntax
reset_move_values()
reset_move_values(attempts)
Parameters
integer attempts: Optional parameter that sends the reset_move_values command multiple times.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.move(2)
drone.reset_move_values() # reset the pitch and roll to 0.
drone.move(2) # after resetting flight variables, move(2) won't move the drone
drone.land()
drone.close()
set_pitch()
Description
This is a setter function that allows you to set the pitch variable. Once you set pitch, you have to use move() to actually execute the movement. The pitch variable will remain what you last set it until the end of the flight sequence, so you will have to set it back to 0 if you don't want the drone to pitch again.
Syntax
set_pitch(power)
Parameters
integer power: Sets the pitch variable (-100 - 100). The number represents the direction and power of the output for that flight motion variable. Negative pitch is backwards, positive pitch is forwards.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone goes forward for 1 second with 50 power
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.move(1) # move command executes the movement for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
set_roll()
Description
This is a setter function that allows you to set the roll variable. Once you set roll, you have to use move() to actually execute the movement. The roll variable will remain what you last set it until the end of the flight sequence, so you will have to set it back to 0 if you don't want the drone to roll again.
Syntax
set_roll(power)
Parameters
integer power: Sets the roll variable (-100 - 100). The number represents the direction and power of the output for that flight motion variable. Negative roll is left, positive roll is right.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone goes right for 1 second with 50 power
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.move(1) # move command executes the movement for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
set_throttle()
Description
This is a setter function that allows you to set the throttle variable. Once you set throttle, you have to use move() to actually execute the movement. The throttle variable will remain what you last set it until the end of the flight sequence, so you will have to set it back to 0 if you don't want the drone to throttle again.
Syntax
set_throttle(power)
Parameters
integer power: Sets the throttle variable (-100 - 100). The number represents the direction and power of the output for that flight motion variable. Negative throttle is down, positive throttle is up.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone goes up for 1 second with 50 power
drone.set_throttle(50)
drone.move(1) # move command executes the movement for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
set_yaw()
Description
This is a setter function that allows you to set the yaw variable. Once you set yaw, you have to use move()to actually execute the movement. The yaw variable will remain what you last set it until the end of the flight sequence, so you will have to set it back to 0 if you don't want the drone to yaw again.
Syntax
set_yaw(power)
Parameters
integer power: Sets the yaw variable (-100 - 100). The number represents the direction and power of the output for that flight motion variable. Negative yaw is right, positive yaw is left.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# Drone turns left for 1 second with 50 power
drone.set_yaw(50)
drone.move(1) # move command executes the movement for 1 second
drone.land()
drone.close()
LED
controller_LED_off()
Description
Turns off the controller LEDs.
Syntax
controller_LED_off()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.controller_LED_off()
drone.close()
drone_LED_off()
Description
Turns off the drone LED.
Syntax
drone_LED_off()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.drone_LED_off()
drone.close()
set_controller_LED()
Description
This function sets the LED color and brightness of the CoDrone EDU controller's LEDs. This is done by setting RGB values (0 - 255) and brightness level (0 - 100).
Syntax
set_controller_LED(red, green, blue, brightness)
Parameters
integer red: pixel value for the color red (0 - 255)
integer green: pixel value for the color green (0 - 255)
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue (0 - 255)
integer brightness: brightness of the controller LED (0 - 255)
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_controller_LED(0, 0, 255, 100)
drone.close()
set_drone_LED()
Description
This function sets the LED color and brightness of the CoDrone EDU's LED. This is done by setting RGB values (0 - 255) and brightness level (0 - 100).
Syntax
set_drone_LED(red, green, blue, brightness)
Parameters
integer red: pixel value for the color red (0 - 255)
integer green: pixel value for the color green (0 - 255)
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue (0 - 255)
integer brightness: brightness of the drone LED (0 - 255)
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_drone_LED(0, 0, 255, 100)
drone.close()
set_controller_LED_mode()
Description
This function sets the color, mode, and speed of the mode of the CoDrone EDU controller's LED. The mode is the light pattern that the LED will have. Please note that the rainbow mode cannot be affected by the RGB values given.
Syntax
set_controller_LED_mode(r, g, b, mode, speed)
Parameters
integer red: pixel value for the color red (0 - 255)
integer green: pixel value for the color green (0 - 255)
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue (0 - 255)
string/Enum mode: the LED's light pattern, which can be an string or Enum. The available modes are:
"dimming"orControllerLEDMode.Dimming"fade_in"orControllerLEDMode.Fade_In"fade_out"orControllerLEDMode.Fade_Out"blink"orControllerLEDMode.Blink"double_blink"orControllerLEDMode.Double_Blink"rainbow"orControllerLEDMode.Rainbow
integer speed: speed of the mode (1 - 10).
Returns
None
Example Code 1
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_controller_LED_mode(0, 0, 255, "dimming", 10) # the controller's LED will have a blue dimming pattern at speed 10. The 'mode' argument is a string
drone.close()
Example Code 2
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_controller_LED_mode(0, 255, 0, ControllerLEDMode.Double_Blink, 10) # the controller's LED will have a green double-blink pattern at speed 10. The 'mode' argument is an Enum
drone.close()
Example Code 3
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_controller_LED_mode(255, 255, 255, "rainbow", 10) # the controller's LED will have a rainbow pattern at speed 10. Notice how the RGB values will not affect the rainbow pattern.
drone.close()
set_drone_LED_mode()
Description
This function sets the color, mode, and speed of the mode of the CoDrone EDU drone's LED. The mode is the light pattern that the LED will have. Please note that the rainbow mode cannot be affected by the RGB values given.
Syntax
set_drone_LED_mode(r, g, b, mode, speed)
Parameters
integer red: pixel value for the color red (0 - 255)
integer green: pixel value for the color green (0 - 255)
integer blue: pixel value for the color blue (0 - 255)
string/Enum mode: the LED's light pattern, which can be an string or Enum. The available modes are:
"dimming"orDroneLEDMode.Dimming"fade_in"orDroneLEDMode.Fade_In"fade_out"orDroneLEDMode.Fade_Out"blink"orDroneLEDMode.Blink"double_blink"orDroneLEDMode.Double_Blink"rainbow"orDroneLEDMode.Rainbow
integer speed: speed of the mode (1 - 10).
Returns
None
Example Code 1
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_drone_LED_mode(0, 0, 255, "dimming", 10) # the drone's LED will have a blue dimming pattern at speed 10. The 'mode' argument is a string
drone.close()
Example Code 2
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_drone_LED_mode(0, 255, 0, DroneLEDMode.Double_Blink, 10) # the drone's LED will have a green double-blink pattern at speed 10. The 'mode' argument is an Enum
drone.close()
Example Code 3
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_drone_LED_mode(255, 255, 255, "rainbow", 10) # the drone's LED will have a rainbow pattern at speed 10. Notice how the RGB values will not affect the rainbow pattern.
drone.close()
Sounds
controller_buzzer()
Description
Plays a note using the controller's buzzer.
Syntax
controller_buzzer(note, duration)
Parameters
integer/Note note: frequency of the note, in Hertz or a Note object
integer duration: Duration of the note in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.controller_buzzer(400, 300)
drone.controller_buzzer(600, 300)
drone.close()
drone_buzzer()
Description
Plays a note using the drone's buzzer.
Syntax
drone_buzzer(note, duration)
Parameters
integer/Note note: frequency of the note, in Hertz or a Note object
integer duration: Duration of the note in milliseconds
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.drone_buzzer(400, 300)
drone.drone_buzzer(600, 300)
drone.close()
start_drone_buzzer()
Description
This function allows the drone buzzer to be played in the background while other commands are given to the drone.
Syntax
start_drone_buzzer(note)
Parameters
integer/Note note: the frequency of the note, in Hertz or a Note object
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.start_drone_buzzer(500) # starting the buzzer
# these commands run while the buzzer runs in the background
for i in range(5):
drone.set_drone_LED(255, 0, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.set_drone_LED(0, 255, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.stop_drone_buzzer() # stops the buzzer
drone.close()
stop_drone_buzzer()
Description
Stops the drone buzzer if started in the background.
Syntax
stop_drone_buzzer()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.start_drone_buzzer(500) # starting the buzzer
# these commands run while the buzzer runs in the background
for i in range(5):
drone.set_drone_LED(255, 0, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.set_drone_LED(0, 255, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.stop_drone_buzzer() # stops the buzzer
drone.close()
start_controller_buzzer()
Description
This function allows the controller buzzer to be played in the background while other commands are given to the drone.
Syntax
start_controller_buzzer(note)
Parameters
integer/Note note: the frequency of the note, in Hertz or a Note object
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.start_controller_buzzer(Note.A4) # starting the buzzer
# these commands run while the buzzer runs in the background
for i in range(3):
drone.set_controller_LED(255, 0, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.set_controller_LED(0, 255, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.stop_controller_buzzer() # stops the buzzer
drone.close()
stop_controller_buzzer()
Description
Stops the controller buzzer if started in the background.
Syntax
stop_controller_buzzer()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.start_controller_buzzer(440) # starting the buzzer
# these commands run while the buzzer runs in the background
for i in range(3):
drone.set_controller_LED(255, 0, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.set_controller_LED(0, 255, 0, 100)
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.stop_controller_buzzer() # stops the buzzer
drone.close()
drone_buzzer_sequence()
Description
This function will create a sound sequence using the drone's buzzer. This function can be a creative way to indicate the degree of success of the objective that the program is trying to achieve. There are three sound sequences to choose from: 'success', 'warning', 'error'.
Syntax
drone_buzzer_sequence()
Parameters
string kind: The type of sound sequence that the drone's buzzer will create.
Returns
None
Example
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
x = int(input("Enter a number:"))
if x > 5:
drone.drone_buzzer_sequence("success") # drone's buzzer creates 'success' sound sequence
else:
drone.drone_buzzer_sequence("error") # drone's buzzer creates 'error' sound sequence
drone.close()
controller_buzzer_sequence()
Description
This function will create a sound sequence using the controller's buzzer. This function can be a creative way to indicate the degree of success of the objective that the program is trying to achieve. There are three sound sequences to choose from: 'success', 'warning', 'error'.
Syntax
drone_buzzer_sequence()
Parameters
string kind: The type of sound sequence that the controller's buzzer will create.
Returns
None
Example
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
x = int(input("Enter a number:"))
if x > 5:
drone.controller_buzzer_sequence("success") # controller's buzzer creates 'success' sound sequence
else:
drone.controller_buzzer_sequence("error") # controller's buzzer creates 'error' sound sequence
drone.close()
ping()
Description
This function will ping the drone, creating a beeping sound while the drone's LED is blinking. The LED color for the ping command can be specified, but if nothing is specified, then the color's RGB values will be randomly selected. This is a useful, creative way to identify the drone that you are using in an environment full of other drones.
Syntax
ping()
ping(r=None,g=None,b=None)
Parameters
integer r: The red pixel value for the LED color, 0 - 255. Default is None. If None, regardless if the others are defined, the drone will use a random color.
integer g: The green pixel value for the LED color, 0 - 255. Default is None. If None, regardless if the others are defined, the drone will use a random color.
integer b: The blue pixel value for the LED color, 0 - 255. Default is None. If None, regardless if the others are defined, the drone will use a random color.
Returns
None
Example
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.ping() # drone's buzzer beeps and LED blinks a random color
drone.close()
Sensors (Range Sensor)
detect_wall()
Description
Returns True when a distance below the threshold is reached. The sensor range is up to 1.5 meters (150cm)
Syntax
detect_wall()
detect_wall(distance)
Parameters
integer distance: An optional parameter that is the threshold in centimeters that will return True. The default value is 50
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
# if a wall is detected in less than 50cm true will be returned.
if drone.detect_wall():
print("wall detected!")
else:
print("no wall detected!")
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_bottom_range()
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current bottom range of the drone. The default unit of measurement is centimeters. This function uses the bottom range sensor to measure distance from the drone to the surface below the drone.
NOTE: The bottom range sensor will be able to get an exact reading of 0 if the drone is sitting on a surface. If the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range sensor turns off (causing a reading of 0), so that the color sensor can turn on and detect color without any interference. It is safe to assume that if the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range or height is 0.
Syntax
get_bottom_range()
get_bottom_range(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: The unit of measurement that is chosen for the height distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified cm is chosen by default.
Returns
integer bottom range: The current bottom range calculated by the bottom range sensor (cm default). -100 or 0 when the sensor returns an error. 999.9 when the detected object is out of range (1.5 meters) or the sensor timed out.
Example Code
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
max_bottom_range = 100
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_throttle(50)
current_bottom_range = drone.get_bottom_range("cm")
while current_bottom_range <= max_bottom_range:
drone.move()
current_bottom_range = drone.get_bottom_range("cm")
print(current_bottom_range)
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_front_range()
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current front range of the drone. The default unit of measurement is centimeters. This function uses the front range sensor to measure distance from the drone to the surface in front of the drone.
NOTE: The front range sensor will not be able to get an exact reading of 0 due to light scattering and interference. The lowest value you may see is approximately 9mm (0.9cm) by covering the sensor.
Syntax
get_front_range()
get_front_range(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: A string for the unit of measurement that is chosen for the range distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified "cm" is chosen by default.
Returns
integer front range: The current range calculated by the front range sensor (cm by default). -10 or 0 when the sensor returns an error value. 999 when the detected object is out of range (1.5 meters) or the sensor timed out.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and move drone towards and away from a wall to see differences in front range values on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_front_range())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_height()
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current height of the drone. The default unit of measurement is centimeters. This function uses the bottom range sensor to measure distance from the drone to the surface below the drone.
NOTE: The bottom range sensor will be able to get an exact reading of 0 if the drone is sitting on a surface. If the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range sensor turns off (causing a reading of 0), so that the color sensor can turn on and detect color without any interference. It is safe to assume that if the drone is sitting on a surface, the bottom range or height is 0.
Syntax
get_height()
get_height(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: The unit of measurement that is chosen for the height distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified cm is chosen by default.
Returns
integer height: The current range calculated by the bottom range sensor (cm default). -100 or 0 when the sensor returns an error. 999.9 when the detected object is out of range (1.5 meters) or the sensor timed out.
Example Code
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
max_height = 100
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_throttle(50)
current_height = drone.get_height("cm")
while current_height <= max_height:
drone.move()
current_height = drone.get_height("cm")
print(current_height)
drone.land()
drone.close()
Sensors (Optical Flow Sensor)
get_pos_x()
Description
Getter function that gets the x position of the drone. (x is forwards and backwards). NOTE: The drone's position values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.

Syntax
get_pos_x()
get_pos_x(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: The unit of measurement that is chosen for the position distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified cm is chosen by default.
Returns
integer x-position: The current x position of the drone.
Example Code 1
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_pos_x()) # get x-position at takeoff
drone.set_pitch(30)
drone.move(2.00)
drone.hover()
print(drone.get_pos_x()) # get x-position after moving forward
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 2
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
initial = drone.get_pos_x("cm") # define starting point
drone.set_pitch(15)
# drone moves 100 cm forward
while drone.get_pos_x("cm") - initial < 100:
drone.move()
drone.hover(1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_pos_y()
Description
Getter function that gets the y position of the drone. (y is left and right). NOTE: The drone's position values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.

Syntax
get_pos_y()
get_pos_y(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: The unit of measurement that is chosen for the position distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified cm is chosen by default.
Returns
integer y-position: The current y position of the drone.
Example Code 1
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_pos_y()) # get y-position at takeoff
drone.set_roll(-30)
drone.move(2.00)
drone.hover()
print(drone.get_pos_y()) # get y-position after moving left
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 2
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
initial = drone.get_pos_y("cm") # define starting point
drone.set_roll(-15)
# drone moves 100 cm left
while drone.get_pos_y("cm") - initial < 100:
drone.move()
drone.hover(1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_pos_z()
Description
Getter function that gets the z position of the drone. (z is up and down). NOTE: The drone's position values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.

Syntax
get_pos_z()
get_pos_z(unit="cm") — "m", "mm", and "in" are other options for unit
Parameters
string unit: The unit of measurement that is chosen for the position distance. Available units are "m" (meter), "cm" (centimeter), "mm" (millimeter), or "in" (inch). If a parameter is not specified cm is chosen by default.
Returns
integer z-position: The current z position of the drone.
Example Code 1
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_pos_z()) # get z-position at takeoff
drone.set_throttle(55)
drone.move(2.00)
drone.hover()
print(drone.get_pos_z()) # get z-position after moving vertically upward
drone.land()
drone.close()
Example Code 2
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
initial = drone.get_pos_z("cm") # define starting point
drone.set_throttle(50)
# drone moves 50 cm vertically upward
while drone.get_pos_z("cm") - initial < 50:
drone.move()
drone.hover(1)
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_flow_velocity_x()
Description
Previously named get_flow_x(). This getter function gets the raw data that's proportional to the x-velocity (forward and reverse) of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor.

Syntax
get_flow_velocity_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer x-velocity: The velocity of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor in the x direction
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.move(1)
print(drone.get_flow_velocity_x())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_flow_velocity_y()
Description
Previously named get_flow_y(). This getter function gets the raw data that's proportional to the y-velocity (left and right) of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor.

Syntax
get_flow_velocity_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer y-velocity: The velocity of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor in the y direction
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.move(1)
print(drone.get_flow_velocity_y())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_flow_x()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_flow_velocity_x() instead.
Description
This getter function gets the raw data that's proportional to the x-velocity (forward and reverse) of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor.

Syntax
get_flow_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer x-velocity: The velocity of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor in the x direction
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_pitch(50)
drone.move(1)
print(drone.get_flow_x())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_flow_y()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_flow_velocity_y() instead.
Description
This getter function gets the raw data that's proportional to the y-velocity (left and right) of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor.

Syntax
get_flow_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer y-velocity: The velocity of the drone measured by the optical flow sensor in the y direction
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_roll(50)
drone.move(1)
print(drone.get_flow_y())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_position_data()
Description
get_position_data is a getter function that retuns a list of position data for the drone. NOTE: The drone's position values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
The 'x' position of the drone is forwards and reverse.
The 'y' position of the drone is left and right.
The 'z' position of the drone is up and down.


Syntax
get_position_data()
get_position_data(delay)
Parameters
float delay: the delay in seconds before the position data is returned. default value is 0.01.
Returns
list position data: A list of position data for the drone. The list contains the current time of the running program [0], x position data [1], y position data [2], z position data [3].
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
data = drone.get_position_data()
print(data)
drone.land()
drone.close()
Sensors (Gyroscope Sensor)
get_accel_x()
Description
Previously named get_x_accel(). Getter function that gets the x acceleration of the drone. (x is forwards and backwards)

Syntax
get_accel_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer x-acceleration: The current x acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and move drone forward and backward to see changes in acceleration in the x-direction on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# grab and move drone forward and backward
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_accel_x())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_accel_y()
Description
Previously named get_y_accel(). Getter function that gets the y acceleration of the drone. (y is left and right)

Syntax
get_accel_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer y-acceleration: The current y acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and move drone left and right to see changes in acceleration in the y-direction on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# grab and move drone left and right
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_accel_y())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_accel_z()
Description
Previously named get_z_accel(). Getter function that gets the z acceleration of the drone (z is up and down). When the CoDrone EDU is at rest (e.g. sitting on a flat surface or hovering), the gyroscope sensor should be reading a value of 9.8 * 10 meters per second squared (m/s2) due to gravity.

Syntax
get_accel_z()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer z-acceleration: The current z acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and move drone upward and downward to see changes in acceleration in the z-direction on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# grab and move drone up and down
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_accel_z())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angle_x()
Description
Previously named get_x_angle(). This is a getter function which returns the current X angle from the gyroscope in the drone. This angle is on the "roll" axis. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_angle_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer roll angle: The current angle in regards to the X direction in degrees.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and tilt the drone left and right to see changes in x-angle (roll angle) on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# tilt the drone left and right
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_angle_x())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angle_y()
Description
Previously named get_y_angle(). This is a getter function which returns the current Y angle from the gyroscope in the drone. This angle is on the "pitch" axis. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_angle_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer pitch angle: The current angle in regards to the Y direction, in degrees.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and tilt the drone forward and backward to see changes in y-angle (pitch angle) on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# tilt the drone forward and backward
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_angle_y())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angle_z()
Description
Previously named get_z_angle(). This is a getter function which returns the current Z angle from the drone. This is angle is the "yaw" direction. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_angle_z()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer yaw angle: The current angle in regards to the Z direction.
Example Code
This example does not require any flying. Once code is running, grab and turn the drone left and right to see changes in z-angle (yaw angle) on the console.
#Python code
import time
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
start_time = time.time() # set initial time, in seconds
# turn the drone left and right
# loop runs for 20 seconds
while time.time() - start_time < 20:
print(drone.get_angle_z())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angular_speed_x()
Description
This function returns the current angular speed in degrees per second around the x-axis ("roll" axis).
Syntax
get_angular_speed_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer angular speed: positive or negative angle speed in degrees per second
Example Code
Tilt the drone left and right while the program runs to see the angular speed change. Then, hold the drone as still as possible and watch angular speed drop.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
for i in range(100):
print(drone.get_angular_speed_x())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angular_speed_y()
Description
This function returns the current angular speed in degrees per second around the y-axis ("pitch" axis).
Syntax
get_angular_speed_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer angular speed: positive or negative angle speed in degrees per second
Example Code
Tilt the drone forward and backward while the program runs to see the angular speed change. Then, hold the drone as still as possible and watch angular speed drop.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
for i in range(100):
print(drone.get_angular_speed_y())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_angular_speed_z()
Description
This function returns the current angular speed in degrees per second around the z-axis ("yaw" axis).
Syntax
get_angular_speed_z()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer angular speed: positive or negative angle speed in degrees per second
Example Code
Turn the drone left and right on a flat surface while the program runs to see the angular speed change. Then, hold the drone as still as possible and watch angular speed drop.
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
for i in range(100):
print(drone.get_angular_speed_z())
time.sleep(0.05)
drone.close()
get_x_accel()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_accel_x() instead.
Description
Getter function that gets the x acceleration of the drone. (x is forwards and backwards)

Syntax
get_x_accel()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer x-acceleration: The current x acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_x_accel())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_x_angle()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_angle_x() instead.
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current X angle from the gyroscope in the drone. This angle is on the "roll" axis. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_x_angle()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer roll angle: The current angle in regards to the X direction in degrees.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print(drone.get_x_angle())
drone.close()
get_y_accel()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_accel_y() instead.
Description
Getter function that gets the y acceleration of the drone. (y is left and right)

Syntax
get_y_accel()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer y-acceleration: The current y acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_y_accel())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_y_angle()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_angle_y() instead.
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current Y angle from the gyroscope in the drone. This angle is on the "pitch" axis. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_y_angle()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer pitch angle: The current angle in regards to the Y direction, in degrees.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print(drone.get_y_angle())
drone.close()
get_z_accel()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_accel_z() instead.
Description
Getter function that gets the z acceleration of the drone (z is up and down). When the CoDrone EDU is at rest (e.g. sitting on a flat surface or hovering), the gyroscope sensor should be reading a value of 9.8 * 10 meters per second squared (m/s2) due to gravity.

Syntax
get_z_accel()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer z-acceleration: The current z acceleration of the drone.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_z_accel())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_z_angle()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_angle_z() instead.
Description
This is a getter function which returns the current Z angle from the drone. This is angle is the "yaw" direction. NOTE: The drone's angle values are reset to 0 when drone takes off or battery is re-inserted.
Syntax
get_z_angle()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer yaw angle: The current angle in regards to the Z direction.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print(drone.get_z_angle())
drone.close()
reset_gyro()
Description
Previously named reset_sensor(). This function will reset the roll, pitch, and yaw angles back to zero.
Syntax
reset_gyro()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print("Before")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_yaw(50)
drone.move(1)
drone.land()
print("After")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.reset_gyro()
print("Reset")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.close()
reset_sensor()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use reset_gyro() instead.
Description
This function will reset the gyro angles back to zero for roll, pitch, and yaw.
Syntax
reset_sensor()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print("Before")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.takeoff()
drone.set_yaw(50)
drone.move(1)
drone.land()
print("After")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.reset_sensor()
print("Reset")
print("X angle:", drone.get_angle_x())
print("Y angle:", drone.get_angle_y())
print("Z angle:", drone.get_angle_z())
drone.close()
Sensors (Pressure Sensor)
get_drone_temperature()
Description
Previously named get_temperature(). This is a getter function gets the drone's temperature from the barometer.
The sensor reads the drone’s temperature, not the air around it. Default unit is Celsius.
Syntax
get_drone_temperature()
get_drone_temperature(unit)
Parameters
string unit: A string for the unit of temperature of the drone. Available units are "C" (Celsius), "F" (Fahrenheit), and "K" (Kelvin).
Returns
integer temperature: The temperature of the drone in the given unit as a float. Default unit is Celsius.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
temperature = drone.get_drone_temperature()
print(temperature)
drone.close()
get_temperature()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use get_drone_temperature() instead.
Description
This is a getter function gets the drone's temperature from the barometer. The sensor reads the drone’s temperature, not the air around it. Default unit is Celsius.
Syntax
get_temperature()
get_temperature(unit)
Parameters
string unit: A string for the unit of temperature of the drone. Available units are "C" (Celsius), "F" (Fahrenheit), and "K" (Kelvin).
Returns
integer temperature: The temperature of the drone in the given unit as a float. Default unit is Celsius.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
temperature = drone.get_temperature()
print(temperature)
drone.close()
height_from_pressure()
Description
This function gets the drone's current height in centimeters based on the initial pressure sensor reading. You must call set_initial_pressure() to establish a reference point.
Syntax
height_from_pressure()
height_from_pressure(b, m)
Parameters
float b: slope intercept in pascals (default is set to 0)
float m: slope in centimeters/pascals (default is set to 9.34)
Returns
float height: Estimated height in centimeters relative to starting position.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.set_initial_pressure() # Take an initial pressure reading as a reference
for i in range(300):
print(drone.height_from_pressure(), " centimeters")
time.sleep(0.2)
drone.close()
get_elevation()
Description
Returns the estimated elevation data from the CoDrone EDU's barometer.
Syntax
get_elevation()
get_elevation(unit="m")
Parameters
string unit: m (meter), km (kilometer), ft (feet), mi (miles).
Returns
float elevation: float elevation value in units selected
Example
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# print the elevation before taking off
print(drone.get_elevation())
drone.takeoff()
drone.hover(1)
# print the elevation after taking off
print(drone.get_elevation())
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_pressure()
Description
This is a getter function that returns the data from the barometer. The function returns a value in the unit Pascals. Note: 1atm = 101325 Pa
Syntax
get_pressure()
Parameters
None
Returns
float pressure: air pressure measured by barometer in Pascals.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# print the pressure
pressure = drone.get_pressure()
print(pressure)
drone.close()
set_initial_pressure()
Description
This function saves an initial pressure reading to the drone. This function is used in combination with other functions such as height_from_pressure()
Syntax
set_initial_pressure()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# Here is where we save our initial pressure. Now the 'height_from_pressure()' function has a reference for height
drone.set_initial_pressure()
# The drone will not take off in this example but by moving it up and down manually the resulting height will print
for i in range(300):
print(drone.height_from_pressure(), " millimeters")
time.sleep(0.2)
drone.close()
Sensors (Color Sensor)
append_color_data()
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
append_color_data() is a function that adds onto an existing dataset of custom color prediction data. the dataset parameter must already exist in order to use this function.
Syntax
append_color_data(label, data, dataset)
Parameters
string label: label name that will be used for the filename.
list data: HSV data samples
string dataset: Folder name where the text file will be stored.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
dataset = "color_data"
colors = ["green", "purple", "red", "lightblue", "blue", "yellow", "black", "white"]
for color in colors:
data = []
samples = 500
for i in range(1):
print("Sample: ", i+1)
next = input("Press enter to calibrate " + color)
print("0% ", end="")
for j in range(samples):
color_data = drone.get_color_data()[0:9]
data.append(color_data)
time.sleep(0.005)
if j % 10 == 0:
print("-", end="")
print(" 100%")
drone.append_color_data(color, data, dataset)
print("Done calibrating.")
drone.close()
get_back_color()
Description
get_back_color() is a getter function that returns data from the back color sensor. You are able to specify how to retrieve color data: the color name, the HSV, HSL, or RGB value.
Syntax
get_back_color()
Parameters
string kind: A string value that specifies how you want to retrieve color data: "hsv", "hsl", "rgb", or "name" (name of the color). "name" is the default value.
Returns
back color data: Returns color data from the back color sensor. If kind="name", it returns a string ("red", "green", "yellow", "blue", "light blue", "purple", "black", "white", "Unknown"). If kind="hsv", it returns a list, consisting of HSV values. If kind="hsl", it returns a list, consisting of HSL values. If kind="rgb", it returns a list, consisting of RGB values.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
color_data = drone.get_back_color()
print(color_data)
drone.close()
get_color_data()
Description
Getter function that gets a list of color data from the drone.
Syntax
get_color_data()
Parameters
None
Returns
list color data: Returns a list of color data.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
color_data = drone.get_color_data()
drone.close()
get_colors()
Description
get_colors() is a getter function that returns one of the 8 pre-calibrated colors (provided in the color cards). You are able to specify how to retrieve color data: the color name, the HSV, HSL, or RGB value.
Syntax
get_colors()
get_colors(kind="name")
Parameters
string kind: A string value that specifies how you want to retrieve color data: "hsv", "hsl", "rgb", or "name" (name of the color). "name" is the default value.
Returns
list predictions: Returns a list containing data from the front and back color sensor. If kind="name", it returns a list of strings ("red", "green", "yellow", "blue", "light blue", "purple", "black", "white", "Unknown"). If kind="hsv", it returns a list of lists, consisting of HSV values, for the front and back color sensor. If kind="hsl", it returns a list of lists, consisting of HSL values, for the front and back color sensor. If kind="rgb", it returns a list of lists, consisting of RGB values, for the front and back color sensor.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
colors = drone.get_colors()
print(colors)
drone.close()
get_front_color()
Description
get_front_color() is a getter function that only returns data from the front color sensor. You are able to specify how to retrieve color data: the color name, the HSV, HSL, or RGB value.
Syntax
get_front_color()
Parameters
string kind: A string value that specifies how you want to retrieve color data: "hsv", "hsl", "rgb", or "name" (name of the color). "name" is the default value.
Returns
front color data: Returns color data from the front color sensor. If kind="name", it returns a string ("red", "green", "yellow", "blue", "light blue", "purple", "black", "white", "Unknown"). If kind="hsv", it returns a list, consisting of HSV values. If kind="hsl", it returns a list, consisting of HSL values. If kind="rgb", it returns a list, consisting of RGB values.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
color_data = drone.get_front_color()
print(color_data)
drone.close()
load_classifier()
This function has been deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use load_classifier() instead.
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
load_classifier() is a function that can load a custom color set onto the CoDrone EDU. If no custom color set is given then the default color set is loaded. There is also an option to show the color set as a graph.
Syntax
load_classifier()
load_classifier(dataset, show_graph)
Parameters
string dataset: An optional parameter to load a custom color set. If no color set is given then the default color set will be used. boolean show_graph: An optional boolean parameter that will show a graph of the color set data. The default value is False.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# This example assumes the "custom_color_data" directory exists
drone.load_classifier("custom_color_data")
color_data = drone.get_color_data()
color = drone.predict_colors(color_data)
print(color)
drone.close()
load_color_data()
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
Previously name load_classifier(). load_color_data() is a function that can load a custom color set onto the CoDrone EDU. If no custom color set is given then the default color set is loaded. There is also an option to show the color set as a graph.
Syntax
load_color_data()
load_color_data(dataset, show_graph)
Parameters
string dataset: An optional parameter to load a custom color set. If no color set is given then the default color set will be used. boolean show_graph: An optional boolean parameter that will show a graph of the color set data. The default value is False.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# This example assumes the "custom_color_data" directory exists
drone.load_color_data("custom_color_data")
color_data = drone.get_color_data()
color = drone.predict_colors(color_data)
print(color)
drone.close()
new_color_data()
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
new_color_data() is a function that creates a new dataset of custom color prediction data.
Syntax
new_color_data(label, data, dataset)
Parameters
string label: label name that will be used for the filename.
list data: HSV data samples
string dataset: Folder name where the text file will be stored.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
dataset = "color_data"
colors = ["green", "purple", "red", "lightblue", "blue", "yellow", "black", "white"]
for color in colors:
data = []
samples = 500
for i in range(1):
print("Sample: ", i+1)
next = input("Press enter to calibrate " + color)
print("0% ", end="")
for j in range(samples):
color_data = drone.get_color_data()[0:9]
data.append(color_data)
time.sleep(0.005)
if j % 10 == 0:
print("-", end="")
print(" 100%")
drone.new_color_data(color, data, dataset)
print("Done calibrating.")
drone.close()
predict_colors()
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
Predicts what color the color sensors are currently seeing.
Syntax
predict_colors(color_data)
Parameters
list color_data: loaded from drone.get_color_data()
Returns
list predictions: A prediction of which color the front and back color sensors are currently seeing, as a list.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
drone.load_color_data("color_data_file")
color_data = drone.get_color_data()
color = drone.predict_colors(color_data)
print(color)
drone.close()
Sensors (State Data)
get_battery()
Description
This function returns the current battery level percentage of the drone.
Syntax
get_battery()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer battery percentage: The current battery percentage of the drone's battery.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
battery = drone.get_battery()
print(battery)
drone.close()
get_error_data()
Description
This command requests if the drone is in an error state. One or more of the following error states can be printed to console.
-
Motion_Calibrating: Drone is calibrating.
-
Motion_NoAnswer: Gyroscope Accelerometer is unresponsive and may be damaged.
-
Motion_WrongValue: Gyroscope Accelerometer is giving erroneous data.
-
Motion_NotCalibrated: Gyroscope Accelerometer is not calibrated.
-
Pressure_NoAnswer: Barometer is unresponsive.
-
Pressure_WrongValue: Barometer is giving erroneous data.
-
RangeGround_NoAnswer: Bottom Range sensor is unresponsive.
-
RangeGround_WrongValue: Bottom range sensor has given an incorrect value.
-
Flow_NoAnswer: Optical flow sensor is unresponsive.
-
Flow_CannotRecognizeGroundImage: Optical flow sensor is giving erroneous data due to the image.
-
NotRegistered: Device is not registered.
-
FlashReadLock_UnLocked: Flash memory read lock not engaged.
-
BootloaderWriteLock_UnLocked: Bootloader write lock not engaged.
-
LowBattery: Drone has low battery.
-
TakeoffFailure_CheckPropellerAndMotor: Takeoff failure. Check propeller and motor.
-
CheckPropellerVibration: Propeller vibration detected.
-
Attitude_NotStable: Attitude not stable.
-
CanNotFLip_LowBattery: Drone won't flip due to low battery (< 50%).
-
CanNotFlip_TooHeavy: Drone won't flip due to being too heavy (probably due to payload attached to drone).
Syntax
get_error_data()
get_error_data(delay)
Parameters
float delay: The delay in seconds that the command will wait for a response. The default value is 0.1.
Returns
string error state: text consisting of one or more error messages
Example Code
Turn the drone left and right on a flat surface while the program runs to see the angular speed change. Then, hold the drone as still as possible and watch angular speed drop.
#Python code
from time import sleep
from codrone_edu.drone import *
from codrone_edu.protocol import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# For demonstration purposes, activate motion calibration
drone.sendCommand(CommandType.ClearBias)
sleep(0.1)
for i in range(10):
drone.get_error_data() # see motion error state during calibration
time.sleep(0.5)
drone.close()
get_flight_state()
Description
get_flight_state() is a getter function that gets the current flight state of the drone.
Syntax
get_flight_state()
Parameters
None
Returns
string state: The current flight state of the drone.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print(drone.get_flight_state())
drone.close()
get_movement_state()
Description
This command requests the moving state of the drone, whether it is ready to fly, hovering, etc.
Syntax
get_movement_state()
Parameters
None
Returns
enum ModeMovement: The movement state of the drone (None_, Ready, Hovering, ReturnHome)
Example Code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
print(drone.get_movement_state()) # prints "ModeMovement.Ready" after pairing
drone.takeoff()
print(drone.get_movement_state()) # "ModeMovement.Hovering" after takeoff
drone.land()
drone.close()
get_sensor_data()
Description
This functions returns a list of 31 values including time stamps and sensor values. It requests 5 distinct lists of data and compiles them into one list. This function returns data more quickly than individual sensor requests.
Syntax
get_sensor_data()
get_sensor_data(delay)
Parameters
integer delay: The delay in seconds for each sensor request (out of 5). The total delay will be 5x this delay value. The default value is 0.1 seconds.
Returns
list sensor data: A list of length 31 consisted of sensor data.
- data[0] Altitude time stamp
- data[1] Temperature in Celsius
- data[2] Pressure (Pascals)
- data[3] Elevation output from barometer (meters)
- data[4] Height value output from bottom range sensor (meters)
- data[5] Motion data time stamp
- data[6] acceleration X Int16 2 Byte -1568 ~ 1568 (-156.8 ~ 156.8) m/s2 x 10 X
- data[7] acceleration Y Int16 2 Byte -1568 ~ 1568 (-156.8 ~ 156.8) m/s2 x 10 Y
- data[8] acceleration Z Int16 2 Byte -1568 ~ 1568 (-156.8 ~ 156.8) m/s2 x 10 Z
- data[9] gyroRoll: Int16 2 Byte -2000 ~ 2000 degree/second Roll
- data[10] gyroPitch Int16 2 Byte -2000 ~ 2000 degree/second Pitch
- data[11] gyroYaw Int16 2 Byte -2000 ~ 2000 degree/second Yaw
- data[12] angleRoll Int16 2 Byte -180 ~ 180 degree Roll
- data[13] anglePitch Int16 2 Byte -180 ~ 180 degree Pitch
- data[14] angleYaw Int16 2 Byte -180 ~ 180 degree Yaw
- data[15] Position data time stamp
- data[16] x Float32 4 Byte - X axis in meters
- data[17] y Float32 4 Byte - Y axis in meters
- data[18] z Float32 4 Byte - z axis in meters
- data[19] Range sensor data time stamp
- data[20] Front range sensor (millimeters)
- data[21] Bottom range sensor (millimeters)
- data[22] Drone state time stamp
- data[23] modeSystem (system operating mode)
- data[24] modeFlight (flight controller operating mode)
- data[25] modeControlFlight (flight control mode)
- data[26] modeMovement (moving state)
- data[27] headless (headless setting status)
- data[28] sensorOrientation (sensor orientation)
- data[29] battery parcentage level
- data[30] current speed setting
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# collect multiple data points
data = drone.get_sensor_data()
for i in range(len(data)):
print(i, data[i]) # print out each data point
drone.close()
Controller
down_arrow_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's down arrow button has been pressed.
Syntax
down_arrow_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed down: True if the down arrow button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.down_arrow_pressed():
print("down arrow button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
get_button_data()
Description
get_button_data() is a function that will return a list of information about the most recent button pressed.
Syntax
get_button_data()
Parameters
None
Returns
list button data: A list of data that includes the time of the current program, the number associated with the most recent button pressed, and finally the state of the most recent button pressed. (Down, Pressed, Up)
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_button_data())
drone.close()
h_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's H button has been pressed.
Syntax
h_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed H: True if the H button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.h_pressed():
print("H button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
l1_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's L1 button has been pressed.
Syntax
l1_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed L1: True if the L1 button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.l1_pressed():
print("L1 button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
l2_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's L2 button has been pressed.
Syntax
l2_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed L2: True if the L2 button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.l2_pressed():
print("L2 button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
left_arrow_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's left arrow button has been pressed.
Syntax
left_arrow_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed left: True if the left arrow button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.left_arrow_pressed():
print("left arrow button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
p_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's P button has been pressed.
Syntax
p_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed P: True if the P button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.p_pressed():
print("P button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
power_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's power button has been pressed. Since pressing the power button also switches the drone to flight mode, this function only detects alternate button presses. In other words, the function can only detect a power button press when in LINK state.
Syntax
power_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed power: True if the power button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.power_pressed():
print("power button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
r1_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's R1 button has been pressed.
Syntax
r1_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed R1: True if the R1 button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.r1_pressed():
print("R1 button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
r2_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's R2 button has been pressed.
Syntax
r2_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed R2: True if the R2 button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.r2_pressed():
print("R2 button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
right_arrow_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's right arrow button has been pressed.
Syntax
right_arrow_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed right: True if the right arrow button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.right_arrow_pressed():
print("right arrow button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
s_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's S button has been pressed.
Syntax
s_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed S: True if the S button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.s_pressed():
print("S button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
up_arrow_pressed()
Description
A function that determines if the controller's up arrow button has been pressed.
Syntax
up_arrow_pressed()
Parameters
None
Returns
boolean pressed up: True if the up arrow button is pressed or held. Otherwise the function will return false.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
if drone.up_arrow_pressed():
print("up arrow button has been pressed!")
drone.close()
get_joystick_data()
Description
get_joystick_data() is a getter function that gets a list of data about the state of both joysticks on the controller.
Syntax
get_joystick_data()
Parameters
None
Returns
list joystick data: A list of data that includes the time of the current program, and information about the left and right joysticks.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_joystick_data())
drone.close()
get_left_joystick_x()
Description
get_left_joystick_x() is a getter function that gets the position of the left joystick's x position.
Syntax
get_left_joystick_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer left joystick x-value: A value between -100 and 100 depending on the x position of the left joystick.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_left_joystick_x())
drone.close()
get_left_joystick_y()
Description
get_left_joystick_y() is a getter function that gets the position of the left joystick's y position.
Syntax
get_left_joystick_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer left joystick y-value: A value between -100 and 100 depending on the y position of the left joystick.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_left_joystick_y())
drone.close()
get_right_joystick_x()
Description
get_right_joystick_x() is a getter function that gets the position of the right joystick's x position.
Syntax
get_right_joystick_x()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer right joystick x-value: A value between -100 and 100 depending on the x position of the right joystick.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_right_joystick_x())
drone.close()
get_right_joystick_y()
Description
get_right_joystick_y() is a getter function that gets the position of the right joystick's y position.
Syntax
get_right_joystick_y()
Parameters
None
Returns
integer right joystick y-value: A value between -100 and 100 depending on the y position of the right joystick.
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
import time
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(drone.get_right_joystick_y())
drone.close()
Screen
controller_clear_screen()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Clears all drawings from the controller screen
Syntax
controller_clear_screen()
controller_clear_screen(pixel)
Parameters
string pixel: optional parameter that assigns all pixels to either white or black. white is the default value.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas()
drone.controller_draw_rectangle(20, 30, 40, 10, image, 'black')
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image)
time.sleep(3)
drone.controller_clear_screen() # only clears screen, does not modify the image object
time.sleep(3)
image = drone.controller_create_canvas()
drone.controller_draw_string(60, 30, "Hello World!", image)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image)
drone.close()
controller_create_canvas()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Creates a new image object for drawing on the controller. You can create a canvas with a white or black background.
Syntax
controller_create_canvas()
controller_create_canvas(color="white")
Parameters
None
Returns
Image image: Returns a new image object that is 127 x 63 pixels
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
# creates an image object, the canvas
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # see controller_draw_canvas() for how to draw on this new image object
drone.close()
controller_draw_arc()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws an arc (a portion of a circle outline) between the start and end angles, inside the given bounding box.
Syntax
controller_draw_arc(arc_list, start_angle, end_angle, image)
controller_draw_arc(arc_list, start_angle, end_angle, image, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
list arc_list: Two points to define the bounding box. Sequence of [(x0, y0), (x1, y1)], where x1 >= x0 and y1 >= y0.
integer start_angle: Starting angle, in degrees. Angles are measured from 3 o’clock, increasing clockwise.
integer end_angle: Ending angle, in degrees.
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of arc. By default, color is black.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates image object, the canvas
arc_list = [(20, 40), (50, 50)]
drone.controller_draw_arc(arc_list, 0, 180, image) # set arc onto image object
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_canvas()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws custom image canvas onto the controller screen
Syntax
controller_draw_canvas(image)
Parameters
Image image: image object to be drawn onto the controller screen
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates image object, the canvas
arc_list = [(20, 40), (50, 50)]
ellipse_list = [(10, 10), (40, 40)]
chord_list = [(60, 20), (100, 50)]
drone.controller_draw_ellipse(ellipse_list, image) # draw onto image object
drone.controller_draw_arc(arc_list, 0, 180, image)
drone.controller_draw_chord(chord_list, 0, 180, image)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_chord()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Same as controller_draw_arc(), but connects the end points with a straight line.
Syntax
controller_draw_chord(arc_list, start_angle, end_angle, image)
controller_draw_chord(arc_list, start_angle, end_angle, image, color="black", fill_in=None, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
list chord_list: Two points to define the bounding box. Sequence of [(x0, y0), (x1, y1)], where x1 >= x0 and y1 >= y0.
integer start_angle: Starting angle, in degrees. Angles are measured from 3 o’clock, increasing clockwise.
integer end_angle: Ending angle, in degrees.
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of chord. By default, color is black.
string fill_in: color of fill. By default, no fill in.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates image object, the canvas
chord_list = [(20, 40), (50, 50)]
drone.controller_draw_chord(chord_list, 0, 180, image) # set chord onto image object
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_ellipse()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws an ellipse inside the given bounding box.
Syntax
controller_draw_ellipse(ellipse_list, image)
controller_draw_ellipse(ellipse_list, image, color="black", fill_in=None, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
list ellipse_list: Two points to define the bounding box. Sequence of [(x0, y0), (x1, y1)] where x1 >= x0 and y1 >= y0.
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of ellipse. By default, color is black.
string fill_in: color of fill. By default, no fill in.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
ellipse_list = [(10, 10), (40, 40)]
drone.controller_draw_ellipse(ellipse_list, image) # set ellipse onto image object
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_image()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
Draws image when given a pixel_list of image data
Syntax
controller_draw_image(pixel_list)
Parameters
list pixel_list: the list of image data. can be obtained using get_image_data() function.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.get_image_data("example.png") # where example.png is an image in the same directory as the program
drone.controller_draw_image(image) # draws the image onto the controller's screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_line()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a line between points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
(x1,y1) \
\
\
\ (x2,y2)
Syntax
controller_draw_line(x1, y1, x2, y2, image)
controller_draw_line(x1, y1, x2, y2, image, color="black", pixel_width=1)
Parameters
integer x1: point 1 x coordinate
integer y1: point 1 y coordinate
integer x2: point 2 x coordinate
integer y2: point 2 y coordinate
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of line. By default, color is black
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
drone.controller_draw_line(0,0, 60, 60, image) # draws a line from (0,0) to (60,60)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_point()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a single pixel at the point (x,y)
Syntax
controller_draw_point(x, y, image)
controller_draw_point(x, y, image, color="black")
Parameters
integer x: x coordinate
integer y: y coordinate
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas()
string color: color of point. By default, color is black.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
drone.controller_draw_point(10, 10, image) # place a pixel at the (10,10) coordinate of canvas
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_polygon()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
The polygon outline consists of straight lines between the given coordinates, plus a straight line between the last and the first coordinate.
Syntax
controller_draw_polygon(point_list, image)
controller_draw_polygon(point_list, image, color="black", fill_in=None, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
list point_list: the list of coordinates
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of polygon. By default, color is black.
string fill_in: color of fill. By default, no fill in.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
point_list = [(0, 0), (15,15), (30,0)] # list of points that will be connected to draw a polygon
drone.controller_draw_polygon(point_list, image) # forms polygon using list of points
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_rectangle()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a rectangle onto the controller screen starting from point (x,y) and extends to given height and width
width
(x,y)|---------------|
| | height
|_______________|
Syntax
controller_draw_rectangle(x, y, width, height, image)
controller_draw_rectangle(x, y, width, height, image, color="black" fill_in=None, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
integer x: top left corner x coordinate
integer y: top left corner y coordinate
integer width: width of rectangle
integer height: height of rectangle
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of rectangle. By default, color is black.
string fill_in: color of fill. By default, no fill in.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
# draws rectangle starting at (0,0) on canvas with width of 40px and height of 20px
drone.controller_draw_rectangle(0, 0, 40, 20,image)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_square()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a square on the controller screen starting from point (x,y) and will extend to the given width
width
(x,y)|------|
| | width
|______|
Syntax
controller_draw_square(x, y, width, image)
controller_draw_square(x, y, width, image, color="black", fill_in=None, pixel_width=1)
Parameters
integer x: top left corner x coordinate
integer y: top left corner y coordinate
integer width: width of square
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of square. By default, color is black.
string fill_in: color of fill. By default, no fill in.
integer pixel_width: optional parameter that is the line width, in pixels. default value is 1.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
# draws a square on canvas that's 30 x 30px at (0, 0)
drone.controller_draw_square(0, 0, 30, image)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_string_align()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a string from the given x_start, x_end and y positions. The string can be aligned along the x_start and x_end positions.
Syntax
controller_draw_string_align(x_start, x_end, y, string, image)
controller_draw_string_align(x_start, x_end, y, string, image, color="black", alignment="left")
Parameters
integer x_start: starting x position
integer x_end: ending x position
integer y: y position
string string: the string to write
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of string. By default, color is black.
string alignment: optional parameter that is the alignment between x_start and x_end. can align left, right, or center. default value is left
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
# draws string on canvas that is aligned to the right, between x=0 and x=100 at position y=0.
drone.controller_draw_string_align(0, 100, 0, "Hello, world!", image, alignment="right")
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_draw_string()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
Description
Draws a string from the given x_start, x_end and y positions. The string can be aligned along the x_start and x_end positions
Syntax
controller_draw_string(x, y, string, image)
controller_draw_string(x, y, string, image, color="black")
Parameters
integer x: starting x position
integer y: starting y position
string string: the string to write
Image image: image object created from controller_create_canvas().
string color: color of string. By default, color is black.
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # creates an image object, the canvas
drone.controller_draw_string(0, 0, "Hello, world!", image) # draw "Hello, world!" on image object at (0,0)
drone.controller_draw_canvas(image) # draw image onto controller screen
drone.close()
controller_preview_canvas()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
Creates a pop up window to preview image object from the most recent controller_create_canvas() call onto your computer screen. NOTE: Preview image will reset every time controller_create_canvas() is called.
Syntax
controller_preview_canvas()
Parameters
None
Returns
None
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
image = drone.controller_create_canvas() # create image object, the canvas
arc_list = [(20, 40), (50, 50)]
ellipse_list = [(10, 10), (40, 40)]
chord_list = [(60, 20), (100, 50)]
drone.controller_draw_ellipse(ellipse_list, image) # draw onto image object
drone.controller_draw_arc(arc_list, 0, 180, image)
drone.controller_draw_chord(chord_list, 0, 180, image)
drone.controller_preview_canvas() # a window will pop up with your drawing
drone.close()
get_image_data()
This function is currently unavailable for CoDrone EDU (JROTC ed.).
This function is currently unavailable for Python for Robolink.
Description
This function retrieves .png or .jpg file and resizes to fit inside controller.
Syntax
get_image_data(image_file_name)
Parameters
string image_file_name: the name of the image file, including file extension (ex. "image.png")
Returns
list image_data: list consisting of RGB values
Example Code
#Python code
from codrone_edu.drone import *
drone = Drone()
drone.pair()
img_list = ("images/boom.png", "images/flower.png", "images/mario.png", "images/pikachu.jpg", "images/rose.jpg", "images/troll_face.png", "images/pixel_dino.png")
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img = drone.get_image_data(img_list[i]) # img stores image data
drone.controller_draw_image(img) # draws image on controller
time.sleep(1)
drone.close()